By David Snowball
Dear friends,
It’s spring! Sort of. Despite the steady, light snow falling outside my window, March 1 is the beginning of “meteorological spring” and I’m indisputably in the middle of Augustana’s Spring Break. (It always looked better on MTV.) Spring training, both for major leaguers and my son’s high school team, has begun. There are stirrings in my garden and a couple newly-arrived catalogs (yes, I still get real mail) are encouraging horticultural fantasies: a swath of pollinator-friendly native plants taking over the southwest corner of the yard, a new home for my towering wall of sunflowers, some experiments with carrots, replacing more of the lawn with a rain garden to reduce run-off, regrowing a full head of hair … anything’s imaginable and everything’s possible, at least until I have to figure out how to pull it off.

Sadly, as Rudyard Kipling observed, “gardens are not made by sitting in the shade.”
For one more month, at least, I focus on tidying up my financial garden. We start this month’s issue with three of the most important kind of story: ones that actually affect me.
Artisan pulls the plug
 Artisan has announced the liquidation of Artisan Small Cap Value (ARTVX), my oldest holding. My first fund, purchased when I was young and dumb, was AIM Constellation, then a very good mid-cap growth fund that carried a 5.5% load. After a bit, I learned that paying sales loads without any compensating benefit was stupid, so I stopped. I sold my shares and, shortly before it closed, invested the proceeds in Artisan Small Cap (ARTSX). Shortly after Artisan launched Small Cap Value in 1997, I moved my investment over from Small Cap. The $367 million fund, down from a peak of $3 billion in 2011, will be merged into Artisan Mid Cap Value (ARTQX) in May, 2016.
Artisan has announced the liquidation of Artisan Small Cap Value (ARTVX), my oldest holding. My first fund, purchased when I was young and dumb, was AIM Constellation, then a very good mid-cap growth fund that carried a 5.5% load. After a bit, I learned that paying sales loads without any compensating benefit was stupid, so I stopped. I sold my shares and, shortly before it closed, invested the proceeds in Artisan Small Cap (ARTSX). Shortly after Artisan launched Small Cap Value in 1997, I moved my investment over from Small Cap. The $367 million fund, down from a peak of $3 billion in 2011, will be merged into Artisan Mid Cap Value (ARTQX) in May, 2016.
After a couple withdrawals and almost 19 years of paying taxes on the account, I’m disconcerted to report that I’ll be able to report a 30% tax loss on my 2016 taxes.
What happened? The managers’ discipline (and the dictates of marketing to advisors who want to execute their own asset allocation plans) does not encompass holding significant cash. And so, despite the fact that “We’ve complained for a long time now that too much of the market is fully- or fairly valued,” they stayed fully-invested. Their discipline also pushed them toward overweighting the best-valued stocks they could find and those turned out to be in two of the market’s worst areas: energy and industrials, that latter of which “have backdoor exposure to energy.” They eventually overweighted those areas by more than 2:1. That’s, at best, a very partial explanation for the fact that the fund trailed 90% or more of its small-value peers in five of the past six years, including years with high oil prices.
The folks at Artisan position this as a simple economic decision: “a determination was made that the strategy/fund was no longer commercially viable… Given our past few years of underperformance, we have seen outflows (and passive has been an asset flow winner here). We are also hearing that fewer folks plan to use dedicated small-cap value allocations going forward.” The management team “drove the decision” and they “still believe in the asset class.”
This is the first fund liquidation in Artisan’s history.
The team manages two other funds, Mid Cap Value (ARTQX) and the large-cap oriented Value (ARTLX). Over the full market cycle, ARTQX modestly leads its peer group in performance (40 bps/year) with subdued volatility. ARTLX trails its Lipper peers (80 bps/year) with somewhat higher volatility.
Bottom line
I prefer to maintain exposure to small value stocks, so I won’t wait around for the impending transition to the team’s mid-cap value fund. I’ll book my tax loss and move on.
The finalists for this slot in my portfolio are two cash-rich, low-vol funds: John Deysher’s Pinnacle Value Fund (PVFIX) and the team-managed Intrepid Endurance Fund (ICMAX, formerly Intrepid Small Cap). Both are run by absolute value investors. They have similar expense ratios, though Intrepid is five times Pinnacle’s size. Intrepid’s about two-thirds cash right now, Pinnacle about 50%. They are, by far, the two least volatile small cap funds around. Pinnacle’s market cap and turnover are both far lower.
We profiled Pinnacle one year ago. I think we’ll try to prepare a profile of Intrepid for our April issue and see if that helps decide things.
The tough question remaining
How long should you wait before you write off a manager or a fund? My normal rule is pretty straightforward: if I haven’t changed and they haven’t changed, then we’re not going to change. That is, if my portfolio needs remain the same, the management team remains intact and true to their discipline, then I’m not going to second-guess my due diligence. This may be the first time I’ve sold a fund in a decade. Leigh Walzer’s research on stumbling funds suggests that I should have sold in mid-2014 which would have spared me about a 10% loss assuming that I’d put it in a merely average SCV fund.
Romick stares reality in the face, and turns away
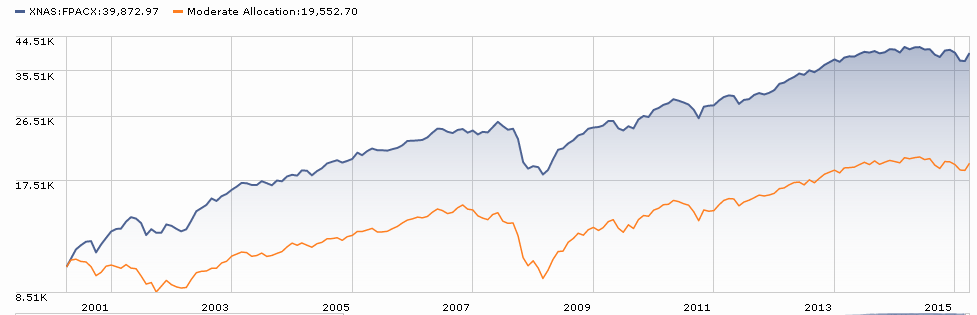
 My single largest non-retirement holding is FPA Crescent (FPACX), which has always struck me as the quintessence of active management. While other managers were constrained to invest in a single asset class or in a single country, or to remain fully invested or unhedged, manager Steve Romick declared himself to be “the free-range chicken” of the investing world. He’d look for firms that offered compelling advantages, would analyze their capital structure and then invest in whatever instrument – common stock, warrants, senior debt – offered the most compelling opportunities. If nothing was compelling, he sat on cash.
My single largest non-retirement holding is FPA Crescent (FPACX), which has always struck me as the quintessence of active management. While other managers were constrained to invest in a single asset class or in a single country, or to remain fully invested or unhedged, manager Steve Romick declared himself to be “the free-range chicken” of the investing world. He’d look for firms that offered compelling advantages, would analyze their capital structure and then invest in whatever instrument – common stock, warrants, senior debt – offered the most compelling opportunities. If nothing was compelling, he sat on cash.
That strategy performed wonderfully for years. Over the past decade the fund has led its Morningstar peer group by 1.12% annually though, by freakish coincidence, Morningstar also calculates that you lost 1.12% annually to taxes over the same period. Over the past three years, the fund has either been about average (using Morningstar’s “moderate allocation” peer group) or well-above average (using Lipper’s “flexible portfolio” one). In 2015, the fund lost money and finished in the bottom third of its Morningstar peer group.
Those two things do not bother me. Two others do. First, the fund has ballooned in size with no apparent effort at gatekeeping. In 2005, it performed gloriously but had under $1 billion in assets. In 2010, it performed solidly with $2.7 billion. It hit $10 billion in 2013 and $20 billion in 2015 and remains open today. While some funds have doubtless thrived in the face of huge, continual inflows, those are rare.
Second, Romick blinked. His recently released Annual Report offered the following announcement on page two:
At first glance, it appears that we’ve declined as much as the market — down 11.71% since May 2015’s market peak against the S&P 500’s 11.30% decline — but that’s looking at the market only through the lens of the S&P 500. However, roughly half of our equity holdings (totaling almost a third of the Fund’s equity exposure) are not included in the S&P 500 index. Our quest for value has increasingly taken us overseas and our portfolio is more global than it has been in the past. We therefore consider the MSCI ACWI a pertinent alternative benchmark.
What?
“We look pretty good compared to a global all-equity benchmark”?
Uhhh … the fund is 37% cash. Morningstar reports a net exposure (11% long minus 3% short) of only 8.5% to international stocks. The most recent report on FPA’s website suggests 16% but doesn’t separate long/short. If Morningstar is right, net exposure is way less global than either its Morningstar benchmark or Morningstar peer group.
Underperformance doesn’t bother me. Obfuscation does. The irony is that it bothers Mr. Romick as well, at least when it’s being practiced by others. In a 2012 letter criticizing the Fed, he explained what we ought to demand of our leaders and ourselves:
Blind faith has gotten us into trouble repeatedly throughout history. Just consider the rogue’s gallery of false idols, dictators, and charlatans we have followed, hoping for something different, something better. That misplaced conviction corrupts and destroys. Daily life does require we put our trust in others, but we should do so judiciously.
Nobody has all the answers. Genius fails. Experts goof. Rather than blind faith, we need our leaders to admit failure, learn from it, recalibrate, and move forward with something better… As the author Malcolm Gladwell so eloquently said, “Incompetence is the disease of idiots. Overconfidence is the mistake of experts…. Incompetence irritates me. Overconfidence terrifies me.”
FPA once ran funds in a couple of different styles, Mr. Romick’s and the other one. They’ve now purged themselves of their quality-growth team and have renamed and repurposed those funds. In repurposing Paramount, they raised the expense ratio, ostensibly to create parity with the Perennial fund. In a private exchange I asked why they didn’t simply lower Perennial’s e.r. rather than raising it and was assured that they really needed the extra cash for as-yet undisclosed enhancements.
I’ve lost faith.
Bottom line
I’m not sure whether FPA is now being driven by investment discipline, demands for ideological purity or a rising interest in gathering assets. Regardless, I’m going. I have long respected the folks at the Leuthold Group and we recently profiled their flagship Leuthold Core Investment Fund (LCORX). Leuthold has delivered on such promises more consistently, with more discipline, for a longer period than virtually any competitor.” They’re apt to be the home for the proceeds from an FPA sale plus closing two small accounts.
Morningstar doesn’t share my reservations and FPACX retains a “Gold” analyst rating from the firm.
The tough question remaining
How do we account for cultural change in assessing a firm? Firms never admit to their internal machinations, the story is always “a long heritage and a strict discipline, honored, preserved, extended!” They say it because they must and, often, because they believe it. From the outside, it’s about impossible to test those claims and people get downright offended when you even broach the subject. Some folks have managed beautifully; Mairs and Power come to mind. Some have been disasters, Third Avenue most recently. And others, such as Royce Funds, are just now trying to navigate it. Without access to contacts within the organization or with their peers, we only see shadows and flickers, “as through a glass, darkly.”
Hate it when that happens.
Update:
We’ve had a chance to speak with Steve Romick from FPA about our concerns. We will share Mr. Romick’s reflections on them in our April issue.
Andrew Foster, Sufi master
Sell your cleverness and buy bewilderment.
Cleverness is mere opinion, bewilderment intuition.
― Rumi, Masnavi I Ma’navi,ca. 1270
I like Andrew Foster, manager of Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX). I also respect him. The confluence of those two is rare.
In his essay “Self Reliance,” Emerson describes “foolish consistency” as “the hobgoblin of little minds.” The rough translation is the people don’t like to admit that they’re unsure, whether it’s about what to think or what to do, even to themselves. And so they come up with procedures, policies, explanations, Great Insights and Magic Rules and claim you can stop thinking worrying now. You’ll notice this in the classroom: young teachers are terrified at losing control or losing respect while really experienced ones are comfortable admitting that they simply don’t have nearly as many answers as they’ve got questions, suspicions or possibilities.
That came to mind in reading two of Mr. Foster’s recent pieces, his Fourth Quarter 2015 Portfolio Review and his Semi-Annual Report. Between the two, you get a sense of a guy who is really sharp but not under the illusion of his own omniscience.
The short version of investing in the emerging markets over the last couple years: things have been wildly volatile and mostly negative, China’s been a concern, Seafarer’s doing better than the great majority of its peers.
Most managers, whether they’re small minded or they think you are, would have said that in about three paragraph – emphasizing their own excellence in the latter – and hit “send.”
Mr. Foster approached things differently. His analysis was more nuanced, sharper, more self-effacing and more respectful of his readers’ intelligence than almost any of what I’ve read in the professional press. You should read it, but only if you have the time to think about what you’ve read because you’ll encounter more careful speculation than illusory certainty.
Why was the market rising at the start of the fourth quarter?
Between October 1 and November 4, the benchmark index rose 9.72%. There was no obvious reason for this gain.
Okay, so what explains Seafarer’s outperformance?
The Fund’s marginal outperformance was due to selected holdings in China, Japan, Indonesia and Turkey. Those holdings had no unifying theme or idea that could explain the basis for their performance during the quarter.
Perhaps it’s because you were defensively positioned on China?
Unfortunately, my notion of “defensive” valuations proved faulty.
Oh. Dja do any better on currencies?
My prediction [there] was terribly wrong.
Ah, I see. You’ve described Seafarer as a China-centric portfolio. What’s going on there?
I wish I knew with certainty. Unfortunately, the situation is sufficiently opaque that facts are scant, and thus I can only speculate as to the cause behind the A-share market’s sudden collapse.
Well, how about a guess then? Surely you’ll do better than the bobbleheads in the media.
Unfortunately, I can only speculate as to the actual cause of the decline, so my thoughts on the matter are frankly no better than the media’s. I have very few facts to substantiate my arguments; all I can do is look at the pattern of events that has unfolded, and speculate as to the causes.
I’m getting desperate here, Andrew. Why not just fling a wild speculation or two at us?
I would suggest two possible scenarios that might have caused the sell-off:
- The Renminbi’s weakness is not the direct cause of the decline, but it is a precursor for a growing liquidity shortage within the Chinese financial system. The currency’s persistent weakness may indicate that one or more banks, or perhaps some portion of the “shadow banking system,” may soon experience a liquidity crisis. This explanation would suggest the currency is signaling stressed liquidity within the financial system, to which stocks have reacted swiftly and punitively.
- The current government is unstable. Over the past three years, the government has propagated a sweeping anti-corruption campaign that has sometimes terminated in controversial political purges. The government has also introduced bold economic reforms – reforms that I largely support – but that have undoubtedly alienated powerful vested interests. Meanwhile, the current president has sought to consolidate power in a manner not seen since Mao’s era. It might be that such dramatic actions have silently eroded support for the current government among powerful factions within the Communist party. If so, the weakness in the currency and the stock market might portend a deeper source of instability.
Either scenario might have been the root cause of the volatility we observed; it is also possible that both acted in tandem.
You get the idea, I think: rather more insight than ego, important arguments made in a clear and accessible style.
In terms of portfolio positioning, he’s finding better values in Latin America and Emerging Europe than in Asia, so the portfolio is the least Asia-centered in its history. Similarly, there are intriguing opportunities in larger firms than in smaller ones right now; he’s actually been surprised at his portfolio’s small- to mid-cap positioning, but that’s where the value has been.
Bottom line
Seafarer remains a core position in my non-retirement portfolio and I’ve been adding to it steadily. Valuations in the emerging markets are compelling, with stocks trading at P/E ratios of 5 or 6. I’m tempted to sell my holdings in Matthews Asia Growth & Income (MACSX) and roll them into Seafarer, mostly as an attempt to simplify, but the two really do seem to be driven by diverse forces.
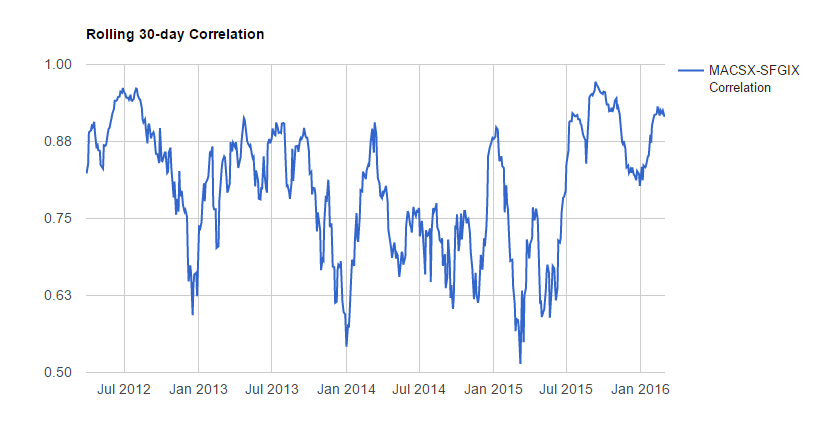
For now, I’ll continue to invest in each and, mostly, ignore the noise.
The tough question remaining
If emerging markets are simultaneously our best and our worst investment option, what on earth do we do with them? There’s a near-universal agreement that they represent the cheapest stocks and most dynamic economies in the world. And yet, collectively, over the last decade EM equity funds have made 1.3% annually with a standard deviation of 23. Run away? Pretend that investing in Nestle is the same just because they sell a lot in emerging markets? Hedge, which is tough? Hybrid? Hope? The worst case is “hire Greed and Panic to manage your investments,” though that seems awfully popular.
The source of my opening couplet was Jalal al-Din Muhammad Balkhi, a13th century Persian Sufi poet, mystic, teacher. “Rumi” is a nod to where he grew up, Rûm. Today we call it Turkey but since it had long been a Roman province, it got tagged with the term “Roman.”
He’s famous for his erotic poetry, but I like his description of the writing process at least as much:
All day I think about it, then at night I say it.
Where did I come from, and what am I supposed to be doing?
I have no idea.
Whoever Brought Me Here Will Have to Take Me Home
Fans of that damned annoying inspiration wall art would appreciate this question of his, “If you are irritated by every rub, how will your mirror be polished?”
The Weather
By Edward Studzinski
 “When we unleash the dogs of war, we must go where they take us.”
“When we unleash the dogs of war, we must go where they take us.”
Dowager Countess of Grantham
Starting off one of these monthly discussions with a title about the weather should be indicative that this piece will perhaps be more disjointed than usual, but that is how the world and markets look to me at present. And there is very little in the way of rational explanation for why the things that are happening are happening. My friend Larry Jeddeloh, of The Institutional Strategist, would argue that this country has been on a credit cycle rather than a business cycle for more than fifteen years now. Growth in the economy is tied to the price and availability of credit. But the cost of high yield debt is rising as spreads blow out, so having lots of cheap credit available is not doing much to grow the economy. Put another way, those who need to be able to borrow to either sustain or grow their business, can’t. A friend in the investment banking business told me yesterday about a charter school that has been trying to refinance a debt package for several years now, and has not been able to (thank you, Dodd-Frank). So once again we find ourselves in a situation where those who don’t need the money can easily borrow, and those who need it, are having difficulty obtaining it. We see this in another area, where consumers, rather than spend and take on more debt, have pulled back.
Why? We truly are in a moment of deflation on the one hand (think fuel and energy costs) and the hints of inflation on the other (think food, property taxes, and prescription drug costs on the other). And the debt overload, especially public debt, has reached a point where something has to be done other than kicking the can down the road, or other major crisis. I would argue we are on the cusp of that crisis now, where illiquidity and an inability to refinance, is increasingly a problem in the capital markets. And we see that, where the business models of businesses such as energy-related master limited partnerships, premised on always being able to refinance or raise more equity, face issues.
I was reading through some old articles recently, and came across the transcript in Hermes, the Columbia Business School publication, of a seminar held in May 1985 there. The speakers were Warren Buffett, James Rogers, Jr., and Donald Kurtz. As is often the case, sifting through the older Buffett can be rewarding albeit frustrating when you realize he saw something way before its time. One of the things Buffett said then was that, based on his observations of our political system, “ … there is a small but not insignificant probability that we will lose fiscal control at some point.” His point was that given a choice, politicians will always opt for an implicit tax rather than an explicit tax. If expenditures should determine the level of explicit taxes, than taxes should cover expenditures. Instead, we have built in implicit taxation, expecting inflation to cover things without the citizens realizing it (just as you are not supposed to notice how much smaller the contents are with the packaging changes in food products – dramatically increasing your food budget).
The easier way to think of this is that politicians will always do what allows them to keep doing what they like, which is to stay in office. Hence, the bias ends up being to debase the currency through the printing presses. So you say, what’s the problem? We have more deflation than inflation at this point?
And the problem is, if you look at history, especially Weimar Germany, you see that you had bouts of severe inflation and sharp deflationary periods – things did not move in a straight line.
Now we have had many years of a bull market in stocks and other assets, which was supposed to create wealth, which would than drive increases in consumption. The wealth aspect happened, especially for the top 5%, but the consumption did not necessarily follow, especially for those lower on the economic ladder. So now we see stock and asset prices not rising, and the unspoken fear is – is recession coming?
My take on it, is that we have been in a huge jobless recovery for most of the country, that the energy patch and those industries related to it (and the banks that lent money) are now beyond entering recession, and that those effects will continue to ripple through the rest of the economy. Already we see that, with earnings estimates for the S&P 500 continuing to drift lower. So for most of you, again, my suggestion is to pay attention to what your investment time horizons and risk tolerances are.
Moving totally down a different path, I would like to suggest that an article in the February 28, 2016 New York Sunday Times Magazine entitled “Stocks & Bots” is well worth a read. The focus of the article is about the extent to which automation will eliminate jobs in the financial services industry going forward. We are not talking about clerks and order entry positions. That revolution has already taken place, with computerized trading over the last twenty years cutting by way of example, the number of employees buying and selling stock over the phone from 600 to 4 at one of the major investment banking firms. No, we are talking about the next level of change, where the analysts start getting replaced by search programs and algorithms. And it then moves on from there to the people who provide financial advice. Will the Millennials seek financial advice from programs rather than stock brokers? Will the demand grow exponentially for cheaper investment products?
I think the answer to these questions is yes, the Millennials will do things very differently in terms of utilizing financial services, and the profit margins of many of today’s investment products, such as mutual funds, will be driven much lower in the not too distant future. Anecdotally, when one has a year in the markets like 2015 and the beginning of 2016, many investment firms would push down the bonus levels and payments from the highest paid to take care of the lower ranks of employees. I was not surprised however to hear that one of the largest asset managers in the world, based in Boston, had its senior employees elect to keep the bonuses high at the “partner” levels and not take care of the next levels down this past year. They could see the handwriting on the wall.
All of which brings me back to the weather. Probably suggesting that one should read a politically incorrect writer like Mark Twain is anathema to many today, but I do so love his speech on the New England weather. For a preview for those so inclined, “The lightning there is peculiar; it is so convincing that, when it strikes a thing it doesn’t leave enough of that thing behind for you tell whether – Well, you’d think it was something valuable, and a Congressman had been there.”
At a future point I will come back for a discussion of Mr. Twain’s essay “On the Decay of the Art of Lying” which might be essential reading as this year’s elections take shape.
High Dividends, Low Volatility
 From the Trapezoid Mailbag:
From the Trapezoid Mailbag:
A financial advisor in Florida is interested in low-volatility products. With the market so choppy, he would like to dial down risk in his client’s portfolio. He wondered whether SEI Institutional Managed Trust Tax-Managed Volatility Fund (TMMAX) was a suitable choice.
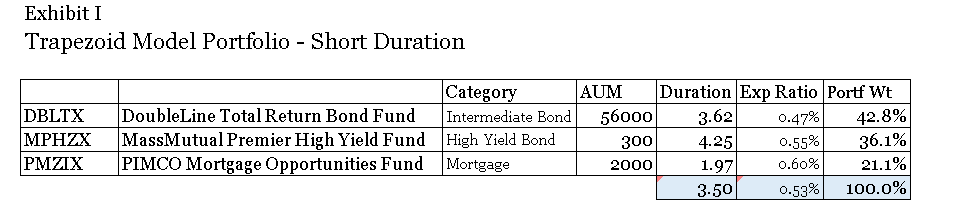
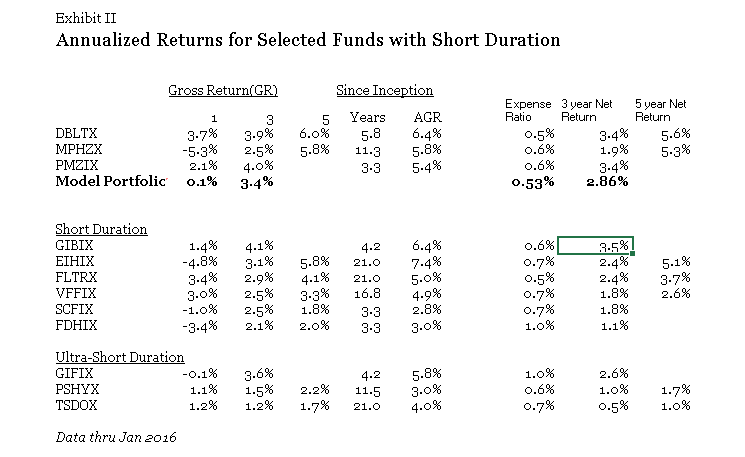
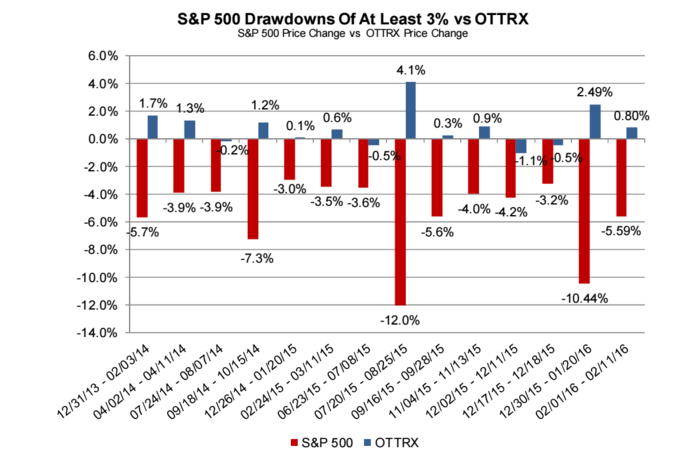
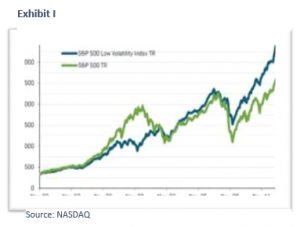 As Exhibit I illustrates low-volatility has been a successful investment strategy in recent years. A good argument can be made that historically, low-volatility stocks were mispriced. Players like Berkshire Hathaway and private equity capitalized on this by levering up these firms to deliver strong risk-adjusted returns. There is a heavy overlap between the low-volatility universe and the high-dividend universe. Many high-dividend stocks have dropped assets into REITs in recent years which have fueled better returns for this sector. Low volatility has outperformed the broad market meaningfully for the past two quarters, partly due its lower beta.
As Exhibit I illustrates low-volatility has been a successful investment strategy in recent years. A good argument can be made that historically, low-volatility stocks were mispriced. Players like Berkshire Hathaway and private equity capitalized on this by levering up these firms to deliver strong risk-adjusted returns. There is a heavy overlap between the low-volatility universe and the high-dividend universe. Many high-dividend stocks have dropped assets into REITs in recent years which have fueled better returns for this sector. Low volatility has outperformed the broad market meaningfully for the past two quarters, partly due its lower beta.
Trapezoid doesn’t take a view on whether these trends will continue or whether low-volatility is the best place to hide out in a tough market. In this instance, we wonder whether the “private equity bid” which contributed to the sector’s strong performance will be as reliable as corporate credit markets tighten and whether the increasing use of REIT/MLP structures has about run its course. What Trapezoid does do is help investors, advisors, and allocators find the best instruments to express their investment strategy based on extrapolation of historic skill in relation to risk.
There are several passive strategies which express the same theme. For example, Power Shares markets an S&P 500 Low Volatility Portfolio (SPLV) and an S&P 500 High Dividend Low Volatility Portfolio (SPHD). Those two funds move virtually in lockstep, underscoring the overlap between high dividend and low volatility. The correlation between the PowerShares indices and TMMAX is 98.5% and the expense ratio is 70-75 basis points lower.
Despite the availability of good passive indices, we would nonetheless consider TMMAX. The fund’s track record has been slightly above average, making us slightly confident (53%) it is worth the added cost. SEI also manages the SEI US Managed Volatility Fund which has a 50% confidence rating (slightly lower due mainly to higher expense ratio.)
SEI relies on three subadvisors to manage the fund. The largest sleeve is managed by Analytic Investors (39%) followed by LSV (35%) and AJO. While we don’t have sleeve-level data, we can evaluate the body of work by Analytic and LSV looking at comparable sole-managed funds. Analytic’s track record the past five years on Touchstone Dynamic Equity Fund (TDELX) is good but the previous five years were poor. LSV’s record at LSV Conservative Value Equity Fund (LSVVX) and Harbor Mid-Cap Value Fund (HIMVX) was middling.
We have discussed in the past that Morningstar star ratings have some predictive value but that even a five-star rating is not sufficient to make an investment decision. The SEI funds are good examples. TMMAX, SEVIX, and SXMAX all carry five star ratings, and we agree investors are better off choosing these funds than many of the alternatives but the evidence of manager skill is inconclusive.
If the advisor is willing to expand his horizons a little, he can find similar funds which improve the odds a little. We used the Orthogonal Attribution Engine to find highly correlated funds with better confidence ratings and came up with the following.
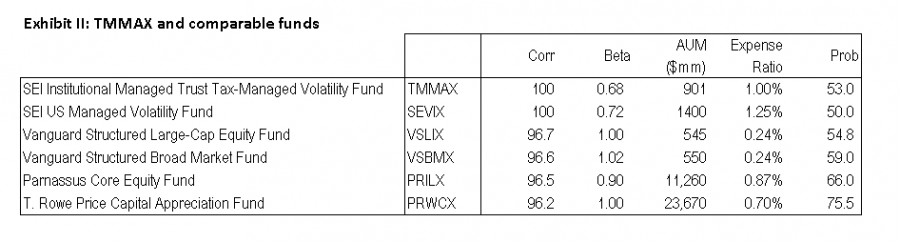
A few observations
- T. Rowe Price Capital Appreciation Fund (PRWCX) is closed to new investors
- The two Vanguard funds attempt to outperform their benchmark indices using a quantitative strategy.
- Many of the other similar funds have higher betas, which may be a deal breaker for our advisor who wants to reduce his client’s market exposure
- Many of these funds are large blend funds, accessible to demo customers at the www.fundattribution.com website.
- Our confidence ratings are based on data through 10/30/15. In the subsequent months TMMAX’s performance lagged the lower-cost PowerShares indices. This may serve to erode our confidence that active management pays for itself. Updated data will be posted shortly
The heightened appeal of low-volatility funds might suggest something else: Advisors are more focused on extreme negative outcomes which could get them fired than extreme positive outcomes. In a choppy market, low-volatility funds have the allure of a safe haven. We don’t have a view on the wisdom of this. But we are interested in helping allocators avoid individual managers who have the potential to “blow up.” One of Trapezoid’s forthcoming new metrics hones in on this risk by focusing on the likelihood of extreme negative outcomes.
 What’s the Trapezoid story? Leigh Walzer has over 25 years of experience in the investment management industry as a portfolio manager and investment analyst. He’s worked with and for some frighteningly good folks. He holds an A.B. in Statistics from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from Harvard University. Leigh is the CEO and founder of Trapezoid, LLC, as well as the creator of the Orthogonal Attribution Engine. The Orthogonal Attribution Engine isolates the skill delivered by fund managers in excess of what is available through investable passive alternatives and other indices. The system aspires to, and already shows encouraging signs of, a fair degree of predictive validity.
What’s the Trapezoid story? Leigh Walzer has over 25 years of experience in the investment management industry as a portfolio manager and investment analyst. He’s worked with and for some frighteningly good folks. He holds an A.B. in Statistics from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from Harvard University. Leigh is the CEO and founder of Trapezoid, LLC, as well as the creator of the Orthogonal Attribution Engine. The Orthogonal Attribution Engine isolates the skill delivered by fund managers in excess of what is available through investable passive alternatives and other indices. The system aspires to, and already shows encouraging signs of, a fair degree of predictive validity.
The stuff Leigh shares here reflects the richness of the analytics available on his site and through Trapezoid’s services. If you’re an independent RIA or an individual investor who need serious data to make serious decisions, Leigh offers something no one else comes close to. More complete information can be found at www.fundattribution.com. MFO readers can sign up for a free demo.
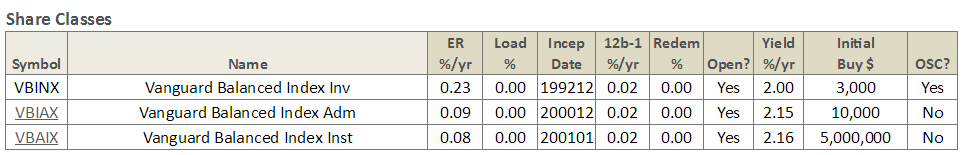
Offered without comment: Your American Funds share class options
MFO Rating Metrics
 When MFO introduced its rating system in June of 2013, it chose Martin Ratio as the principal performance rating metric. Martin is a risk adjusted return metric that is the ratio between excess return, which is the compounded annualized total return above risk free T-Bill return, divided by the so-called Ulcer Index, which is a measure of extent and duration of drawdown. Our friend Peter Matin formulated the Ulcer Index as described in An Alternative Approach to the Measurement of Investment Risk & Risk-Adjusted Performance.
When MFO introduced its rating system in June of 2013, it chose Martin Ratio as the principal performance rating metric. Martin is a risk adjusted return metric that is the ratio between excess return, which is the compounded annualized total return above risk free T-Bill return, divided by the so-called Ulcer Index, which is a measure of extent and duration of drawdown. Our friend Peter Matin formulated the Ulcer Index as described in An Alternative Approach to the Measurement of Investment Risk & Risk-Adjusted Performance.
For each fund category, like Large Growth or Moderate Allocation, the MFO Rating system divides funds into five groups or “quintiles” based on the risk adjusted return over selected evaluation periods. Funds with the highest Martin in each category are assigned a 5, while those with the lowest receive a 1.
While this approach suits many MFO readers just fine, especially having lived through two 50 percent equity market drawdowns in the past 15 years, others like Investor on the MFO Discussion Board, were less interested in risk adjusted return and wanted to see ratings based on absolute return. Others wanted to see ratings based on the more traditional risk adjusted Sharpe Ratio. (For more definitions, see A Look A Risk Adjusted Returns.)
It took a while, but subscribers on our MFO Premium site can now choose which rating metric they prefer, including multiple rating metrics simultaneously.
For example, since the start of the current market cycle in November 2007, which Small Cap funds have delivered the best absolute return (APR) and the best Martin Ratio and the best Sharpe Ratio? To find the answer, enter the selection criteria on the MFO MultiSearch tool, as depicted below (click image to enlarge), then hit the “Submit Search” button …
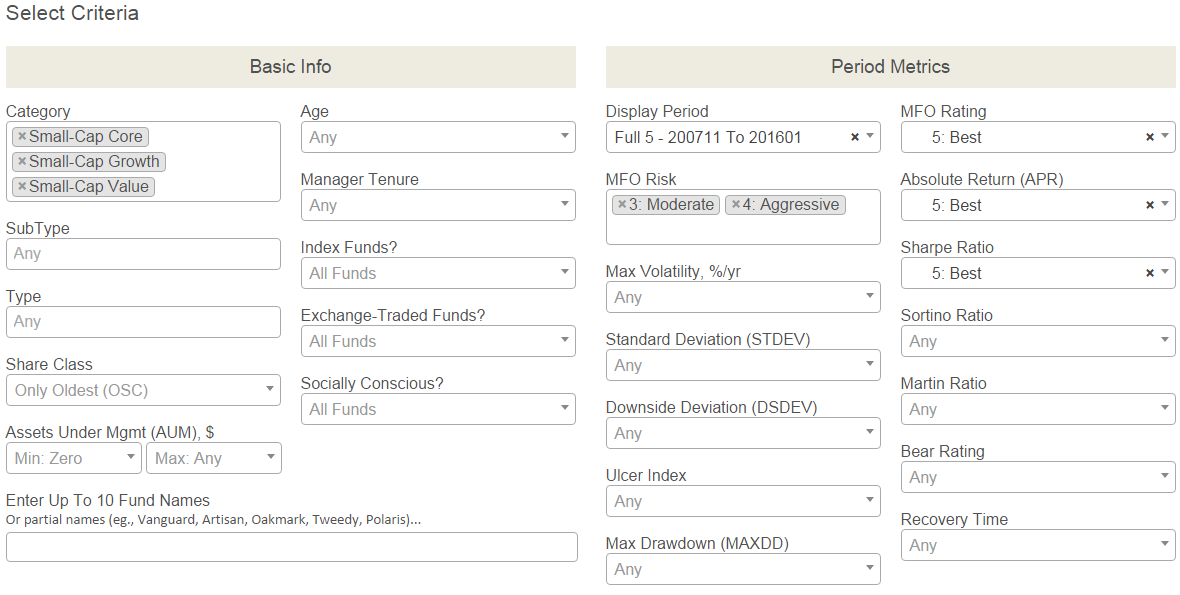
A total of 28 funds appear from the more than 9,000 unique funds in the MFO database. Here are the first 10, sorted by MFO Risk and then name:
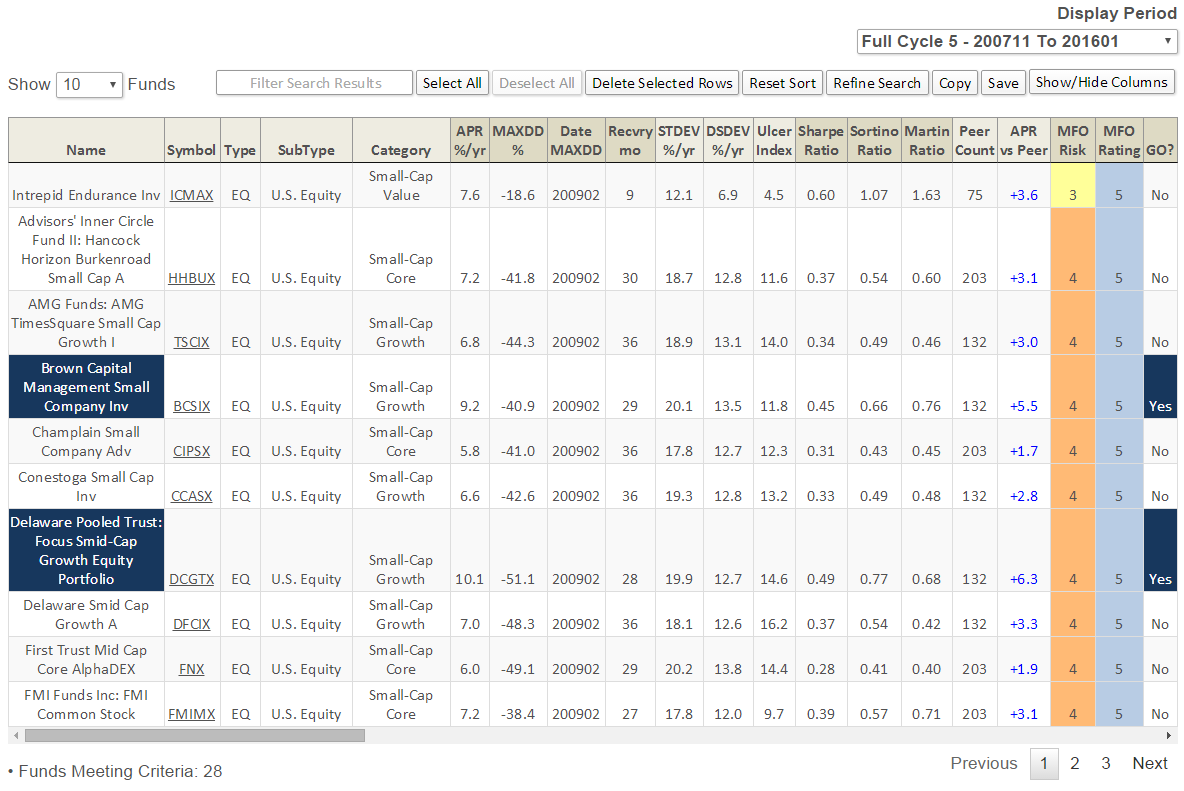
Notables include Brown Capital Mgmt Small Company (BCSIX), Champlain Small (CIPSX), Conestoga Small Cap (CCASX), and FMI Common Stock (FMIMX). The closed BCSIX is both an MFO Great Owl and Fund Alarm Honor Roll fund. It is also a Morningstar Gold Medal fund, while Silver goes to CIPSX and CCASX.
Intrepid Endurance (ICMAX) has the lowest risk rating with a MFO Risk of 3, which means this fund has historically carried volatility suited for investors with Moderate risk tolerance. Unlike other metrics in the MFO ratings system, and in fact the risk metric in Morningstar’s rating system, which assign risk relative to other funds in category, the MFO Risk metric assigns its rating based on volatility relative to the overall market.
The MFO MultiSearch tool now enables searches using more than 55 screening criteria, organized by Basic Info, Period Metrics, Composite Period Metrics, MFO Designations, Portfolio Characteristics, and Purchase Info. A list of current criteria can be found here.
The Alt Perspective: Commentary and news from DailyAlts.
 Pruning Season
Pruning Season
You can call it a cycle, a season, or even a cleansing process, but when one looks at the liquid alternatives market, it’s apparent that there is some pruning going on. Some cleaning out of the products that no longer appeal to investors, those that hit a performance patch from which it would be near impossible to recover, or just didn’t gather the requisite assets for a fund to be viable. Clean out the funds that are not producing the intended results, or just aren’t resonating with investors.
This is all a healthy process as it makes room for newer products, the next generation. It also allows for a greater investment into existing products. Interestingly, we have already seen 9 alternative funds liquidated in the first two months of the year (and at least two more schedule to be liquidated) – some announced late last year, but nonetheless, fully liquidated in 2016. And these are from some bigger names in the industry, such as Lazard, Collins, Whitebox, Virtus, Ramius and Clinton. Some seasoned hedge fund managers in there, along with seasoned asset management firms.
Four of the liquidate funds were long/short equity funds, two were multi-alternative funds, and the remaining three included market neutral, event driven and non-traditional bonds. All in all, I think we will see more pruning in the coming months as fund managers rationalize their fund lineup as markets sell off, and begin thinking about the next set of products to introduce to the market.
The pruning process is healthy and helps future growth, so don’t be surprised to see more down the road. It’s just part of the natural cycle.
Asset Flows
January saw a continuation of 2015 where investors continued to pour money into multi-alternative funds and managed futures funds (inflows of $1.2 billion and $1.5 billion, respectively), while pulling assets from non-traditional bond funds, long/short equity and market neutral (-$3 billion, -$390 million and -$340 million, respectively). Excluding non-traditional bond funds and commodities, alternative mutual funds and ETFs gathered a total of $2.4 billion in January, bringing the total 12-month haul to $18.7 billion, third of any category behind international equity and municipal bonds and 11.5% of all net asset inflows.
Commodities bounced back in January with total inflows of $3.3 billion, led primarily by flows to precious metals funds, and gold funds in particular. Non-traditional bond funds, viewed as an alternative to long-only bond funds and a protective hedge against interest rate increases, have continued to disappoint in the aggregate. As a result, investors have pulled $17.9 billion of assets from these funds over the past 12 months.
Extended Reading
What did DailyAlts readers enjoy the most this past month? The three of the most widely read articles this past month were:
While it appears to be pruning season, that doesn’t mean it is time to stop looking for alternative funds. With Spring approaching, now is a good time to take a look across your portfolio at the risks you have exposure to, and perhaps do a bit of pruning of your own to balance risks and hedge for what might be more volatility ahead.
Have a great March, and to keep up with daily or weekly news in the liquid alts market, be sure to sign up for our newsletter.
Observer Fund Profiles: LSOFX / RYSFX
Each month the Observer provides in-depth profiles of between two and four funds. Our “Most Intriguing New Funds” are funds launched within the past couple years that most frequently feature experienced managers leading innovative newer funds. “Stars in the Shadows” are older funds that have attracted far less attention than they deserve.
LS Opportunity Fund (LSOFX): this was a really solid long/short fund that had to press the “reset” button last May when their sub-advisor decided to pack it up and call it a career. In Prospector Partners, they may have found a team that executes the same stock-by-stock discipline even more excellently than their predecessors.
Royce Global Financial Services (RYFSX): when you think “financial services,” you likely think “monstrous big banks with tendrils everywhere and eight-figure bonuses.” Royce thinks differently, and their focus on smaller firms that dominate financial niches worldwide has made a remarkable difference for their investors.
Elevator Talk: Jim Robinson, Robinson Tax-Advantaged Income (ROBAX)
 Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
 Jim Robinson formed Robinson Capital Management, located in Detroit’s ritzy Grosse Pointe suburb, in December, 2012. The firm manages about a quarter billion in assets for a handful of high net worth clients and advises two (soon to be three) mutual funds.
Jim Robinson formed Robinson Capital Management, located in Detroit’s ritzy Grosse Pointe suburb, in December, 2012. The firm manages about a quarter billion in assets for a handful of high net worth clients and advises two (soon to be three) mutual funds.
From 1987-1999, Mr. Robinson served as the Fixed Income CIO for the Munder Funds. During his stint, he grew fixed income AUM from $100 million to $20 billion. Eventually promoted to Chairman, CEO and President, he was responsible for about $38 billion in assets. He left Munder for Telemus Capital Partners, LLC, with whom his firm still has a relationship.
Robinson Capital uses a variety of strategies in their separate accounts. The Tax-Advantaged Income Fund pursues one strategy: it invests in closed-end muni bond funds. Closed-end funds (CEFs) are strange creatures, the forerunners of today’s actively-managed ETFs. They have managers and portfolios like open-end mutual funds do, but trade on exchanges like stocks and ETFs do. Such funds have several relevant characteristics:
- They are far more likely to pursue income-oriented strategies than are open-end funds
- They are far more likely to make extensive use of leverage and hold more illiquid securities than are open-end funds
- Because they trade on exchanges, the managers never need to worry about meeting redemptions or closing the fund to new investors; they issue a set number of shares of the CEF during their initial public offering but after that they let buyers and sellers find each other.
- Because they trade on exchanges, the market price of their shares changes minute-by-minute, and
- Because they trade on exchanges, the net asset value of a share (the market value of all of the fund’s holdings divided by the number of shares outstanding) can diverge dramatically from that share’s market price (that is, the amount a potential seller can get at one particular moment for a share of the fund).
When shareholders panic, they may succumb to the temptation to sell shares of their fund for 15, 20 or even 40% less than they’re nominally worth, just because the seller really wants cash-in-hand. That’s mostly irrational. A handful of mutual fund firms – RiverNorth, Matisse, and Robinson among them – look to profit from panic. Using various metrics, they decide when to move in and buy shares that are selling at an unsustainable discount to their net asset values.
If everything goes according to plan, that strategy offers the potential for sustained, substantial, market-neutral gains: as soon as panic subsides, even if the market is still falling, a degree of rationality returns, investors start buying the discounted CEF shares, that bids up the price and the discount closes. If you invest before the crowd, you benefit when the shares you bought at, say, a 25% discount can now be sold at just a 5% discount.
Here’s a hypothetical illustration: the NAV of the Odd Income Fund is $100/share but, when rumors of dinosaurs rampaging down Wall Street rattles people, its market price drops to $75/share. Robinson moves in. In six months, the panic has passed, Odd Income’s NAV has risen a couple percent and its discount contracted to its non-panic norm of 5%. In such a scenario, Odd Income has earned 2% but folks who bought shares during the panic earned 29%.
There are distinct risks to playing this game, of course. The falling knife might continue to fall harder and faster than you’d imagined so that the 25% discount might widen to 35%. The manager of the underlying CEF might find that using leverage in a panicky market drives down the fund’s NAV as well as its market price. And, too, the CEF manager might simply do something stupid. It happens.
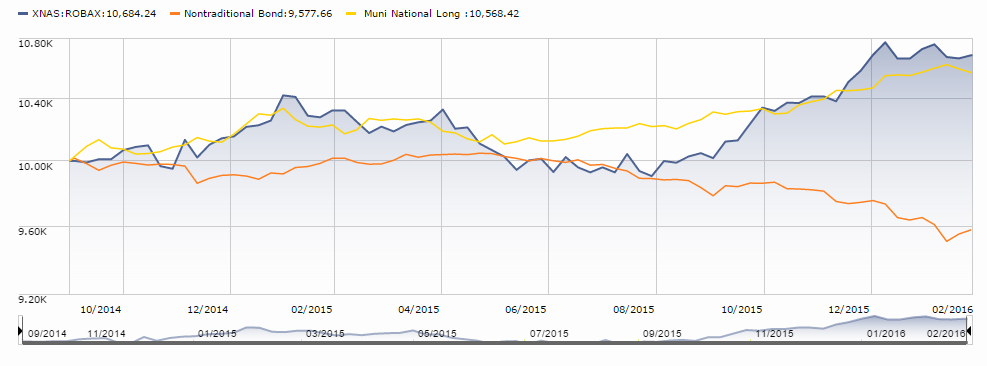
The folks who manage CEF-focused funds argue that downside risks are manageable through a combination of careful security selection, position-size limits and hedging. The upside can be dramatic. Here is the performance chart for ROBAX against two possible benchmarks: its Morningstar non-traditional bond peer group (orange) and long-term national muni bond group (yellow).
Here are Mr. Robinson’s 200 words on why investors concerned about income and income taxes should add ROBAX to their due-diligence list:
I generally tell people that the first three things you need to know about our fund are these:
- We pay out 40 basis points a month in tax-exempt income, on average
- We present very little credit risk; our portfolio’s credit quality is A/A+
- We hedge out interest rate risk, such that our effective duration is under a year.
There are 191 Tax-exempt closed-end funds. Today, 150 are trading at a discount to NAV. Some of those discounts are rational; if you have a poorly-managed fund buying difficult-to-price securities and misusing leverage, it should be trading at a discount. Heck, I analyze some of these funds and suspect the discount should be bigger than it is.
What we do is move money from rationally discounted funds to irrationally discounted ones. Six large fund companies – BlackRock, PIMCO, Nuveen and company – dominate the CEF space. That’s important because those companies have pretty good governance practices in place; BlackRock is aggressive about merging funds to harvest economies of scale, others do share buybacks and so on. When funds with good management, good governance and good portfolios sell at irrational discounts, we move. Bill Gross did me a big favor. Two days before we launched, he resigned from PIMCO. Gross had nothing to do with PIMCO’s CEFs but suddenly funds that always trade at a premium were available at a discount. We moved in, the discount predictably reversed, and we closed the position at a nice profit. That discount arbitrage adds about 200 bps to our performance.
The other thing we do that individual investors can’t, and that most advisors would find tough, time-consuming and expensive, is we largely hedge interest rate risk out of the portfolio. Tax-exempt CEFs tend to be long-dated and leveraged so they typically have 10-12 year weighted durations. In a year like 2013 when rates rise 1%, they lose 10-12% in principal value. Our hedge is not perfect, since Treasuries and munis don’t trade in perfect sync, but it’s pretty good.
Robinson Tax-Advantaged Income has a $2500 minimum initial investment for the “A” shares and $1,000,0000 for “I” shares. While there’s a sales load, load-waived shares are widely available. Direct expenses are capped at 1.60% on the “A” shares. Since the fund invests in other funds, you indirectly pay (through lower returns) a portion of those funds’ expenses. In 2014, that added 1.14% to ROBAX’s today expenses. The fund has about gathered about $74 million in assets since its September 2014 launch. Here’s the fund’s homepage.
Funds in Registration
Funds need to submit their prospectuses for SEC review before they’re permitted to offer the fund to the public. The SEC has 75 days in which to ponder the matter, which means that proposed new funds cool their heels for about two and a half months. During that time their prospectuses are available for review on the SEC’s website but fund advisors are forbidden to talk publicly about them. Each month Funds in Reg gives you a heads-up about what’s in the SEC pipeline.
Except for last month, when I stupidly forgot to include the file in our February issue. As a result, this month we cover the last two sets of no-load retail funds that will become available between March and May. We found 17 funds that qualify. Particularly interesting morsels include:
- 361 Domestic Long/Short Equity Fund, which will be managed by a really renowned investor – Harindra de Silva – who has a earned a great deal of respect in the industry and who already manages a number of top-ranked funds.
- Matthews Asia Credit Opportunities, which appears to be a high-yield, distressed securities version of the very fine Matthews Asia Strategic Income Fund.
- RiverPark Commercial Real Estate Fund, the latest entry in RiverPark’s quest to bring hedge fund strategies to “the mass affluent.” This fund has been running as a hedge fund for about five years now.
Sadly, there are a handful of future “Off to the Dustbin of History” nominees as well but I suppose that’s the magic of capitalism: 90% of the stuff we try fails, 9% does okay and 1% changes the world.
Uzès Grands Crus I
The French, being French, have their financial priorities in order. In February, Financière D’uzès announced the launch of their third mutual fund devoted to the investment potential of bottles of fine wine. At least 75% of the fund’s assets will be bottles of fine and their aim is “to outperform the annual rate for the five-year French treasury bond (OAT) with a minimum return of 5%.”
I reflected, very very briefly, on the investment value of the bottle of Lambrusco I bought at Trader Joe’s for $4.99, then made mid-winter sangria instead.
Manager Changes
The biggest news, by far, this month is the impending departure of Taymour R. Tamaddon from T. Rowe Price Health Sciences (PRHSX) and Donald Yacktman from his namesake funds. When Kris Jenner left the fund three years ago (how time flies!), the accepted wisdom was that nobody could live up to his legacy. Mr. Tamaddon then led the fund to 22.4% annualized returns, nearly 500 bps above his peers and good enough for a top 2% record.
Mr. Tamaddon steps down on July 1, 2016, is succeeded by Ziad Bakri then becomes manager of the $12 billion T. Rowe Price Institutional Large-Cap Growth Fund (TRLGX) on January 1, 2017.
 Effective May 1, 2016, Donald A. Yacktman will transition to an advisory role and will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for AMG Yacktman (YACKX) and AMG Yacktman Focused (YAFFX) funds. The roughly corresponds with his 75th birthday. Mr. Yacktman has been managing mutual funds since 1968, starting with Stein, Roe and the Selected American Shares before founding Yacktman Asset Management in 1992. $10,000 invested in YACKX that year would have grown to $95,000 today, which compares well to the returns on an investment in the S&P500 ($76,000) or the average large-value fund ($56,000). He was named Morningstar’s Manager of the Year in 1991 and was joined on the management team by his son, Stephen, in 2002. Stephen Yacktman and Jason Subotky will manage the funds after the transition.
Effective May 1, 2016, Donald A. Yacktman will transition to an advisory role and will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for AMG Yacktman (YACKX) and AMG Yacktman Focused (YAFFX) funds. The roughly corresponds with his 75th birthday. Mr. Yacktman has been managing mutual funds since 1968, starting with Stein, Roe and the Selected American Shares before founding Yacktman Asset Management in 1992. $10,000 invested in YACKX that year would have grown to $95,000 today, which compares well to the returns on an investment in the S&P500 ($76,000) or the average large-value fund ($56,000). He was named Morningstar’s Manager of the Year in 1991 and was joined on the management team by his son, Stephen, in 2002. Stephen Yacktman and Jason Subotky will manage the funds after the transition.
Other than that, we found about 36 manager changes, a few years overdue.
Updates
Sequoia Fund (SEQUX) continues its defense of Valeant Pharmaceuticals in its Annual Report (2016) and they continued dodging the issue.
For the stock to regain credibility with long-term investors, Valeant will need to generate strong earnings and cash flow this year, make progress in paying down some of its debt, demonstrate that it can launch new drugs from its own development pipeline and avoid provoking health care payers and the government. The company has committed to doing all of these things and we are confident interim CEO Howard Schiller and interim board chairman Robert Ingram are focused on the right metrics. Before CEO J. Michael Pearson went out on an extended medical leave, he also seemed committed to this path.
“Avoid provoking health care payers.” Oh, right. That would be the predatory pricing model that attracted Sequoia to Valeant in the first place: Valeant would borrow money to buy a small pharmaceutical firm, then quintuple the price of the firm’s products. If that meant putting a few inexpensive lives at risk, well, that wasn’t Valeant’s problem.
Until it was. Before the blow-up, manager David Poppe’s tone was openly affectionate about “Mike,” Valeant’s president and almost giddy about the prospects. Valeant’s high-profile implosion cost Sequoia a lot:
As the largest shareholder of Valeant, our own credibility as investors has been damaged by this saga. We’ve seen higher-than-normal redemptions in the Fund, had two of our five independent directors resign in October and been sued by two Sequoia shareholders over our concentration in Valeant. We do not believe the lawsuit has merit and intend to defend ourselves vigorously in court. Moving along …
“Moving along”? No, it’s not time to move along, guys. Barron’s Chris Dieterich provides a nice synopsis of developments that transpired on February 29, the day Sequoia released their report:
Monday ushered in a nightmarish combination of trouble. First, Valeant said it would delay the release of its quarterly results. Then, news broke that Allergan (AGN) is challenging the patent to Xifaxan. Third, Moody’s Investors Service warned that it may need to downgrade portions of the company’s $31 billion of debt. Finally, headlines crossed the tape that Valeant faces a previously undisclosed investigation by the Securities and Exchange Commission.
All told, the stock plunged 18% to $65.80 — a fresh three-year low (“Sequoia Fund Picked A Bad Time To Stick Up For Valeant”).
The bigger, unanswered question is what does this say about you as investors? Any damage to your credibility is (a) self-inflicted and (b) deserved. You committed one third of your fund and all of your credibility to an amoral little schemer who, on his best days, stayed right at the edge of what’s legal. That’s a fact you acknowledged. Then you implicitly compared him to Warren Buffett, an investor whose moral compass, operating style and record makes him utterly incomparable.
Investors might, heck, investors must, ask: where was your brain? Were you so blinded by the prospect of easy money that you chose to ignore the hard questions? The most optimistic interpretation is that you’re not addressing such questions because you’re being sued and you can’t afford to admit to whatever idiocy led to the resignations of 40% of your board last fall. The worrisome interpretation is that Sequoia isn’t Sequoia anymore; that the clarity of thought that guided it to renown in decades past mostly now serves to mask a less exalted management.
Think it can’t happen? Check Magellan, Fidelity (FMAGX), the other Titan which has now managed to trail its peers over the past five, ten, fifteen and twenty year periods. Utterly dominant in the market cycle from 1973-1987 when it beat its peers by 1000 basis points/year, the fund hasn’t even managed consistent mediocrity since.
Morningstar doesn’t share my reservations and SEQUX retains a “Gold” analyst rating from the firm. Their equity analyst also doesn’t share my concerns about Valeant, which they rate (on 3/1/16) as a five-star stock whose shares are selling at about one-third of their fair value. Senior equity analyst Michael Waterhouse doesn’t “anticipate any major shift in our long-term thinking for the company.”
Briefly Noted . . .
SMALL WINS FOR INVESTORS
Chou has voluntarily decided to waive its entire advisory fee on the Chou Opportunity Fund (CHOEX) beginning on January 1, 2016. In addition, on February 18, 2016 Chou made a voluntary capital contribution to the Opportunity Fund in the amount of $918,468, which approximates the advisory fees retained by Chou with respect the Opportunity Fund last year. Why, you ask? The advisor describes it as “a gesture of goodwill … in recognition of the fund’s underperformance” in 2015. That’s an oblique reference to having lost 22% in 2015 and another 20% in the first two months of 2016.
The advisor to the Great Lakes Bond Fund has closed the fund’s Investor Class (GLBDX) and converted the former Investor accounts into Institutional Class (GLBNX) ones. They then lowered the minimum on the Institutional shares by 99%, from $100,000 to $1,000. Net, potential retail investors save 25 bps.
Hotchkis & Wiley Mid-Cap Value Fund (HWMAX) has reopened to new investors.
RS Partners Fund (RSPFX) reopened to new investors on March 1, 2016. None of the fund’s independent trustees have chosen to partner with you by investing in the fund. The managers’ investment in the fund ranges between “modest” and “none.”
Walthausen Small Cap Value Fund (WSCVX) reopened to new investors on March 1, 2016.
Wasatch Emerging Markets Small Cap Fund (WAEMX) has reopened to new investors. Thanks for the heads up, Openice!
CLOSINGS (and related inconveniences)
Nope, turns out “turning away money” wasn’t a popular move in February. We found no funds closing their doors.
OLD WINE, NEW BOTTLES
Armor Alternative Income Fund (AAIFX) has become Crow Point Alternative Income Fund.
Diamond Hill Strategic Income Fund (DSIAX) has been renamed the Diamond Hill Corporate Credit Fund to better reflect what it’s up to.
Forward no more. On May 1, 2016, the name “Forward” disappears from the world of mutual funds. In general, all of the former Forward Funds will be renamed as Salient Funds, which no change other than substituting “Salient” for “Forward” in the name. There are a few exceptions,
| Current Forward Name |
New Salient Name |
| Commodity Long/Short Strategy |
Commodity Long/Short Strategy |
| Credit Analysis Long/Short |
Tactical Muni Strategy |
| Dynamic Income |
US Dividend Signal |
| EM Corporate Debt |
EM Corporate Debt |
| Emerging Markets |
EM Dividend Signal |
| Frontier Strategy |
Frontier Strategy |
| Global Infrastructure |
EM Infrastructure |
| Growth Allocation |
Adaptive Balanced |
| High Yield Bond |
High Yield |
| Income Builder |
Adaptive Income |
| International Dividend |
International Dividend Signal |
| International Real Estate |
International Real Estate |
| International Small Companies |
International Small Cap |
| Investment Grade Fixed-Income |
Investment Grade |
| Real Estate |
Real Estate |
| Real Estate Long/Short |
Tactical Real Estate |
| Select Income |
Select Income |
| Select Opportunity |
Select Opportunity |
| Tactical Growth |
Tactical Growth |
| Total MarketPlus |
Adaptive US Equity |
TIAA-CREF has boldly rebranded itself as TIAA.


Straightforward. Yep. 74%. Unless you’re buying the retail share class in which case it’s nine of 33 funds excluding money markets, or 27%. 32.5% of all funds receive either four- or five-stars from Morningstar.
And about that “uncomplicated” thing? Count the number of clicks it takes you to get to any particular fund. It took me two cups of coffee before I finally got to the one I wanted.
As of May 9, 2016, Transparent Value becomes … well, insert your own snark here. In any case, the Transparent Value Funds become Guggenheim Funds.
| Current Name |
New Name |
| Trans Value Directional Allocation |
Guggenheim Directional Allocation |
| Trans Value Dividend |
Guggenheim RBP® Dividend |
| Trans Value Large-Cap Defensive |
Guggenheim RBP® Large-Cap Defensive |
| Trans Value Large-Cap Market |
Guggenheim RBP® Large-Cap Market |
| Trans Value Large-Cap Value |
Guggenheim RBP® Large-Cap Value |
On March 1, 2016, The Wall Street Fund (WALLX) became Evercore Equity Fund (EWMCX). The word “Equity” in the name also triggered a new promise in the prospectus that the fund, which already invests in equities, promises to invest in equities.
OFF TO THE DUSTBIN OF HISTORY
On whole, fund companies would be well-advised to extract their heads from their behinds. If you’re not willing to stick with a new fund for, say, a whole market cycle, then don’t launch the damned thing. The hypocrisy of declaring that you’re “long-term investors” and that you want to be “partners” with your investors, then closing a fund after 12-24 months, is toxic. It conveys some combination of the following three messages: (1) we’re panicked. (2) We have no ability to plan. (3) Pretty much everything we said when we launched the fund was cynical B.S. crafted by marketers who were, themselves, probably disgusted with us.
Which of those messages do you really want to be associated with?
Okay, back to the ranks of the walking dead and the dead dead after a short word of thanks to The Shadow, one of the stalwarts of our discussion board whose daily updates on the comings and goings is enormously helpful in keeping this list current.
Let’s go to Plan B: Under Plan A, Arden Alternative Strategies Fund (ARDNX) was slated to become Aberdeen Multi-Manager Alternative Strategies Fund (no ticker) on March 31, 2016. That made perfect sense since Aberdeen acquired Arden. Plan A survived for about a week when someone likely noticed that the fund wasn’t actually very good, was shrinking in size and required an annual expense subsidy from the adviser, whereupon Plan B emerged: kill it. Same date.
BPV Core Diversification Fund (BPADX) has closed and will be terminated on March 11, 2016. It’s a tiny, conservative fund that’s still managed to lose money over the past three years and trail 90% of its peers.
On February 17, 2016, the CGM Advisor Targeted Equity Fund (NEFGX, reflecting its birth name: New England Growth Fund) was liquidated. Financial Advisor magazine managed to wax nostalgic over the loss of a “venerable” and “once-vaunted” fund. Two quick notes about this: (1) the fund hasn’t earned its keep over the past 20 years. Its closing NAV was below its NAV in 1994. The 20 year performance chart is the very image of what to avoid in your investments:
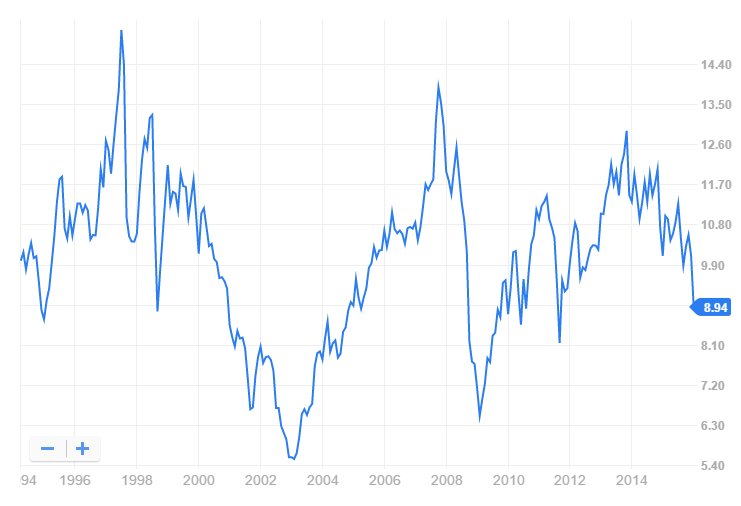
And (2) you can still access the manager’s skills, if you’d like. Natixis, the fund’s sponsor, no longer has an ownership stake in CGM and so they had no interest in continuing to sponsor a fund. Mr. Heebner continues to run three other CGM funds. Their website would also win the award for the industry’s least useful.
Collins Alternative Solutions Fund (CLLAX) liquidated on February 26, 2016. The fund had about $19 million in assets and dropped 19% in its final year of operation.
Crystal Strategy Absolute Income Fund (CSTFX), Crystal Strategy Absolute Return Fund (CSRAX) and Crystal Strategy Absolute Return Plus Fund (CSLFX) will, based on the recommendation of Brinker Capital, LLC, the investment adviser, be liquidated on March 18, 2016. The funds are just past their second anniversary. Between them they have $16 million in assets and a sorrowful performance record.
Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund (DOUAX) will liquidate in mid-April.
The Fortress has fallen! Fortress Long/Short Credit Fund (LPLAX) liquidated on February 12, 2016, about three years too late. The fund lost about 25% over its lifetime. It peaked in December 2012 and its chart since then looks, for all the world, like a child’s drawing of steps leading down to the basement.
Frost International Equity Fund (FANTX) will liquidate on March 31, 2016. The announcement helpfully notes that they’ll refer to that as “the liquidation date.” I think I went on one of those in college.
Gottex Endowment Strategy Fund (GTEAX) is liquidating after about 20 months of operation. In that time it lost about 12% for its few investors.
Guidestone Real Assets Fund (GRAZX) will liquidate on April 29, 2016. It’s a tiny fund-of-funds that’s designed to protect you from inflation by investing in things that are cratering. That’s not intentional, of course, but sectors that would be durable if inflation arose – energy, natural resources, real estate – have been disasters.
The $3 million JPMorgan Asia Pacific Fund (JAPFX) will liquidate on April 6, 2016.
Investors in the Lazard Master Alternatives Portfolio (LALOX) need to find an alternative since the fund was liquidated on March 1, 2016. The fund was 14 months old.
MassMutual Barings Dynamic Allocation Fund (MLBAX) will be dissolved on July 8, 2016. It isn’t an awful tactical allocation fund but it’s tiny and misallocated in the last year, costing its investors 11.5%.
Merk Asian Currency Fund (MEAFX) liquidated on February 29, 2016. From inception in 2008 until liquidation, the fund was above water once, briefly, in 2011.
Meyers Capital Aggressive Growth Fund (MAGFX) liquidated on February 29, 2016, on about three weeks’ notice. Since the manager owns 87% of the funds’ shares, he might have seen it coming. The oddest development is the collapse of the fund’s asset base: in May, Mr. Meyers owned over $1,000,000 in fund shares. By February 2016,the fund only had $130,000 in assets.
Oberweis Asia Opportunities Fund (OBAOX) will be merged into Oberweis China Opportunities Fund (OBCHX) on or about April 29, 2016.
Philadelphia Investment Partners New Generation Fund (PIPGX), having lost 35% in the past 12 months, is now going to lose its head. The execution is March 30, 2016.
After the advisor concluded that Satuit Capital U.S. SMID Cap Fund (SATDX) was not economically viable, they decided “to close the Fund, wind up its affairs, liquidate its portfolio.” I’ve never seen “wind up its affairs,” which the announcement uses twice, in a fund liquidation filling before. Huh. The fund is not yet two years old and had attracted only a couple million, despite a really strong record. The deed is done on April 30, 2016.
Having concluded that the Smith Group Small Cap Focused Growth Fund (SGSVX) has “limited prospects for meaningful growth,” its board authorized liquidation of the fund on March 31, 2016. One can’t fault the managers for a lack of commitment: internal ownership accounted for about two-thirds of the fund’s $600,000 in assets.
Strategic Latin America Fund (SLATX) liquidated in late February, 2016.
Touchstone Global Real Estate Fund (TGAAX) will liquidate on March 30, 2016. The board attributes the decision to “the Fund’s small size and limited growth potential.” An interim manager, apparently someone who specializes in “safeguard[ing] shareholder interests during the liquidation period,” has been appointed. It’s the sad case of a good fund not finding its audience: top 25% returns over the past five years and even better returns recently, but still only $17 million in assets.
Sometime in mid-summer Victory CEMP Multi-Asset Balanced Fund (CTMAX) will be absorbed by Victory Strategic Allocation Fund (SBALX). As is so often the case, CTMAX is larger and weaker so they’ll bury its record while tripling SBALX’s assets.
On February 5, 2016, Virtus Dynamic Trend Fund merged into Virtus Equity Trend Fund (VAPAX). I’m slightly startled to report that, despite trailing 98—99% of its peers over the intermediate term, VAPAX retains $1.5 billion in assets.
Wanger International Select (WAFFX) will liquidate at the end of March. It appears to be available only through insurance products.
WHV/EAM Emerging Markets Small Cap Equity Fund (WVEAX) and WHV/EAM International Small Cap Equity Fund (WHSAX), rather less than two years old, will liquidate on or about March 31, 2016. Both funds had very strong performance. WHV/Seizert Small Cap Value Equity Fund (WVSAX), a bit more than two years old, will liquidate a month later.
In Closing . . .
Thanks, as always, to folks who’ve supported the Observer in thought, word or deed. Welcome, especially, to Nick Burnett, long-time friend, grad school roommate and mastermind behind the CapRadioCurriculum which helps teachers connect public radio content with classroom lessons. There’s a cool one on multilingual public relations that I rather liked. Thanks, as ever to the ongoing generosity of the folks at Gardey Financial and our first subscribers, Deb and Greg. Thanks to Gary, who didn’t particularly want premium access but did want to help out. Mission accomplished, big guy! Too, to MaryRose, we’re trying to help. Welcome to Abdon Bolivar, working hard to get people to understand the role that plan administrators play in creating and sustaining bad options for investors. By coincidence, Tony Isola and the folks are Ritholtz Wealth Management are pursuing a parallel track trying to educate educators about what to do if they’re getting screwed by the 403(b). And, in a horrifying number of cases, they are.
And so, thanks to you all, not just for your support of the Observer but for all the good work you’re doing for a lot of people.
We’re waiting to talk with the folks at Otter Creek Partners, a hedge fund firm with a small long/short fund that’s performed splendidly. That conversation will let us finish up our profile of Otter Creek Long/Short Opportunity (OTCRX) and share it with you. We’ll add a look at Intrepid Endurance (ICMAX) in conjunction with my own portfolio review. We’ll look for the launch of Seafarer Overseas Value, likely around the 75th day of 2016. We’ll look for you.



 Here’s the brief version of recent events:
Here’s the brief version of recent events:
 “Advertising is the modern substitute for argument; its function is to make the worse appear the better.”
“Advertising is the modern substitute for argument; its function is to make the worse appear the better.”
 Last month, David
Last month, David 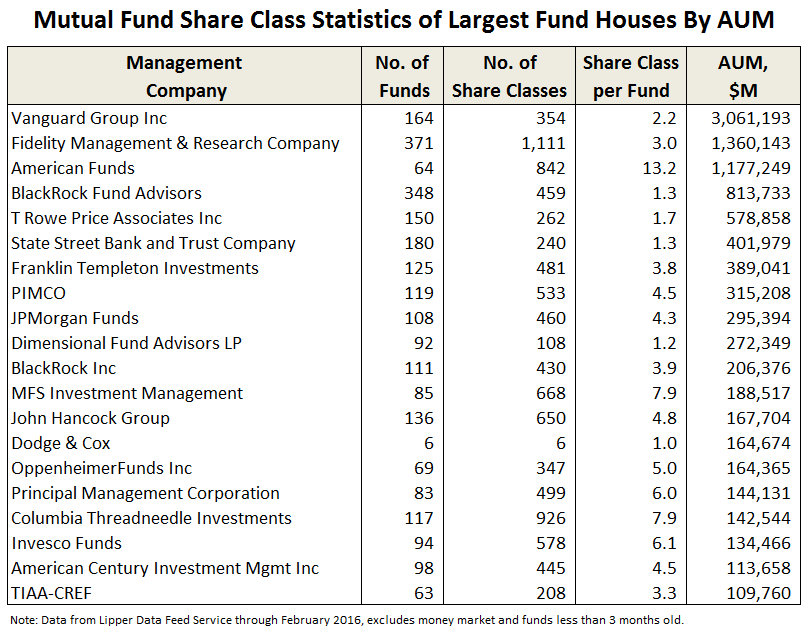
 What’s the Trapezoid story? Leigh Walzer has over 25 years of experience in the investment management industry as a portfolio manager and investment analyst. He’s worked with and for some frighteningly good folks. He holds an A.B. in Statistics from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from Harvard University. Leigh is the CEO and founder of Trapezoid, LLC, as well as the creator of the Orthogonal Attribution Engine. The Orthogonal Attribution Engine isolates the skill delivered by fund managers in excess of what is available through investable passive alternatives and other indices. The system aspires to, and already shows encouraging signs of, a fair degree of predictive validity.
What’s the Trapezoid story? Leigh Walzer has over 25 years of experience in the investment management industry as a portfolio manager and investment analyst. He’s worked with and for some frighteningly good folks. He holds an A.B. in Statistics from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from Harvard University. Leigh is the CEO and founder of Trapezoid, LLC, as well as the creator of the Orthogonal Attribution Engine. The Orthogonal Attribution Engine isolates the skill delivered by fund managers in excess of what is available through investable passive alternatives and other indices. The system aspires to, and already shows encouraging signs of, a fair degree of predictive validity. For anyone who enjoys roller coasters, Q1 2016 was for you. While it seemed a bit wild at times, it was really just a trip down to the bottom of a trough, and a consistent tick back up to where we started. Thanks to a coordinated plan of attack on part of global sovereign bankers, and reiterated by new policy actions from the European Central Bank, the markets shrugged off early losses in the year with a very solid recovery in March. As they say, don’t fight the Fed. And in this case, don’t fight the globally coordinated Fed.
For anyone who enjoys roller coasters, Q1 2016 was for you. While it seemed a bit wild at times, it was really just a trip down to the bottom of a trough, and a consistent tick back up to where we started. Thanks to a coordinated plan of attack on part of global sovereign bankers, and reiterated by new policy actions from the European Central Bank, the markets shrugged off early losses in the year with a very solid recovery in March. As they say, don’t fight the Fed. And in this case, don’t fight the globally coordinated Fed.


 Artisan has announced the liquidation of Artisan Small Cap Value (ARTVX), my oldest holding. My first fund, purchased when I was young and dumb, was AIM Constellation, then a very good mid-cap growth fund that carried a 5.5% load. After a bit, I learned that paying sales loads without any compensating benefit was stupid, so I stopped. I sold my shares and, shortly before it closed, invested the proceeds in Artisan Small Cap (ARTSX). Shortly after Artisan launched Small Cap Value in 1997, I moved my investment over from Small Cap. The $367 million fund, down from a peak of $3 billion in 2011, will be merged into Artisan Mid Cap Value (ARTQX) in May, 2016.
Artisan has announced the liquidation of Artisan Small Cap Value (ARTVX), my oldest holding. My first fund, purchased when I was young and dumb, was AIM Constellation, then a very good mid-cap growth fund that carried a 5.5% load. After a bit, I learned that paying sales loads without any compensating benefit was stupid, so I stopped. I sold my shares and, shortly before it closed, invested the proceeds in Artisan Small Cap (ARTSX). Shortly after Artisan launched Small Cap Value in 1997, I moved my investment over from Small Cap. The $367 million fund, down from a peak of $3 billion in 2011, will be merged into Artisan Mid Cap Value (ARTQX) in May, 2016. My single largest non-retirement holding is FPA Crescent (FPACX), which has always struck me as the quintessence of active management. While other managers were constrained to invest in a single asset class or in a single country, or to remain fully invested or unhedged, manager Steve Romick declared himself to be “the free-range chicken” of the investing world. He’d look for firms that offered compelling advantages, would analyze their capital structure and then invest in whatever instrument – common stock, warrants, senior debt – offered the most compelling opportunities. If nothing was compelling, he sat on cash.
My single largest non-retirement holding is FPA Crescent (FPACX), which has always struck me as the quintessence of active management. While other managers were constrained to invest in a single asset class or in a single country, or to remain fully invested or unhedged, manager Steve Romick declared himself to be “the free-range chicken” of the investing world. He’d look for firms that offered compelling advantages, would analyze their capital structure and then invest in whatever instrument – common stock, warrants, senior debt – offered the most compelling opportunities. If nothing was compelling, he sat on cash.
 “When we unleash the dogs of war, we must go where they take us.”
“When we unleash the dogs of war, we must go where they take us.” As Exhibit I illustrates low-volatility has been a successful investment strategy in recent years. A good argument can be made that historically, low-volatility stocks were mispriced. Players like Berkshire Hathaway and private equity capitalized on this by levering up these firms to deliver strong risk-adjusted returns. There is a heavy overlap between the low-volatility universe and the high-dividend universe. Many high-dividend stocks have dropped assets into REITs in recent years which have fueled better returns for this sector. Low volatility has outperformed the broad market meaningfully for the past two quarters, partly due its lower beta.
As Exhibit I illustrates low-volatility has been a successful investment strategy in recent years. A good argument can be made that historically, low-volatility stocks were mispriced. Players like Berkshire Hathaway and private equity capitalized on this by levering up these firms to deliver strong risk-adjusted returns. There is a heavy overlap between the low-volatility universe and the high-dividend universe. Many high-dividend stocks have dropped assets into REITs in recent years which have fueled better returns for this sector. Low volatility has outperformed the broad market meaningfully for the past two quarters, partly due its lower beta.



 Pruning Season
Pruning Season Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more. Jim Robinson formed Robinson Capital Management, located in Detroit’s ritzy Grosse Pointe suburb, in December, 2012. The firm manages about a quarter billion in assets for a handful of high net worth clients and advises two (soon to be three) mutual funds.
Jim Robinson formed Robinson Capital Management, located in Detroit’s ritzy Grosse Pointe suburb, in December, 2012. The firm manages about a quarter billion in assets for a handful of high net worth clients and advises two (soon to be three) mutual funds.
 Effective May 1, 2016, Donald A. Yacktman will transition to an advisory role and will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for AMG Yacktman (YACKX) and AMG Yacktman Focused (YAFFX) funds. The roughly corresponds with his 75th birthday. Mr. Yacktman has been managing mutual funds since 1968, starting with Stein, Roe and the Selected American Shares before founding Yacktman Asset Management in 1992. $10,000 invested in YACKX that year would have grown to $95,000 today, which compares well to the returns on an investment in the S&P500 ($76,000) or the average large-value fund ($56,000). He was named Morningstar’s Manager of the Year in 1991 and was joined on the management team by his son, Stephen, in 2002. Stephen Yacktman and Jason Subotky will manage the funds after the transition.
Effective May 1, 2016, Donald A. Yacktman will transition to an advisory role and will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for AMG Yacktman (YACKX) and AMG Yacktman Focused (YAFFX) funds. The roughly corresponds with his 75th birthday. Mr. Yacktman has been managing mutual funds since 1968, starting with Stein, Roe and the Selected American Shares before founding Yacktman Asset Management in 1992. $10,000 invested in YACKX that year would have grown to $95,000 today, which compares well to the returns on an investment in the S&P500 ($76,000) or the average large-value fund ($56,000). He was named Morningstar’s Manager of the Year in 1991 and was joined on the management team by his son, Stephen, in 2002. Stephen Yacktman and Jason Subotky will manage the funds after the transition.


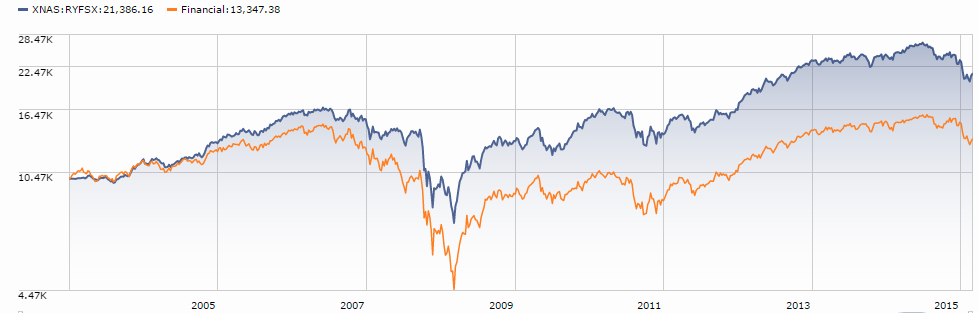
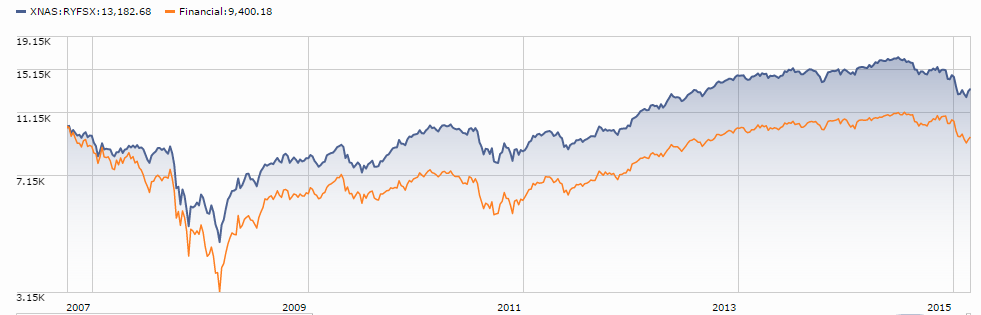
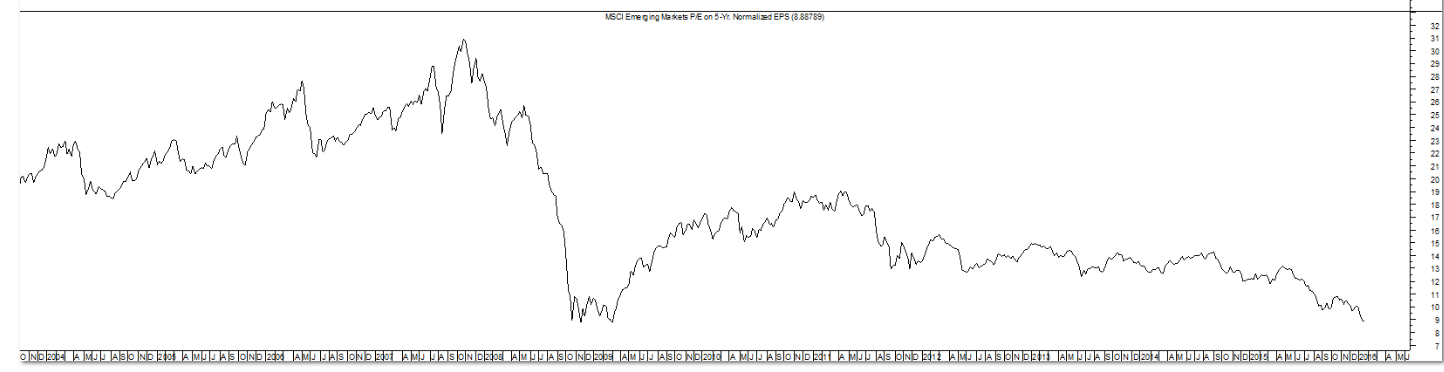
 This Time It Really Is Different!
This Time It Really Is Different!
 For those of you who watched the World Series a few months ago, the NY Mets had a number of very young pitchers with fastballs close to 100 miles per hour. They also had some veteran pitchers like John Niese and the 42-year-old ageless wonder Bartolo Colon who couldn’t muster the same heat but had established their skill and consistency over a long period of time. We don’t know whether Bartolo Colon drank from the fountain of youth; he served a lengthy suspension a few years ago for using a banned substance. But his statistics in his 40s are on par with his prime ten year ago.
For those of you who watched the World Series a few months ago, the NY Mets had a number of very young pitchers with fastballs close to 100 miles per hour. They also had some veteran pitchers like John Niese and the 42-year-old ageless wonder Bartolo Colon who couldn’t muster the same heat but had established their skill and consistency over a long period of time. We don’t know whether Bartolo Colon drank from the fountain of youth; he served a lengthy suspension a few years ago for using a banned substance. But his statistics in his 40s are on par with his prime ten year ago. 
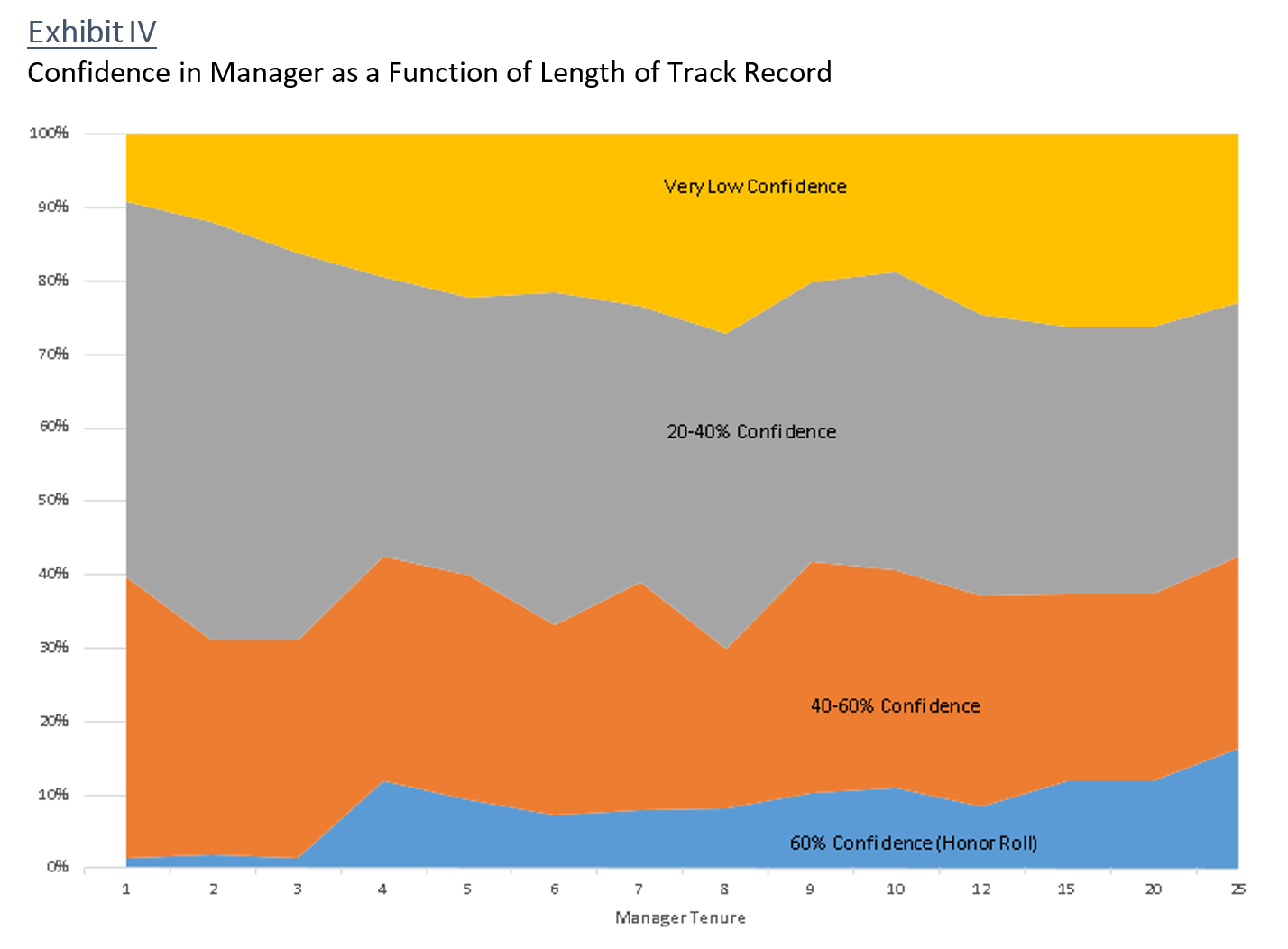

 Sam Lee and
Sam Lee and  David invariably cuts to the chase when it comes to assessing mutual funds. It’s a gift he shares with us each month.
David invariably cuts to the chase when it comes to assessing mutual funds. It’s a gift he shares with us each month.
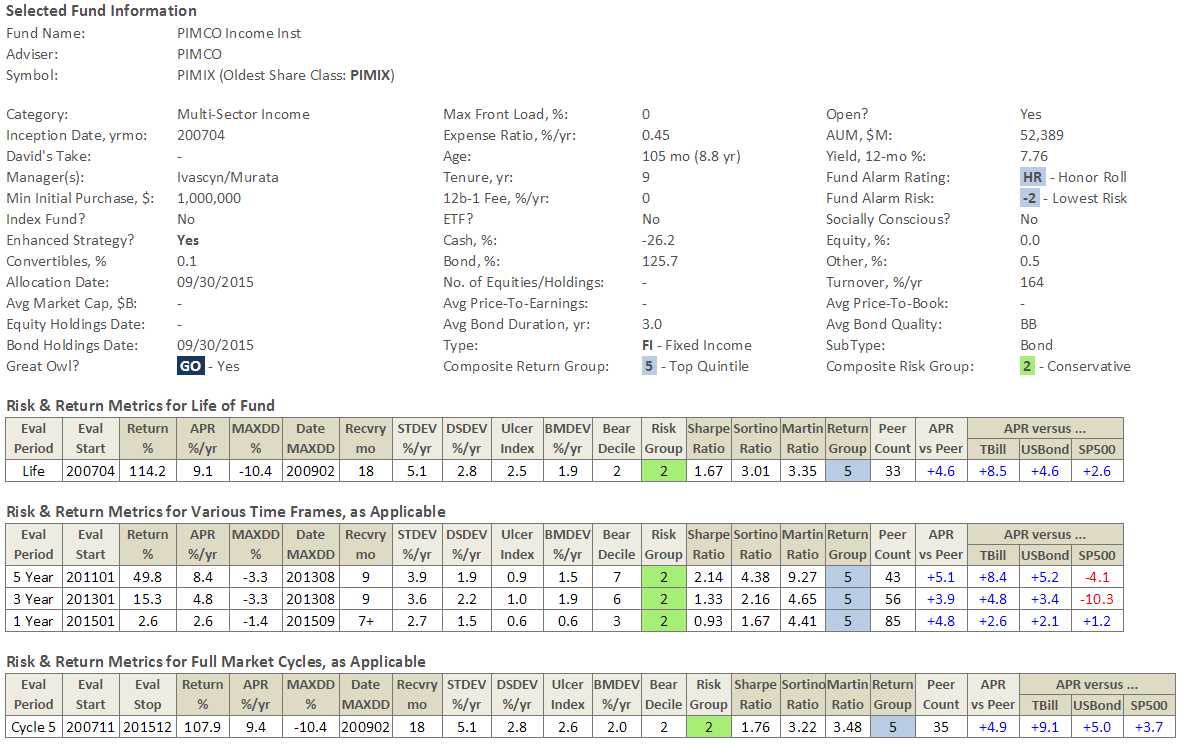
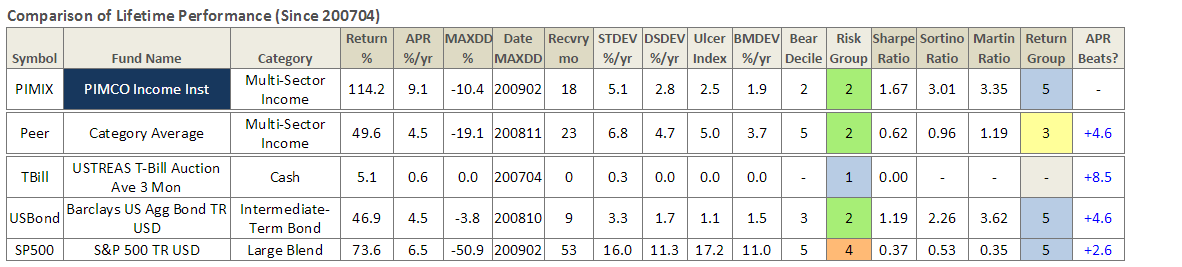
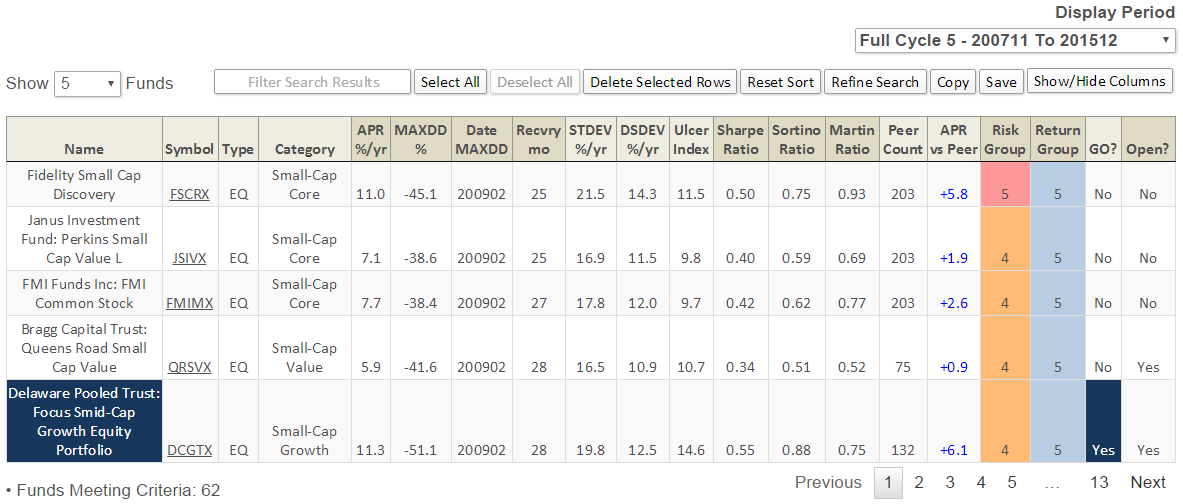
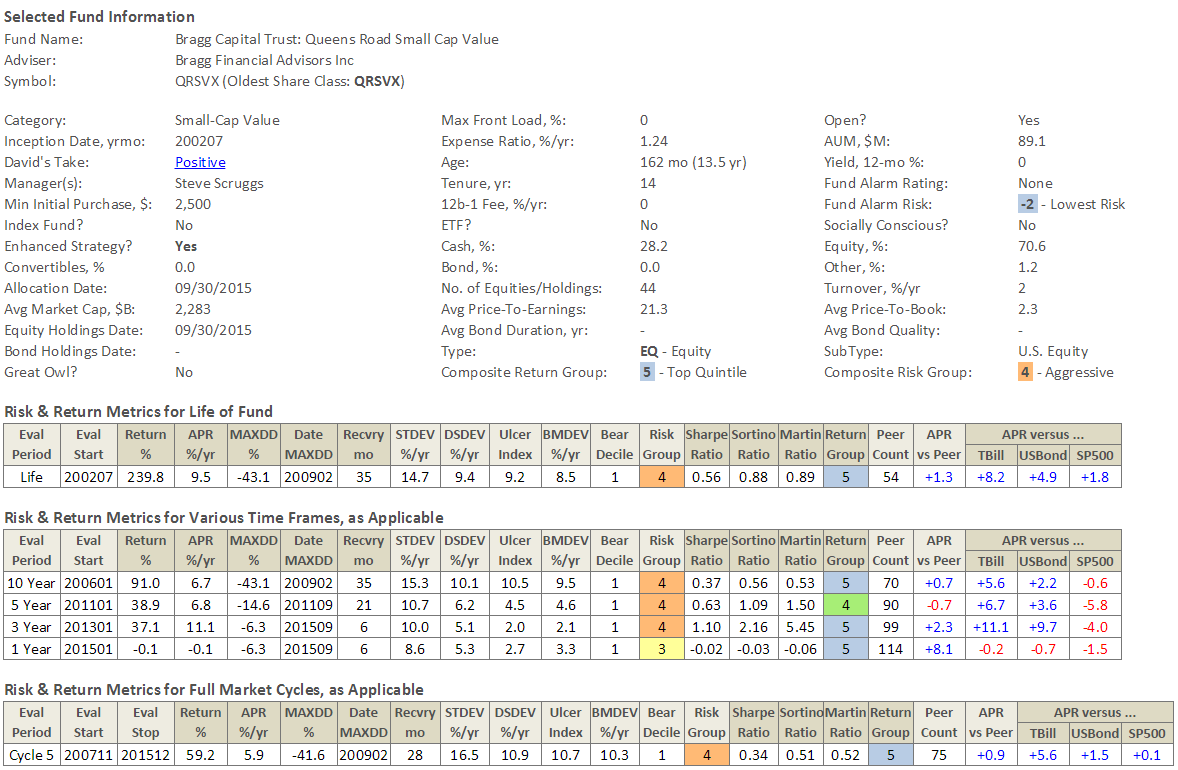
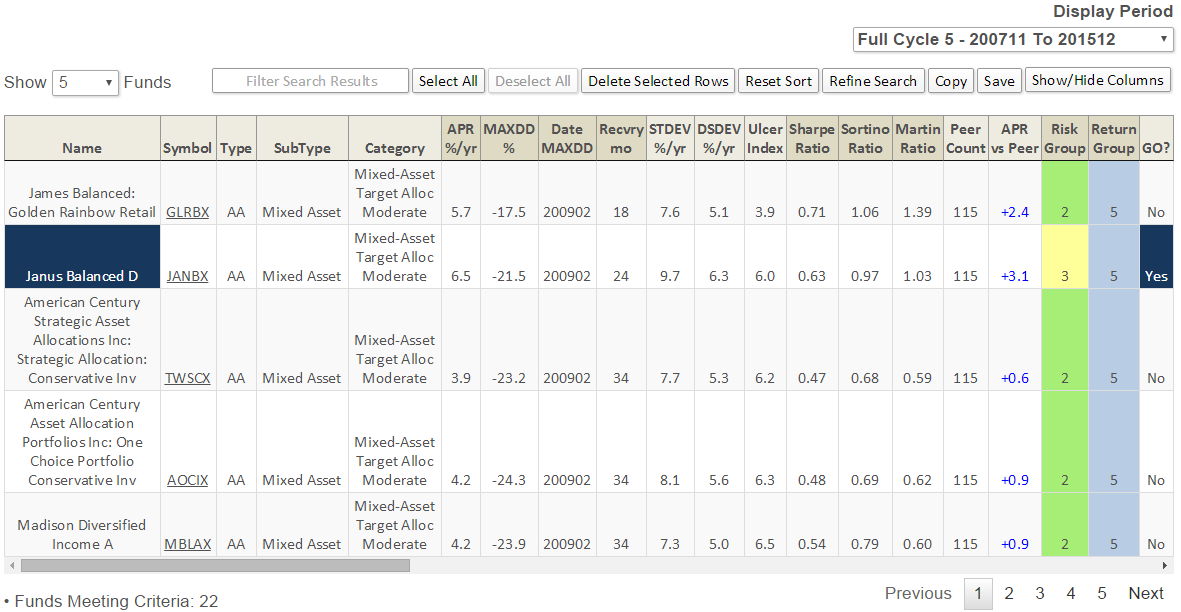
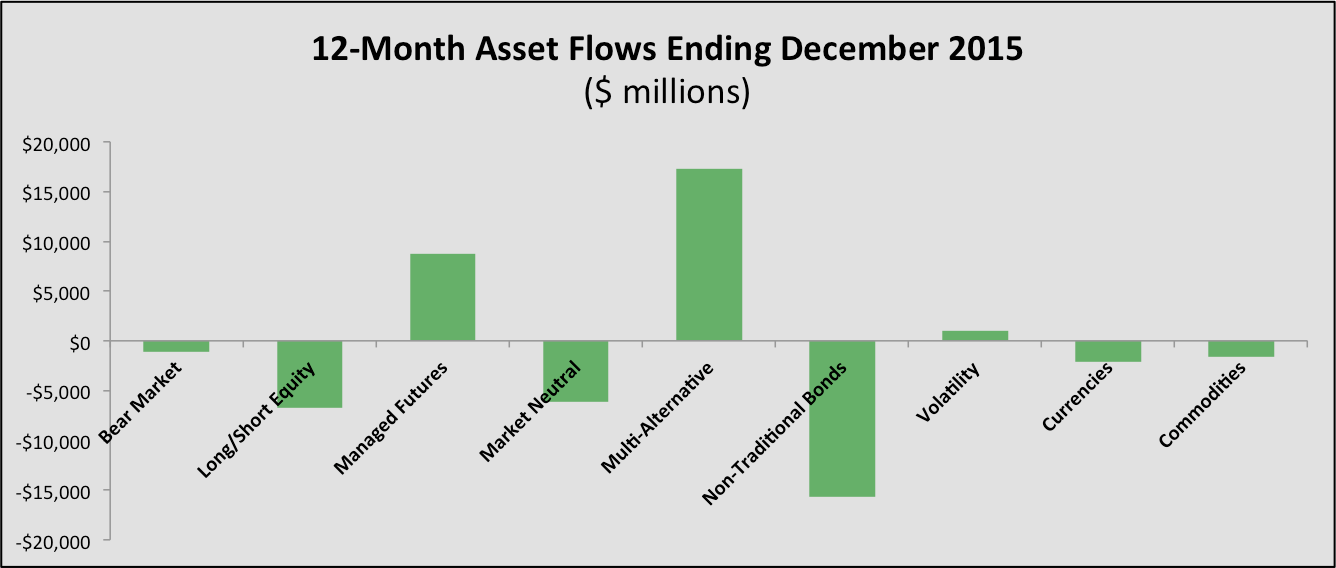
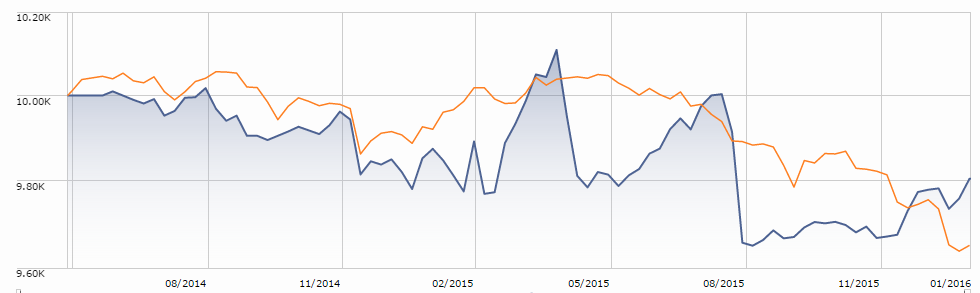
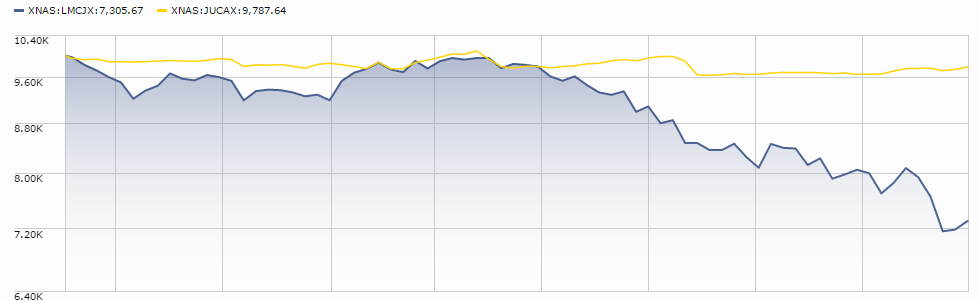
 There was
There was