Dear friends,
And now, we wait. After the frenzy of recent months, that seems odd and unnatural.
Will and his minions wait for the holidays, anxious for the last few weeks of school to pass but secure in the knowledge that their folks are dutifully keeping the retail economy afloat.

Photo by Drew Barnes ’14, Augustana Photo Bureau
My colleagues at Augustana are waiting for winter and then for spring. The seemingly endless string of warm, dry weeks has left much of our fall foliage intact as we enter December. As beautiful as it is, we’re sort of rooting for winter, or at least the hope of seasonal weather, to reassert itself. And we’re waiting for spring, when the $13 million renovation of Old Main will be complete and we escape our warren of temporary offices and ersatz classrooms. I’ve toured the half-complete renovation. It’s going to be so cool.
And investors wait. Most of us are waiting for a resolution of “the fiscal cliff” (alternately: fiscal slope, obstacle course, whatchamacallit or, my favorite, Fiscal Clifford the Big Red Dog), half fearful that they won’t find a compromise and half fearful that they will.
Then there are The Two Who Wouldn’t Wait. And they worry me. A lot. We’ve written for a year or so about our concerns that the bond market is increasingly unstable. That concern has driven our search for tools, other than Treasuries or a bond aggregate, that investors might use to manage volatility. In the past month, the urgency of that search has been highlighted by The Two. One of The Two is Jeffrey Gundlach, founder of the DoubleLine funds and widely acknowledged as one of the best fixed-income managers anyway. Gundlach believes that “[d]eeply indebted countries and companies, which Gundlach doesn’t name, will default sometime after 2013” (Bond Investor Gundlach Buys Stocks, Sees ‘Kaboom’ Ahead, 11/30/2012). Gundlach says, “I don’t believe you’re going to get some sort of an early warning. You should be moving now.” Gundlach, apparently, is moving into fine art.
GMO, the other of The Two, has moved. GMO (Grantham, Mayo, van Otterloo) has an outstanding record for anticipating asset class crashes. They moved decisively in 2000 and again in 2007, knowing that they were likely early and knowing that leaving the party early would cost them billions (one quarter of the firm’s assets) as angry investors left. But when the evidence says “run,” they ran. In a late-November interview with the Financial Times, GMO’s head of asset allocation revealed that, firm-wide, GMO had sold off all of their bond holdings (GMO abandons bond market, 11/26/2012). “We’ve largely given up on traditional fixed income,” Inker says, including government and corporate debt in the same condemnation. They don’t have any great alternatives (high quality US stocks are about the best option), but would prefer to keep billions in cash to the alternatives.
I don’t know whether you should wait. But I do believe that you should acquaint yourself with those who didn’t.
The Last Ten: PIMCO in the Past Decade
In October we launched “The Last Ten,” a monthly series, running between now and February, looking at the strategies and funds launched by the Big Five fund companies (Fido, Vanguard, T Rowe, American and PIMCO) in the last decade.
Here are our findings so far:
Fidelity, once fabled for the predictable success of its new fund launches, has created no compelling new investment option and only one retail fund that has earned Morningstar’s five-star designation, Fidelity International Growth (FIGFX). We suggested three causes: the need to grow assets, a cautious culture and a firm that’s too big to risk innovative funds.
T. Rowe Price continues to deliver on its promises. Of the 22 funds launched, only Strategic Income (PRSNX) has been a consistent laggard; it has trailed its peer group in four consecutive years but trailed disastrously only once (2009). Investing with Price is the equivalent of putting a strong singles-hitter on a baseball team; it’s a bet that you’ll win with consistency and effort, rather than the occasional spectacular play.
And just as you’re about to conclude that large fund companies will necessarily produce cautious funds that can aspire just to “pretty good,” along comes PIMCO. PIMCO was once known as an almost purely fixed-income investor. Its flagship PIMCO Total Return Fund has gathered over a quarter trillion dollars in assets and tends to finish in the top 10% of its peer group over most trailing time periods.
But PIMCO has become more. This former separate accounts managers for Pacific Life Insurance Company now declares, “We continue to evolve. Throughout our four decades we have been pioneers and continue to evolve as a provider of investment solutions across all asset classes.”
Indeed they have. PIMCO has spent more time thinking about, and talking about, the global economic future than any firm other, perhaps, than GMO. More than talk about the changing sources of alpha and the changing shape of risk, PIMCO has launched a bunch of unique funds targeting emerging challenges and opportunities that other firms would prefer simply to ignore (or to eventually react to).
Perhaps as a result, PIMCO has created more five-star funds in the last decade than any other firm and, among larger firms, has a greater fraction of their funds earning four- or five-stars than anyone else. Here’s the snapshot:
- PIMCO has 84 funds (which are sold in over 536 packages or share classes)
- 56 of their funds were launched in the past decade
- 61 of them are old enough to have earned Morningstar ratings
- 20 of them have five-star ratings (as of 11/14/12)
- 15 more earned four-star ratings.
How likely this that? In each Morningstar category, the top 10 percent of funds receive five stars, the next 22.5 percent receive four stars, and the next 35 percent receive three. In the table below, those are the “expected values.” If PIMCO had just ordinary skill or luck, you’d expect to see the numbers in the expected values column. But you don’t.
|
Expected Value |
Observed value |
|
| PIMCO, Five Star Funds, overall |
8 |
20 |
| PIMCO, Four and Five Star Funds, overall |
20 |
35 |
| Five Star funds, launched since 9/2002 |
3 |
9 |
| Four and Five Star funds, launched since 9/2002 |
11 |
14 |
Only their RealRetirement funds move between bad and mediocre, and even those funds made yet be redeemed. The RealRetirement funds, like PIMCO’s other “Real” funds, are designed to be especially sensitive to inflation. That’s the factor that poses the greatest long-term risk to most of our portfolios, especially as they become more conservative. Until we see a sustained uptick in inflation, we can’t be sure of how well the RealRetirement funds will meet their mandates. But, frankly, PIMCO’s record counsels patience.
Here are all of the funds that PIMCO has launched in the last 10 years, which their Morningstar rating (as of mid-November, 2012), category and approximate assets under management.
| All Asset All Authority | ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ |
World Allocation |
25,380 |
| CA Short Duration Muni Income | ★ |
Muni Bond |
260 |
| Diversified Income | ★ ★ ★ ★ |
Multisector Bond |
6,450 |
| Emerging Markets Fundamental IndexPLUS TR Strategy | ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ |
Emerging Markets Stock |
5,620 |
| Emerging Local Bond | ★ ★ |
Emerging Markets Bond |
13,950 |
| Emerging Markets Corporate Bond | ★ ★ |
Emerging Markets Bond |
1,180 |
| Emerging Markets Currency | ★ |
Currency |
7060 |
| Extended Duration | ★ ★ ★ ★ |
Long Government |
340 |
| Floating Income | ★ ★ |
Nontraditional Bond |
4,030 |
| Foreign Bond (Unhedged) | ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ |
World Bond |
5,430 |
| Fundamental Advantage Total Return | ★ ★ ★ |
Intermediate-Term Bond |
2,730 |
| Fundamental IndexPLUS TR | ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ |
Large Blend |
1,150 |
| Global Advantage Strategy | ★ ★ ★ |
World Bond |
5,220 |
| Global Multi-Asset | ★ ★ |
World Allocation |
5,280 |
| High Yield Municipal Bond | ★ ★ |
Muni Bond |
530 |
| Income | ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ |
Multisector Bond |
16,660 |
| International StocksPLUS | ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ |
Foreign Large Blend |
210 |
| International StocksPLUS TR Strategy (Unhedged) | ★ ★ ★ ★ |
Foreign Large Blend |
1,010 |
| Long Duration Total Return | ★ ★ ★ ★ |
Long-Term Bond |
6,030 |
| Long-Term Credit | ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ |
Long-Term Bond |
2,890 |
| Real Estate Real Return | ★ ★ ★ |
Real Estate |
2,030 |
| Real Income 2019 | ★ |
Retirement Income |
30 |
| Real Income 2029 | ★ ★ ★ ★ |
Retirement Income |
20 |
| RealRetirement 2020 | ★ |
Target Date |
70 |
| RealRetirement 2030 | ★ |
Target Date |
70 |
| RealRetirement 2040 | ★ ★ |
Target Date |
60 |
| RealRetirement 2050 | ★ ★ |
Target Date |
40 |
| RealRetirement Income & Distribution | ★ ★ |
Retirement Income |
40 |
| Small Cap StocksPLUS TR | ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ |
Small Blend |
470 |
| StocksPLUS Long Duration | ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ |
Large Blend |
790 |
| Tax Managed Real Return | ★ |
Muni Bond |
70 |
| Unconstrained Bond | ★ ★ ★ |
Nontraditional Bond |
17,200 |
| Unconstrained Tax Managed Bond | ★ ★ |
Nontraditional Bond |
350 |
In January, we’ll continue the series of a look at Vanguard. We know that Vanguard inspires more passion among its core investors than pretty much any other firm. Since we’re genial outsiders to the Vanguard culture, if you’ve got insights, concerns, tips, kudos or rants you’d like to share, dear Bogleheads, drop me a note.
RiverPark Long/Short Opportunity Conference Call
 Volatility is tremendously exciting for many investment managers. You’d be amazed by the number who get up every morning, hoping for a market panic. For the rest of us, it’s simply terrifying.
Volatility is tremendously exciting for many investment managers. You’d be amazed by the number who get up every morning, hoping for a market panic. For the rest of us, it’s simply terrifying.
For the past thirty years, the simple, all-purpose answer to unacceptable volatility has been “add Treasuries.” The question we began debating last spring is, “where might investors look if Treasuries stop functioning as the universal answer?” We started by looking at long/short equity funds as one possible answer. Our research quickly led to one conclusion, and slowly to a second.
The quick conclusion: long/short funds, as a group, are a flop. They’re ridiculously expensive, with several dozen charging 2.75% or more plus another 1.5-2% in short interest charges. They offered some protection in 2008, though several did manage to lose more that year than did the stock market. But their longer term returns have been solidly dismal. The group returned 0.15% over the past five years, which means they trailed far behind the stock market, a simple 60/40 hybrid, moderate allocation funds, very conservative short-term bond funds . . . about the only way to make this bunch look good is to compare them to “market neutral” funds (whose motto seems to be, “we can lose money in up markets and down!”).
The slower conclusion: some long-short funds have consistently, in a variety of markets, managed to treat their investors well and a couple more show the real promise of doing so. The indisputable gold standard among such funds, Robeco Long Short (BPLEX) returned 16% annually over the past five years. The second-best performer, Marketfield (MFLDX) made 9% while funds #3 (Guggenheim Alpha) and #4 (Wasatch Long/Short) made 4%. Sadly, BPLEX is closed to new investors, Guggenheim has always had a sales load and Marketfield just acquired one. Wasatch Long-Short (FMLSX), which we first profiled three years ago, remains a strong, steady performer with reasonable expenses.
Ultimately we identified (and profiled) just three, newer long-short funds worthy of serious attention: Marketfield, RiverPark Long/Short Opportunity (RPLSX) and ASTON/River Road Long Short (ARLSX).
For about an hour on November 29th, Mitch Rubin, manager of RiverPark Long/Short Opportunity(RLSFX) fielded questions from Observer readers about his fund’s strategy and its risk-return profile. Nearly 60 people signed up for the call.
For folks interested but unable to join us, here’s the complete audio of the hour-long conversation. It starts with Morty Schaja, RiverPark’s president, talking about the fund’s genesis and Mr. Rubin talking about its strategy. After that, I posed five questions of Rubin and callers chimed in with another half dozen.
| http://78449.choruscall.com/dataconf/productusers/riverpark/media/riverpark121129.mp3 |
| When you click on the link, the file will load in your browser and will begin playing after it’s partially loaded. If the file downloads, instead, you may have to double-click to play it. |
If you’d like a preview before deciding whether you listen in, you might want to read our profile of RLSFX (there’s a printable .pdf of the profile on RiverPark’s website). Here are some of the highlights of the conversation:
Rubin believes that many long/short mutual fund managers (as opposed to the hedge fund guys) are too timid about using the leverage allowed them. As a result, they’re not able to harvest the full returns potential of their funds. Schaja describes RLSFX’s leverage as “moderate,” which generally means having investments equal to 150-200% of assets.
The second problem with long/short managers as a group, he believes, is that they’re too skittish. They obsess about short-term macro-events (the fiscal cliff) and dilute their insights by trying to bet for or against industry groups (by shorting ETFs, for example) rather than focusing on identifying the best firms in the best industries.
One source of RLSFX’s competitive advantage is the team’s long history of long investing. They started following many of the firms in their portfolio nearly two decades ago, following their trajectory from promising growth stocks (in which they invested), stodgy mature firms (which they’d sold) and now old firms in challenged industries (which are appearing in the short portfolio).
A second source of advantage is the team’s longer time horizon. Their aim is to find companies which might double their money over the next five years and then to buy them when their price is temporarily low.
I’d like to especially thank Bill Fuller, Jeff Mayer and Richard Falk for the half dozen really sharp, thoughtful questions that they posed during the closing segment. If you catch no other part of the call, you might zoom in on those last 15 minutes to hear Mitch and the guys in conversation.
Mr. Rubin is an articulate advocate for the fund, as well as being a manager with a decades-long record of success. In addition to listening to his conversation, there are two documents on the Long/Short fund’s homepage that interested parties should consult. First, the fund profile has a lot of information about the fund’s performance back when it was a hedge fund which should give you a much better sense of its composition and performance over time. Second, the manager’s commentary offers an intriguing list of industries which they believe to be ascendant or failing. It’s sort of thought-provoking.
Conference Calls Upcoming: Great managers on-deck
As promised, we’re continuing our moderated conference calls through the winter. You should consider joining in. Here’s the story:
- Each call lasts about an hour
- About one third of the call is devoted to the manager’s explanation of their fund’s genesis and strategy, about one third is a Q&A that I lead, and about one third is Q&A between our callers and the manager.
- The call is, for you, free. Your line is muted during the first two parts of the call (so you can feel free to shout at the danged cat or whatever) and you get to join the question queue during the last third by pressing the star key.
 Our next conference call features Matt Moran and Dan Johnson, co-managers of ASTON / River Road Long Short (ARLSX). I’ve had several conversations with the team and they strike me as singularly bright, articulate and disciplined. When we profiled the fund in June, we noted:
Our next conference call features Matt Moran and Dan Johnson, co-managers of ASTON / River Road Long Short (ARLSX). I’ve had several conversations with the team and they strike me as singularly bright, articulate and disciplined. When we profiled the fund in June, we noted:
The strategy’s risk-management measures are striking. Through the end of Q1 2012, River Road’s Sharpe ratio (a measure of risk-adjusted returns) was 1.89 while its peers were at 0.49. Its maximum drawdown (the drop from a previous high) was substantially smaller than its peers, it captured less of the market’s downside and more of its upside, in consequence of which its annualized return was nearly four times as great.
Among the crop of newer offerings, few are more sensibly-constructed or carefully managed that ARLSX seems to be. It deserves attention.
If you’d like to share your attention with them, our call with ASTON / River Road Long Short is Monday, December 17, from 7:00 – 8:00 Eastern. To register for the call, just click on this link and follow the instructions. I’ll send a reminder email on the day of the call to all of the registered parties.
 We’re hoping to start 2013 with a conversation with Andrew Foster of Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX), one of the best of a new generation of emerging markets funds. We’re also in conversation with the managers of several seriously concentrated equity funds, including David Rolfe of RiverPark/Wedgewood Fund (RWGFX) and Steve Dodson of Bretton Fund (BRTNX).
We’re hoping to start 2013 with a conversation with Andrew Foster of Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX), one of the best of a new generation of emerging markets funds. We’re also in conversation with the managers of several seriously concentrated equity funds, including David Rolfe of RiverPark/Wedgewood Fund (RWGFX) and Steve Dodson of Bretton Fund (BRTNX).
As a service to our readers, we’ve constructed a mailing list that we’ll use to notify folks of upcoming conference call opportunities. If you’d like to join but haven’t yet, feel free to drop me a note.
Fidelity’s Advice to Emerging Markets Investors: Avoid Us
Fidelity runs several distinct sets of funds, including Fidelity, Fidelity Advisor, Fidelity Select, and Fidelity Series. In many ways, the most interesting are their Strategic Adviser funds which don’t even bear the Fidelity name. The Strategic Adviser funds are “exclusive to clients of Portfolio Advisory Services. . . They allow Strategic Advisers to hire (and fire) sub-advisers as well as to buy, sell, and hold mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) within the fund.” In short, these are sort of “best ideas” funds, two of which are funds of funds.
Which led to the question: would the smartest folks Fidelity could find, who could choose any funds around which to build a portfolio, choose Fidelity?
In the case of emerging markets, the answer is “uhh … no.” Here’s the portfolio for Strategic Advisers Emerging Markets Fund of Funds (FLILX).
|
Total portfolio weights as of |
10/2012 |
03/2012 |
| Aberdeen Emerging Markets |
14.7% |
11.4% |
| GMO Emerging Markets V |
14.5 |
13.6 |
| Lazard Emerging Markets Equity |
14.2 |
15.7 |
| Acadian Emerging Markets |
13.9 |
8.2 |
| T. Rowe Price Emerging Markets Stock |
10.7 |
12.9 |
| Fidelity Emerging Markets |
10.2 |
13.4 |
| SSgA Emerging Markets Select |
6.9 |
7.2 |
| Oppenheimer Developing Markets |
5.2 |
4.9 |
| Eaton Vance Parametric Structured Em Mkts |
5.0 |
5.1 |
| Thornburg Developing World |
4.14 |
n/a |
| Vanguard MSCI Emerging Markets ETF |
0.70 |
n/a |
What should you notice?
- The fund’s managers seem to find many funds more compelling than Fidelity Emerging Markets, and so it ends up sixth on the list. Fidelity’s corporate folks seem to agree and they replaced the long-time manager of this one-star fund in mid October, 2012.
- Measured against the March 2012 portfolio, Fidelity E.M. has seen the greatest decrease in its weighing (about 3.2%) of any fund in the portfolio.
- Missing entirely from the list: Fidelity’s entire regional lineup including China Region, Emerging Asia, Emerging Middle East and Latin America.
- For that matter, missing entirely from the list are anything but diversified large cap emerging markets stock funds.
Fidelity does noticeably better in the only other Strategic Advisers fund of funds, the Strategic Advisers® Income Opportunities Fund of Funds (FSADX).
|
% of fund’s |
|
| T. Rowe Price High Yield Fund |
24.2 |
| Fidelity Capital & Income Fund |
20.5 |
| Fidelity High Income Fund |
14.7 |
| PIMCO High Yield Fund |
9.6 |
| Janus High-Yield Fund |
9.0 |
| BlackRock High Yield Bond Portfolio |
8.2 |
| MainStay High Yield Corporate Bond |
4.5 |
| Eaton Vance Income Fund of Boston |
3.3 |
| Fidelity Advisor High Income Advantage Fund |
3.2 |
| Fidelity Advisor High Income Fund |
2.8 |
Why, exactly, the managers have invested in three different classes of the same Fidelity fund is a bit unclear but at least they are willing to invest with Fido. It may also speak to the continuing decline of the Fidelity equity-investing side of the house while fixed-income becomes increasingly
A Site Worth Following: Learn Bonds
 Junior Yearwood, our friend and contributing editor who has been responsible for our Best of the Web reviews, has been in conversation with Marc Prosser, a Forbes contributor and proprietor of the Learn Bonds website. While the greatest part of Marc’s work focuses broadly on bond investing, he also offers ratings for a select group of bond mutual funds. He has a sort of barbell approach, focusing on the largest bond fund companies and on the smallest. His fund ratings, like Morningstar’s analyst ratings, are primarily qualitative and process-focused.
Junior Yearwood, our friend and contributing editor who has been responsible for our Best of the Web reviews, has been in conversation with Marc Prosser, a Forbes contributor and proprietor of the Learn Bonds website. While the greatest part of Marc’s work focuses broadly on bond investing, he also offers ratings for a select group of bond mutual funds. He has a sort of barbell approach, focusing on the largest bond fund companies and on the smallest. His fund ratings, like Morningstar’s analyst ratings, are primarily qualitative and process-focused.
Marc doesn’t yet have data by which to assess the validity of his ratings (and, indeed, is articulately skeptical of that whole venture), so we can’t describe him as a Best of the Web site. That said, Junior concluded that his site was clean, interesting, and worth investigating. It was, he concluded, a new and notable site.
Launch Alert: Whitebox Long Short Equity (WBLSX,WBLRX,WBLFX)
 On November 1, Whitebox Advisors converted their Whitebox Long Short Equity Partners hedge fund into the Whitebox Long Short Equity Fund which has three share classes. As a hedge fund, Whitebox pretty much kicked butt. From 2004 – 2012, it returned 15.8% annually while the S&P500 earned 5.2%. At last report, the fund was just slightly net-long with a major short against the Russell 2000.
On November 1, Whitebox Advisors converted their Whitebox Long Short Equity Partners hedge fund into the Whitebox Long Short Equity Fund which has three share classes. As a hedge fund, Whitebox pretty much kicked butt. From 2004 – 2012, it returned 15.8% annually while the S&P500 earned 5.2%. At last report, the fund was just slightly net-long with a major short against the Russell 2000.
There’s great enthusiasm among the Observer’s discussion board members about Whitebox’s first mutual fund, Whitebox Tactical Opportunities (WBMAX) , which strongly suggests this one warrants some attention, if only from advisors who can buy it without a sales load. The Investor shares carry at 4.5% front load, 2.48% expense ratio and a $5000 minimum initial investment. You might check the fund’s homepage for additional details.
Observer Fund Profiles

Had I mentioned that we visited RiverNorth?
Each month the Observer provides in-depth profiles of between two and four funds. Our “Most Intriguing New Funds” are funds launched within the past couple years that most frequently feature experienced managers leading innovative newer funds. “Stars in the Shadows” are older funds that have attracted far less attention than they deserve. This month’s lineup features
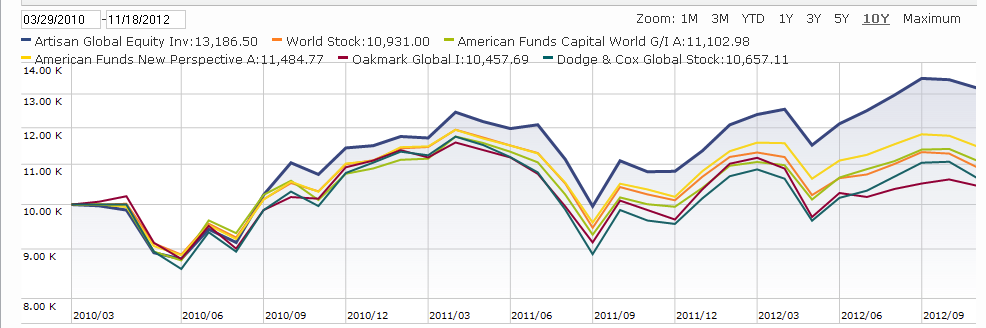
Artisan Global Equity Fund (ARTHX): you know a firm is in a good place when the most compelling alternatives to one of their funds are their other funds. Global, run by Mark Yockey and his team, extends on the long-term success of Artisan International and International Small Cap.
RiverNorth Dynamic Buy Write (RNBWX): one of the most consistently successful (and rarely employed) strategies for managing portfolios in volatile markets is the use of covered calls. After spending several hours with the RiverNorth team and several weeks reading the research, we may have an answer to a version of the old Ghostbusters question, “who you gonna (covered) call?”
Funds in Registration
New mutual funds must be registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission before they can be offered for sale to the public. The SEC has a 75-day window during which to call for revisions of a prospectus; fund companies sometimes use that same time to tweak a fund’s fee structure or operating details. Every day we scour new SEC filings to see what opportunities might be about to present themselves. Many of the proposed funds offer nothing new, distinctive or interesting. Some are downright horrors of Dilbertesque babble.
Funds in registration this month won’t be available for sale until, typically, the beginning of February 2013. Since firms really like launching by December 31st if they can, the number of funds in the pipeline is modest: seven this month, as compared to 29 last month. That said, two of the largest fixed-income teams are among those preparing to launch:
DoubleLine Floating Rate Fund, the tenth fund advised or sub-advised by DoubleLine, will seek a high level of current income by investing in floating rate loans and “other floating rate investments.” The fund will be managed by Bonnie Baha and Robert Cohen. Ms. Baha was part of Mr. Gundlach’s original TCW team and co-manages Multi-Asset Growth, Low-Duration Bond and ASTON/DoubleLine Core Plus Fixed Income.
PIMCO Emerging Markets Full Spectrum Bond Fund will invest in “a broad range of emerging market fixed income asset classes, such as external debt obligations of sovereign, quasi-sovereign, and corporate entities; currencies, and local currency-denominated obligations of sovereigns, quasi-sovereigns, and corporate issuers.” The manager has not yet been named but, as we noted in our lead story, the odds are that this is going to be a top-of-class performer.
Details on these funds and the list of all of the funds in registration are available at the Observer’s Funds in Registration page or by clicking “Funds” on the menu atop each page.
On a related note, we also tracked down 40 fund manager changes, down from last month’s bloodbath in which 70 funds changed management.
The Observer in the News
Last month, we ran our annual Honor Roll of Consistently Bearable Funds, which asks the simple question: “which mutual funds are never terrible?” Our basic premise is that funds that earn high returns but crash periodically are, by and large, impossible for investors to hold. And so we offered up a list of funds that have avoided crashing in any of the past ten years. As it turns out, by managing beta, those funds ended up with substantial alpha. In English: they made good money by avoiding losing money.
Chuck Jaffe has been looking at a related strategy for years, which led him to talk about and elaborate on our article. His story, “A fund-picking strategy for nervous investors,” ran on November 19th, ended up briefly (very briefly: no one can afford fifteen minutes of fame any more) on the front page of Google News and caused a couple thousand new folks to poke their heads in at the Observer.
Briefly Noted . . .
Artisan Partners has again filed for an initial public offering. They withdrew a 2011 filing in the face of adverse market conditions. Should you care? Investors can afford to ignore it since it doesn’t appear that the IPO will materially change operations or management; it mostly generates cash to buy back a portion of the firm from outsiders and to compensate some of the portfolio guys. Competitors, frankly, should care. Artisan is about the most successful, best run small firm fund that I know of: they’ve attracted nearly $70 billion in assets, have a suite of uniformly strong funds, stable management teams and a palpable commitment to serving their shareholders. If I were in the business, I’d want to learn a lot – and think a lot – about how they’ve managed that feat. Sudden access to a bunch more information would help.
One of The Wall Street Journal columnists surveyed “financial advisers, mutual-fund experts and academics” in search of the five best books for beginning investors. Other than for the fact that they missed Andrew Tobias’s The Only Investment Guide You’ll Ever Need, it’s a pretty solid list with good works from the efficient market and behavioral finance folks.
SMALL WINS FOR INVESTORS
Clipper (CFIMX), Davis New York Venture (NYVTX), and Selected American Shares (SLASX) have waived their 30-day trading restriction for the rest of 2012, in case investors want to do some repositioning in anticipation of higher capital gains tax rates in 2013.
Dreyfus/The Boston Company Small Cap Growth (SSETX) reopened to new investors on Nov. 1.
Victoria 1522 (VMDIX/VMDAX), an emerging markets stock fund, is cutting its expense ratio by 40 basis points. That’s much better news than you think. Glance at Morningstar’s profile of the lower-minimum Advisor shares and you’ll see a two-star fund and move on. That reading is, for two reasons, short-sighted. First, the lower expense ratio would make a major difference; the institutional shares, at 25 bps below the Advisor shares, gain a star (as of 11/30/12) and this reduction gives you 40 bps. Second, the three-year record masks an exceedingly strong four-plus year record. From inception (10/08) through the end of 11/12, Victoria 1522 would have turned a $10,000 investment into $19,850. Its peer over the same period would have returned $13,500. That’s partly attributable to good luck: the fund launched in October 2008 and made about 3% in the quarter while its peers dropped nearly 21%. Even excluding that great performance (that is, looking at 1/09 – 11/12), the fund has modestly outperformed its peer group despite the drag of its soon-to-be-lowered expenses. ManagerJosephine Jiménez has a long, distinguished record, including long stints running Montgomery Asset Management’s emerging markets division. (Thanks to Jake Mortell of Candlewood Advisory for the heads up!)
Wells Fargo has reopened the Class A shares of its Wells Fargo Advantage Dow Jones Target funds: Target Today, 2010, 2020, 2030 and 2040.
CLOSINGS
AllianceBernstein Small Cap Growth (QUASX) will close to new investors on January 31, 2013. That’s all I noticed this month.
OLD WINE, NEW BOTTLES
Calvert Enhanced Equity (CMIFX) will be renamed Calvert Large Cap Core in January 2013.
Actually, this one is a little bit more like “old vinegar in new bottles.” Dominion Insight Growth Fund was reorganized into the Shepherd Large Cap Growth Fund in 2002. Shepherd LCG changed its name to the Shepherd Fund in 2008. Then Shepherd Fund became Foxhall Global Trends Fund in 2009, and now Foxhall Global Trends has become Fairfax Global Trends Fund (DOIGX). In all of the name changes, some things have remained constant: low assets, high expenses, wretched performance (they’ve finished in the 98th -99th percentile for the trailing one, three, five and ten year periods).
Forward Aggressive Growth Allocation Fund became Forward Multi-Strategy Fund on December 3, 2012, which is just a bit vanilla. The 50 other multi-strategy funds in Morningstar’s database include Dynamic, Ethical, Global, Hedged and Progressive flavors of the marketing flavor du jour.
In non-news, Marathon Value Portfolio (MVPFX) is moving from the Unified Series Trust to Northern Lights Fund Trust III. That’s their third move and I mention it only because the change causes the SEC to flag MVPFX as a “new” fund. It isn’t new, though it is a five-star, “Star in the Shadows” fund and worth knowing about.
Wells Fargo Advantage Total Return Bond (MBFAX) will be renamed Wells Fargo Advantage Core Bond sometime in December.
OFF TO THE DUSTBIN OF HISTORY
Geez, the dustbin of history is filling up fast . . .
BNY Mellon Intermediate U.S. Government (MOVIX) is merging into BNY Mellon Intermediate Bond (MIIDX) in February, though the manager is the same for both funds.
Buffalo plans to merge Buffalo China (BUFCX) into Buffalo International (BUFIX) in January, 2013. The fund was originally sub-advised by Jayhawk Capital and I long ago wrote a hopeful profile of the then-new fund. Jayhawk ran it for three years, making huge amounts twice (2007 and 2009), lost a huge amount once (2008), lived in the basement of a highly volatile category and were replaced in 2009 by an in-house management team. The fund has been better but never rose to “good” and never drew assets.
Dreman is killing off five of the six funds: Contrarian International Value (DRIVX), Contrarian Mid Cap Value (DRMVX), Contrarian Value Equity (DRVAX), High Opportunity (DRLVX), and Market Over-Reaction (DRQLX). Mr. Dreman has a great reputation and had a great business sub-advising load-bearing funds. Around 2003, Dreman launched a series of in-house, no-load funds. That experiment, by and large, failed. The funds were rebranded and repriced, but never earned their way. The fate of their remaining fund, Dreman Contrarian Small Cap Value (DRSVX), is unknown.
Dreyfus/The Boston Company Small Cap Tax-Sensitive Equity (SDCEX) will liquidate on January 8, 2013 and Dreyfus Small Cap (DSVAX) disappears a week later. Dreyfus is also liquidating a bunch of money market and state bond funds.
Fidelity is pulling a rare 5:1 reverse split by merging Tax Managed Stock (FTXMX), Advisor Strategic Growth (FTQAX), Advisor 130/30 Large Cap (FOATX), and Large Cap Growth (FSLGX) into Fidelity Stock Selector All Cap (FSSKX).
Guggenheim Flexible Strategies (RYBSX) (formerly Guggenheim Long Short Interest Rate Strategies) is slated to merge into Guggenheim Macro Opportunities (GIOAX).
Henderson Global is liquidating their International All Cap Equity (HFNAX) and the Japan Focus (HFJAX) funds in December.
Legg Mason has decided to liquidate Legg Mason Capital Management Disciplined Equity Research (LGMIX), likely on the combination of weak performance and negligible assets.
Munder International Equity (MUIAX) will merge into Munder International Core Equity (MAICX) on Dec. 7.
The board of Northern Funds approved the liquidation of Northern Global Fixed Income (NOIFX) for January 2013.
Pear Tree Columbia Micro Cap (MICRX) just liquidated. They gave the fund all of one year before declaring it to be a failed experiment.
RidgeWorth plans to merge RidgeWorth Large Cap Core Growth Stock (CRVAX) will be absorbed by RidgeWorth Large Cap Growth Stock (STCIX).
Turner is merging Turner Concentrated Growth (TTOPX) into Turner Large Growth (TCGFX) in early 2013.
Westwood has decided to liquidate Westwood Balanced (WHGBX) less than a year after the departure of longtime lead manager Susan Byrne.
In February, Wells Fargo Advantage Diversified Small Cap (NVDSX) disappears into Wells Fargo Advantage Small Company Growth (NVSCX), Advantage Equity Value (WLVAX) into Advantage Intrinsic Value (EIVAX) and Advantage Small/Mid Cap Core (ECOAX) into Advantage Common Stock (SCSAX).
Well Fargo is also liquidating its Wells Fargo Advantage Core builder Series (WFBGX) in early 2013.
Coming Attractions!
 The Observer is trying to help two distinct but complementary groups of folks. One group are investors who are trying to get past all the noise and hype. (CNBC’s ratings are dropping like a rock, which should help.) We’re hoping, in particular, to help folks examine evidence or possibilities that they wouldn’t normally see. The other group are the managers and other folks associated with small funds and fund boutiques. We believe in you. We believe that, as the industry evolves, too much emphasis falls on asset-gathering and on funds launched just for the sake of dangling something new and shiny (uhh … the All Cap Insider Sentiment ETF). We believe that small, independent funds run by smart, passionate investors deserve a lot more consideration than they receive. And so we profile them, write about them and talk with other folks in the media about them.
The Observer is trying to help two distinct but complementary groups of folks. One group are investors who are trying to get past all the noise and hype. (CNBC’s ratings are dropping like a rock, which should help.) We’re hoping, in particular, to help folks examine evidence or possibilities that they wouldn’t normally see. The other group are the managers and other folks associated with small funds and fund boutiques. We believe in you. We believe that, as the industry evolves, too much emphasis falls on asset-gathering and on funds launched just for the sake of dangling something new and shiny (uhh … the All Cap Insider Sentiment ETF). We believe that small, independent funds run by smart, passionate investors deserve a lot more consideration than they receive. And so we profile them, write about them and talk with other folks in the media about them.
As the Observer has become a bit more financially sustainable, we’re now looking at the prospect of launching two sister sites. One of those sites will, we hope, be populated with the best commentaries gathered from the best small fund managers and teams that we can find. Many of you folks write well and some write with grace that far exceeds mine. The problem, managers tell me, is that fewer people than you’d like find their way to your sites and to your insights.
Our technical team, which Chip leads, thinks that they can create an attractive, fairly vibrant site that could engage readers and help them become more aware of some of the smaller fund families and their strategies. We respect intellectual property, and so we’d only use content that was really good and whose sharing was supported by the adviser.
That’s still in development. If you manage a fund or work in support of one and would like to participate in thinking about what would be most helpful, drop Chip a note and we’ll find a way to think through this together. (Thanks!)
Small cap funds tend to have their best performance in the first six weeks of each year and so we’re planned a smallcapfest for our January issue, with new or revised profiles of the most sensible small cap funds as well as a couple outside perspectives on where you might look.
In Closing . . .
I wanted to share leads on three opportunities that you might want to look in on. The Observer has no financial stake in any of this stuff but I like sharing word of things that strike me as really first-rate.
QuoteArts.com is a small shop that consistently offers a bunch of the most attractive, best written greeting cards (and refrigerator magnets) that I’ve seen. Steve Metivier, who runs the site, gave us permission to reproduce one of their images (normally the online version is watermarked):
The text reads “A time to quiet our hearts… (inside) to soften our edges, clear our minds, enjoy our world, and to share best wishes for the season. May these days and all the new year be joyful and peaceful.” It strikes me as an entirely-worthy aspiration.
 The best book there is on the subject of practical persuasion is Robert Cialdini’s Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion (revised edition, 2006). Even if you’re not impressed that I’ve used the book in teaching persuasion over the past 20 years, you might be impressed by Charlie Munger’s strong endorsement of it. In a talk entitled “The Psychology of Human Misjudgment,” Munger reports being so impressed with Cialdini’s work that he read the book, gave copies of it to all his children and sent Cialdini (“chawl-dee-nee,” if you care) a share of Berkshire Hathaway in thanks. Cialdini has since left academe, founded the consulting group Influence at Work and now offers Principles of Persuasion workshops for professionals and the public. While I have not researched the workshops in any depth, I suspect that if I were a small business owner, marketer or financial planner who needed to both attract clients and change their behavior for the better. I’d take a serious look.
The best book there is on the subject of practical persuasion is Robert Cialdini’s Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion (revised edition, 2006). Even if you’re not impressed that I’ve used the book in teaching persuasion over the past 20 years, you might be impressed by Charlie Munger’s strong endorsement of it. In a talk entitled “The Psychology of Human Misjudgment,” Munger reports being so impressed with Cialdini’s work that he read the book, gave copies of it to all his children and sent Cialdini (“chawl-dee-nee,” if you care) a share of Berkshire Hathaway in thanks. Cialdini has since left academe, founded the consulting group Influence at Work and now offers Principles of Persuasion workshops for professionals and the public. While I have not researched the workshops in any depth, I suspect that if I were a small business owner, marketer or financial planner who needed to both attract clients and change their behavior for the better. I’d take a serious look.
Finally, at Amazon’s invitation, I contributed an essay that will be posted at their new “Money and Markets” store from December 5th until about the 12th. Its original title was, “It’s time to go,” but Amazon’s project director and I ended up settling on the less alarming “Trees don’t grow to the sky.” If you’ve shopped at, say, Macy’s, you’re familiar with the store-within-a-store notion: free-standing, branded specialty shops (Levenger’s, LUSH, FAO Schwarz) operating within a larger enterprise. It looks like Amazon is trying an experiment in the same direction and, in November, we mentioned their “Money and Markets” store. Apparently the Amazonians noticed the fact that some of you folks went to look around, they followed your footprints back here and did some reading of their own. One feature of the Money and Markets store is a weekly guest column and the writers have included Jack Bogle and Tadas Viskanta, the founder of Abnormal Returns which is one of the web’s two best financial news aggregators. In any case, they asked if I’d chip in a piece during the second week of December. We’re not allowed to repost the content for a week or so, but I’ll include it in the January cover essay. Feel free to drop by if you’re in the area.
In the meanwhile, I wanted to extend sincere thanks from all of the folks here (chip, Anya, Junior, Accipiter and me) for the year you’ve shared with us. You really do make it all worthwhile and so blessings of the season on you and yours.
As ever,





 Three out of 30 funds managed by Royce outperformed their benchmarks for the 1-year period; 4 out of 24 for the 3-year period; 12 out of 19 for the 5-year period; and all 11 outperformed for the 10-year period.
Three out of 30 funds managed by Royce outperformed their benchmarks for the 1-year period; 4 out of 24 for the 3-year period; 12 out of 19 for the 5-year period; and all 11 outperformed for the 10-year period. On October 12, 2012, RiverNorth launched their fourth fund, RiverNorth Dynamic Buy-Write Fund. “Buy-write” describes a sort of “covered call” strategy in which an investor might own a security and then sell to another investor the option to buy the security at a preset price in a preset time frame. It is, in general, a defensive strategy which generates a bit of income and some downside protection for the investor who owns the security and writes the option.
On October 12, 2012, RiverNorth launched their fourth fund, RiverNorth Dynamic Buy-Write Fund. “Buy-write” describes a sort of “covered call” strategy in which an investor might own a security and then sell to another investor the option to buy the security at a preset price in a preset time frame. It is, in general, a defensive strategy which generates a bit of income and some downside protection for the investor who owns the security and writes the option.
 Based on the success of our September conference call with David Sherman of Cohanzick Asset Management and RiverPark’s president, Morty Schaja, we have decided to try to provide our readers with one new opportunity each month to speak with an “A” tier fund manager.
Based on the success of our September conference call with David Sherman of Cohanzick Asset Management and RiverPark’s president, Morty Schaja, we have decided to try to provide our readers with one new opportunity each month to speak with an “A” tier fund manager.
 It’s the time of year when we pause to enjoy two great German traditions: Oktoberfest and Schadenfreude. While one of my favorites, Leinenkugel’s Oktoberfest, was shut out (Bent River Brewery won first, second and third places at the Quad City’s annual Brew Ha Ha festival), it was a great excuse to celebrate fall on the Mississippi.
It’s the time of year when we pause to enjoy two great German traditions: Oktoberfest and Schadenfreude. While one of my favorites, Leinenkugel’s Oktoberfest, was shut out (Bent River Brewery won first, second and third places at the Quad City’s annual Brew Ha Ha festival), it was a great excuse to celebrate fall on the Mississippi.
 For about an hour on September 13th, David Sherman of Cohanzick Management, LLC, manager of RiverPark Short Term High Yield (RPHYX) fielded questions from Observer readers about his fund’s strategy and its risk-return profile. Somewhere between 40-50 people signed up for the RiverPark call but only about two-thirds of them signed-in. For the benefit of folks interested in hearing David’s discussion of the fund, here’s a link to an mp3 version of Thursday night’s conference call. The RiverPark folks guess it will take between 10-30 seconds to load, depending on your connection. At least on my system it loads in the same window that I’m using for my browser, so you might want to right-click and choose the “open in a new tab” option.
For about an hour on September 13th, David Sherman of Cohanzick Management, LLC, manager of RiverPark Short Term High Yield (RPHYX) fielded questions from Observer readers about his fund’s strategy and its risk-return profile. Somewhere between 40-50 people signed up for the RiverPark call but only about two-thirds of them signed-in. For the benefit of folks interested in hearing David’s discussion of the fund, here’s a link to an mp3 version of Thursday night’s conference call. The RiverPark folks guess it will take between 10-30 seconds to load, depending on your connection. At least on my system it loads in the same window that I’m using for my browser, so you might want to right-click and choose the “open in a new tab” option.