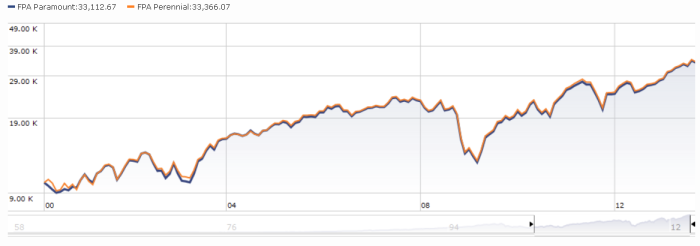
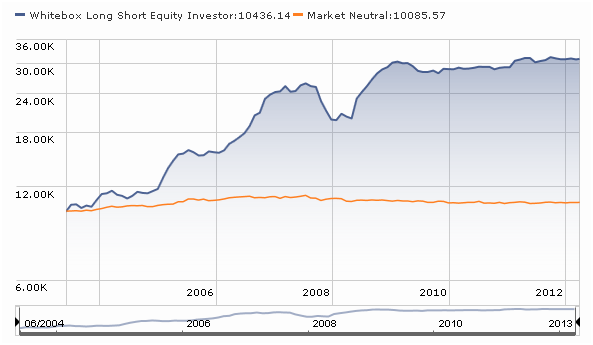
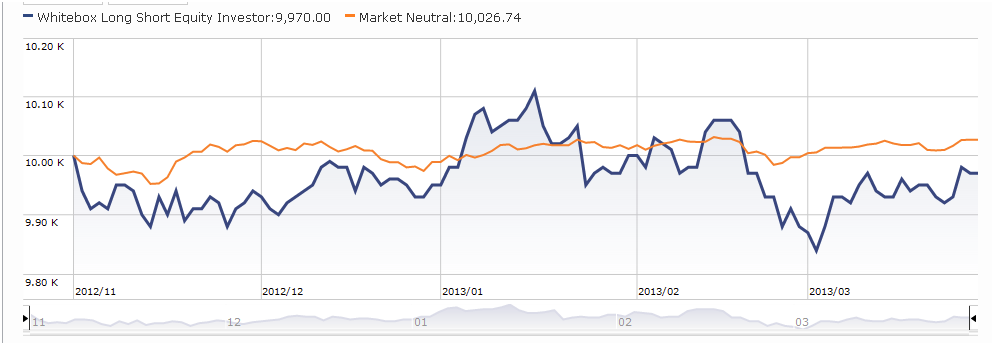
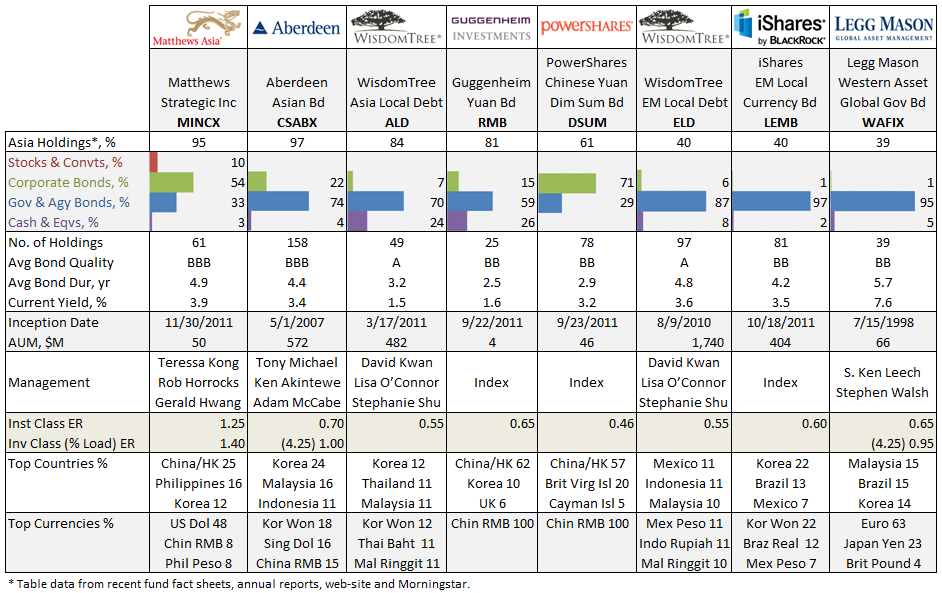
This fund has been liquidated.
Objective and Strategy
The fund seeks maximum long-term capital growth by investing in a compact portfolio of global small cap stocks. In general they pursue “high-quality companies that typically have a sustainable competitive advantage, a superior business model and a high-quality management team.” “Small caps” are stocks with a capitalization under $4 billion at time of purchase. The fund holds about 40 stocks. No more than 50% of the portfolio will be investing in emerging markets and the managers do not expect to hold more than 10%.
Adviser
Artisan Partners, L.P. Artisan is a remarkable operation. They advise the 13 Artisan funds (the 12 funds with a retail share class plus an institutional emerging markets fund), as well as a number of separate accounts. The firm has managed to amass over $105 billion in assets under management, of which approximately $45 billion are in their mutual funds. Despite that, they have a very good track record for closing their funds and, less visibly, their separate account strategies while they’re still nimble. Seven of the firm’s funds are closed to new investors, as of February 2014. Their management teams are stable, autonomous and invest heavily in their own funds.
Manager
Mark Yockey, Charles-Henri Hamker and David Geisler. Mr. Yockey joined Artisan in 1995 and has been repeatedly recognized as one of the industry’s premier international stock investors. He is a portfolio manager for Artisan International, Artisan International Small Cap and Artisan Global Equity Funds. He is, Artisan notes, fluent in French. Charles-Henri Hamker is an associate portfolio manager on Artisan International Fund, and a portfolio manager with Artisan International Small Cap and Artisan Global Equity Funds. He is fluent in French and German. (Take that, Yockey.) Messrs Yockey and Hamker manage rather more than $10 billion in other assets and were nominated as Morningstar’s international-stock fund managers of the year in both 2012 and 2013. Mr. Yockey won the honor in 1998. Mr. Geisler joined Artisan as an analyst in 2007 after working for Cowen and Company. This is his first portfolio management assignment.
Strategy capacity and closure
Between $1 – 2 billion, depending on how quickly money is flowing in and the state of the market. Artisan has an exceptional record for closing funds before they become overly large – seven of their 12 retail funds are, or imminently will be, closed to new investors and Artisan International Small Cap closed in 2003 with about $500 million in assets. As a result, closing the fund well before it hits the $2 billion cap seems likely.
Management’s Stake in the Fund
Mr. Yockey has over $1 million in the fund, Mr. Geisler has between $50,000 – 100,000 and Mr. Hamker has no investment in it. Only one of the funds five independent directors has an investment in the fund; in general, the Artisan directors have invested between hundreds of thousands to millions of their own dollars in the Artisan complex.
Opening date
June 23, 2013
Minimum investment
$1,000
Expense ratio
1.50% after waivers on assets of $53 million, as of January 2014.
Comments
There is a real question about whether early 2014 is a good time to begin investing in small cap stocks. The Leuthold Group reports that small cap stocks are selling at record or near-record premiums to large caps and manager David Geisler concurs that “U.S. small caps are close to peak valuations.” The managers have added just one or two names to the portfolio in recent months; they are not, Mr. Geisler reports, “on a buying strike but we try to be thoughtful.” Perhaps in recognition of those factors, Mike Roos, a vice president and managing director at Artisan (also a consistently thoughtful, articulate guy), reports that Artisan will do no marketing of the fund. “We look forward to organic growth of the fund, but we’re simply not pushing it.”
If you decide that you want to increase your exposure to global small caps, though, there are few safer bets than Artisan. Artisan’s managers are organized into six autonomous teams, each with responsibility for its own portfolios and personnel. The teams are united by four characteristics:
- pervasive alignment of interests with their shareholders – managers, analysts and directors are all deeply invested in their funds, the managers have and have frequently exercised the right to close funds and other manifestations of their strategies, the partners own the firm and the teams are exceedingly stable.
- price sensitivity – while it’s not exclusively a GARP shop, it’s clear that neither the value guys nor the growth guys pursue stocks with extreme valuations.
- a careful, articulate strategy for portfolio weightings – the funds generally have clear criteria for the size of initial positions in the portfolio, the upsizing of those positions with time and their eventual elimination, and
- uniformly high levels of talent. Artisan interviews a lot of potential managers each year, but only hires managers who they believe will be “category killers.”
Those factors have created a tradition of consistent excellence across the Artisan family. By way of illustration:
- Eleven of Artisan’s 12 retail funds are old enough to have Morningstar ratings. Ten of those 11 funds have earned four- or five-stars.
- Ten of the 11 have been recognized as “Silver” or “Gold” funds by Morningstar’s analysts.
- Nine of the 11, including all of the international and global funds, are Lipper Leaders for Total Return.
- Six are MFO Great Owl funds, as well.
- Artisan teams have been nominated for Morningstar’s “manager of the year” award nine times in the past 15 years; they’ve won four times.
And none are weak funds, though some do get out of step with the market from time to time. The managers are finding far better values outside of the US than in it: about 12% of the most recent portfolio are US-domiciled firms, about the same as its UK and China exposure. Despite popular panic about the emerging markets, E.M. stocks are 33% of the portfolio. The average global fund is 50% US, 80% large caps and just 7% EM. That independence is reflected in the fund’s active share: 99.6%.
Bottom Line
You might imagine Global Small Cap as representing the subset of stocks which lies at the intersection of the team’s International Fund (which has had one sub-par year in a decade), it’s International Small Cap fund (which has had two sub-par years in a decade) and its Global Equity fund (which has not yet had a below-average year, though it’s just a bit over three). On face, that’s a very good place to be.
Fund website
By way of disclosure: while the Observer has no financial relationship with or interest in Artisan, I do own shares of two of the Artisan funds (Small Cap Value ARTVX and International Value ARTKX) and have done so since the funds’ inception.
[cr2014]