Dear friends,
In a college with more trees than students, autumn is stunning. Around the campus pond and along wooded paths, trees begin to erupt in glorious color. At first the change is slow, more teasing than apparent. But then we always have a glorious reign of color … followed by a glorious rain of leaves. It’s more apparent then than ever why Augustana was recognized as having one of America’s 25 most beautiful campuses.
Every morning, teaching schedule permitting, I park my car near Old Main then conspire to find the longest possible route into the building. Instead of the simple one block walk east, I head west, uphill and through the residential neighborhoods or south, behind the natural sciences building and up a wooded hillside. I generally walk unencumbered by technology, purpose or companions.
Kicking the leaves is not optional.

photo courtesy of Augustana Photo Bureau
I listen to the crunching of acorns underfoot and to the anxious scouring of black squirrels. I look at the architecture of the houses, some well more than a century old but still sound and beautiful. I breathe, sniffing for the hint of a hardwood fire. And I left my mind wander where it wants to, too. Why are some houses enduringly beautiful, while others are painful before they’re even complete? How might more volatile weather reshape the landscape? Are my students even curious about anything? Would dipping their phones in epoxy make a difference? Maybe investors don’t want to know what their managers actually do? Where would we be if folks actually did spend less? Heck, most of them have already been forced to. I wonder if folks whose incomes and wealth are rapidly rising even think about the implications of stagnation for the rest of us? Why aren’t there any good donut shops anymore? (Nuts.)
You might think of my walks as a luxury or a harmless indulgence by a middle-aged academic. You’d be wrong. Very wrong.
The world has conspired to heap so many demands upon our attention than we can barely focus long enough to button our shirts. Our attention is fragmented, our time is lost (go on, try to remember what you actually did Friday) and our thinking extends no further than the next interruption. It makes us sloppy, unhappy and unimaginative.
Have you ever thought about including those characteristics in a job description: “We’re hoping to find sloppy, unhappy and unimaginative individuals to take us to the next level! If you have the potential to become so distracted by minutiae and incessant interruption that you can’t even remember any other way, we have the position for you.”
Go take a walk, dear friends. Go take a dozen. Take them with someone who makes you want to hold a hand rather than a tablet. The leaves beckon and you’ll be better for it.
On the discreet charm of a stock light portfolio
All the signs point to stocks. The best time of the year to buy stocks is right after Halloween. The best time in the four year presidential cycle to be in stocks is just after the midterm elections. Bonds are poised for a bear market. Markets are steadying. Stocks are plowing ahead; the Total Stock Market Index posted gains of 9.8% through the first 10 months of 2014.
And yet, I’m not plowing into stocks. That’s not a tactical allocation decision, it’s strategic. My non-retirement portfolio, everything outside the 403(b), is always the same: 50% equity, 50% income. Equity is 50% here, 50% there, as well as 50% large and 50% small. Income tends to be the same: 50% short duration/cash-like substances, 50% riskier assets, 50% domestic, 50% international. It is, as a strategy, designed to plod steadily.
My asset allocation has some similarities to Morningstar’s “conservative retirement saver” portfolio, which they gear “toward still-working individuals who expect to retire in 2020 or thereabouts.” Both portfolios are about 50% in equities and both have a medium term time horizon of around 7-10 years. On whole, though, I appear to be both more aggressive and more conservative than Morningstar’s model. I’ve got a lot more exposure to international and, particularly, emerging markets stocks (through Seafarer, Grandeur Peak and Matthews) and bonds (through Matthews and Price) than they do. I favor managers who have the freedom to move opportunistically between asset classes (FPA Crescent is the show piece, but managers at eight of my 10 funds have more than one asset class at their disposal). At the same time, I’ve got a lot more exposure to short-term and cash-management strategies (through Price and two fine RiverPark funds). My funds are cheaper than average (I’m not cheap, I’m rationally cost-conscious) though pricier than Morningstar’s, which reflects their preference for large (no, I didn’t called them “bloated”) funds.
You might benefit from thinking about whether a more diversified stock-light portfolio might help you better balance your personal goals (sleeping well) with your financial ones (eating well). There’s good evidence to guide us.
T. Rowe Price is one of my favorite fund companies, in part because they treat their investors with unusual respect. Price’s publications depart from the normal marketing fluff and generally provide useful, occasionally fascinating, information.
I found two Price studies, in 2004 and again in 2010, particularly provocative. Price constructed a series of portfolios representing different levels of stock exposure and looked at how the various portfolios would have played out over the past 50-60 years.
The original study looked at portfolios with 20, 40, 60, 80 and 100% stocks. The update dropped the 20% portfolio and looked at 0, 40, 60, 80, and 100%. Price updated their research for us and allowed us to release it here.
|
Performance of Various Portfolio Strategies |
|||||
|
December 31, 1949 to December 31, 2013 |
|||||
|
S&P 500 USD |
80 Stocks 20 Bonds 0 Short |
60 Stocks 30 Bonds 10 Short |
40 Stocks 40 Bonds 20 Short |
20 Stocks 50 Bonds 30 Short |
|
|
Return for Best Year |
52.6 |
41.3 |
30.5 |
22.5 |
22.0 |
|
Return for Worst Year |
-37.0 |
-28.7 |
-20.4 |
-11.5 |
-1.9 |
|
Average Annual Nominal Return |
11.3 |
10.5 |
9.3 |
8.1 |
6.8 |
|
Number of Down Years |
14 |
14 |
12 |
11 |
4 |
|
Average Loss (in Down Years) |
-12.5 |
-8.8 |
-6.4 |
-3.0 |
-0.9 |
|
Annualized Standard Deviation |
17.6 |
14.0 |
10.5 |
7.3 |
4.8 |
|
Average Annual Real (Inflation-Adjusted) Return |
7.7 |
6.8 |
5.7 |
4.5 |
3.2 |
T. Rowe Price, October 30 2014. Used with permission.
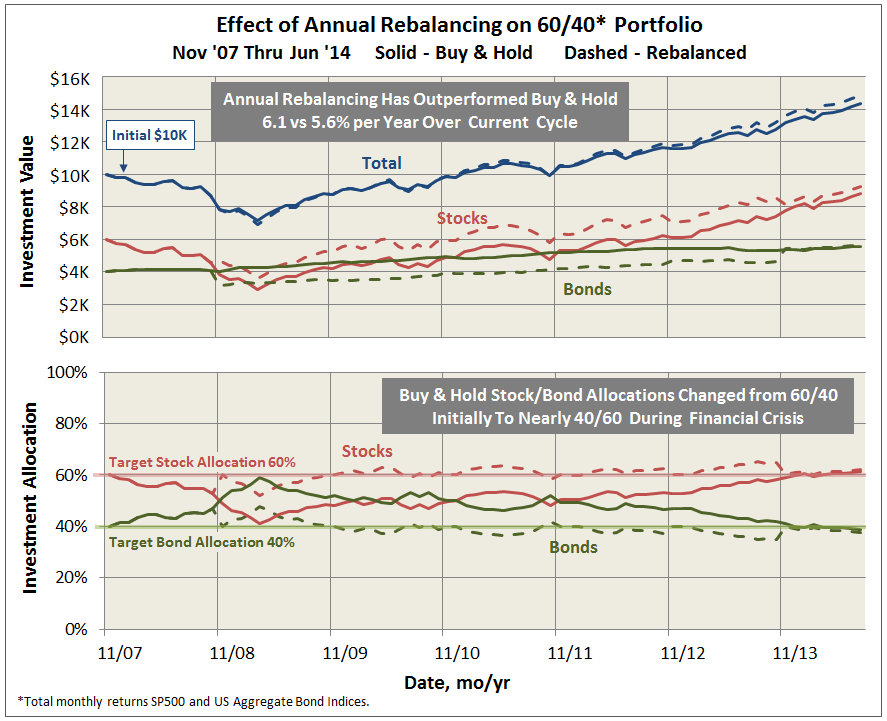
Over the last 65 years, periods which included devastating bear markets for both stocks and bonds, a stock-light portfolio returned 6.8% annually. That translates to receiving about 60% of the returns of an all-equity portfolio with about 25% of the volatility. Going from 20% stocks to 100% increases the chance of having a losing year by 350%, increases the average loss in down years by 1400% and nearly quadruples volatility.
On face, that’s not a compelling case for a huge slug of equities. The findings of behavioral finance research nibbles away at the return advantage of a stock-heavy portfolio by demonstrating that, on average, we’re not capable of holding assets which are so volatile. We run at the wrong time and hide too long. Morningstar’s “Mind the Gap 2014” research suggests that equity investors lose about 166 basis points a year to their ill-timed decisions. Over the past 15 years, S&P 500 investors have lost nearly 200 basis points a year.
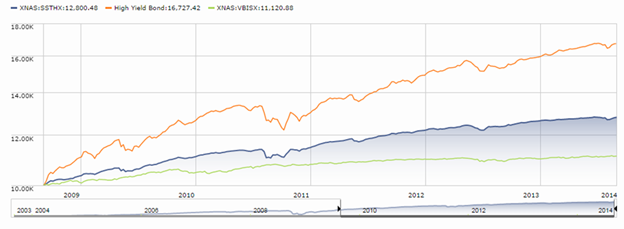
Here’s the argument: you might be better with slow and steady, even if that means saving a bit more or expecting a bit less. For visual learners, here’s a picture of what the result might look like:
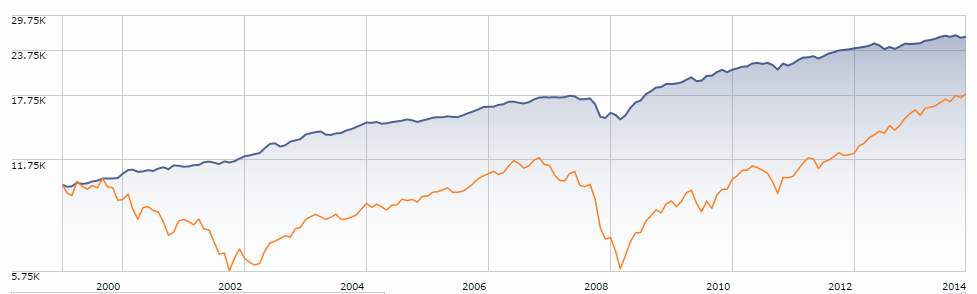
The blue line represents the performance, since January 2000, of T. Rowe Price Spectrum Income (RPSIX) which holds 80% or so in a broadly diversified income portfolio and 20% or so in dividend-paying stocks. The orange line is Vanguard 500 Index (VFINX). I’m happy to admit that maxing-out the graph, charting the funds for 25 years rather than 14, gives a major advantage to the 500 Index. But, as we’re already noted, investors don’t act based on a 25 year horizon.
I know what you’re going to say: (1) we need stocks for the long-run and (2) the bear is about to maul the bond world. Both are true, in a limited sort of way.
First, the mantra “stocks for the long-term” doesn’t say “how much stock” nor does it argue for stocks at any particular juncture; that is, it doesn’t justify stocks now. I’m profoundly sympathetic to the absolute value investors’ argument that you’re actually being paid very poorly for the risks you’re taking. GMO’s latest asset class projections have the broad US market with negative real returns over the next seven years.
Second, a bear market in bonds doesn’t look like a bear market in stocks. A bear market in stocks looks like 25 or 35 or 45% down. Bonds, not so much. A bear market in bonds is generally triggered by rising interest rates. When rates rise, two things happen: the market value of existing low-rate bonds falls while the payouts available from newly issued bonds rises.
The folks at Legg Mason looked at 90 years of bond market returns and graphed them against changes in interest rates. The results were published in Rate-Driven Bond Bear Markets (2013) and they look like this:
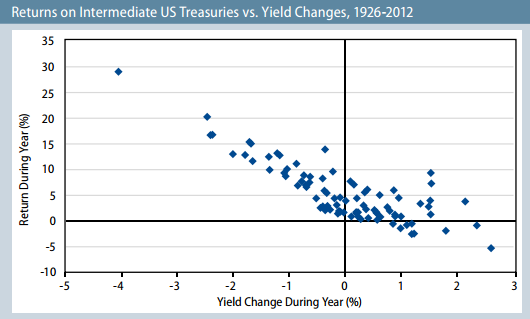
The vertical axis is you, gaining or losing money. The horizontal axis measures rising or falling rates. In the 41 years in which rates have risen, the bond index fell on only nine occasions (the lower right quandrant). In 34 other years, rising rates were accompanied by positive returns, fed by the income payouts of the newly-issued bonds. And even when bonds fall, they typically lose 2-3%. Only 1994 registered a hefty 9% loss.
Price’s research makes things even a bit more positive. They argue that simply using a monolithic measure (intermediate Treasuries, the BarCap aggregate or whatever) underestimates the potential of diversifying within fixed income. Their most recent work suggests that a globally diversified portfolio, even without resort to intricate derivative strategies or illiquid investments, might boost the annual returns of a 60/40 portfolio. A diversified 60/40 portfolio, they find, would have beaten a vanilla one by 130 basis points or so this century. (See “Diversification’s Long-Term Benefits,” 2013.)
This is not an argument against owning stocks or stock funds. Goodness, some of my best friends (the poor dears) own them or manage them. The argument is simpler: fix the roof when it’s not raining. Think now about what’s in your long-term best interest rather than waiting for a sickened panic to make the decision for you. One of the peculiar signs of my portfolio’s success is this: I have no earthly idea of how it’s doing this year. While I do read my managers’ letters eagerly and even talk with them on occasion, I neither know nor care about the performance over the course of a few months of a portfolio designed to serve me over the course of many years.
And as you think about your portfolio’s shape for the year ahead or reflect on Charles’ and Ed’s essays below, you might find the Price data useful. The original 2004 and 2010 studies are available at the T. Rowe Price website.
 Mediocrity and frustration
Mediocrity and frustration
I’ve been fully invested in the market for the past 14 years with little to show for it, except frustration and proclamations of even more frustration ahead. During this time, basically since start of 21st century, my portfolio has returned only 3.9% per year, substantially below historical return of the last century, which includes among many other things The Great Depression.
I’ve suffered two monster drawdowns, each halving my balance. I’ve spent 65 months looking at monthly statements showing retractions of at least 20%. And, each time I seem to climb-out, I’m greeted with headlines telling me the next big drop is just around the corner (e.g., “How to Prepare for the Coming Bear Market,” and “Are You Prepared for a Stock Selloff ?“)
I have one Nobel Prize winner telling me the market is still overpriced, seeming every chance he gets. And another telling me that there is nothing I can do about it…that no amount of research will help me improve my portfolio’s performance.
Welcome to US stock market investing in the new century…in the new millennium.
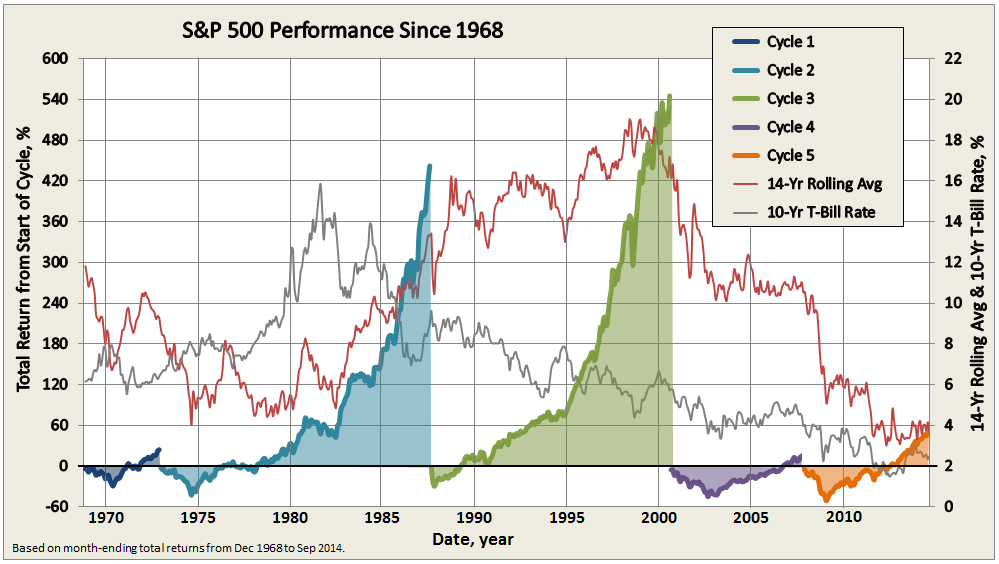
The chart below depicts S&P 500 total return, which includes reinvested dividends, since December 1968, basically during the past 46 years. It uses month-ending returns, so intra-day and intra-month fluctuations are not reflected, as was done in a similar chart presented in Ten Market Cycles. The less frequent perspective discounts, for example, bear sightings from bear markets.
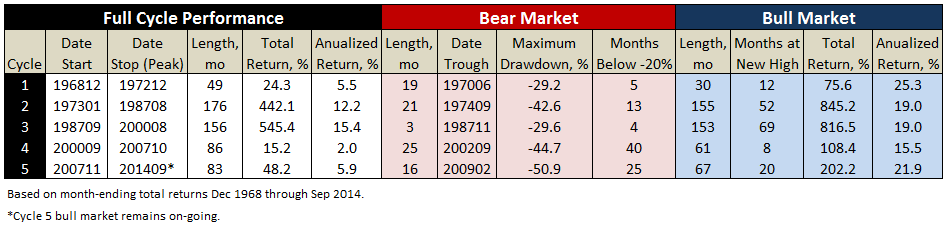
The period holds five market cycles, the last still in progress, each cycle comprising a bear and bull market, defined as a 20% move opposite preceding peak or trough, respectively. The last two cycles account for the mediocre annualized returns of 3.9%, across 14-years, or more precisely 169 months through September 2014.
Journalist hyperbole about how “share prices have almost tripled since the March 2009 low” refers to the performance of the current bull market, which indeed accounts for a great 21.9% annualized return over the past 67 months. Somehow this performance gets decoupled from the preceding -51% return of the financial crisis bear. Cycle 4 holds a similar story, only investors had to suffer 40 months of protracted 20% declines during the tech bubble bear before finally eking out a 2% annualized return across its 7-year full cycle.
Despite advances reflected in the current bull run, 14-year annualized returns (plotted against the secondary axis on the chart above) are among the lowest they been for the S&P 500 since September 1944, when returns reflected impacts of The Great Depression and World War II.
Makes you wonder why anybody invests in the stock market.
I suspect all one needs to do is see the significant potential for upside, as witnessed in Cycles 2-3. Our current bull pales in comparison to the truly remarkable advances of the two bull runs of 1970-80s and 1990s. An investment of $10,000 in October 1974, the trough of 1973-74, resulted in a balance of $610,017 by August 2000 – a 6000% return, or 17.2% for nearly 26 years, which includes the brief bear of 1987 and its coincident Black Monday.
Here’s a summary of results presented in the above graph, showing the dramatic differences between the two great bull markets at the end of the last century with the first two of the new century, so far:
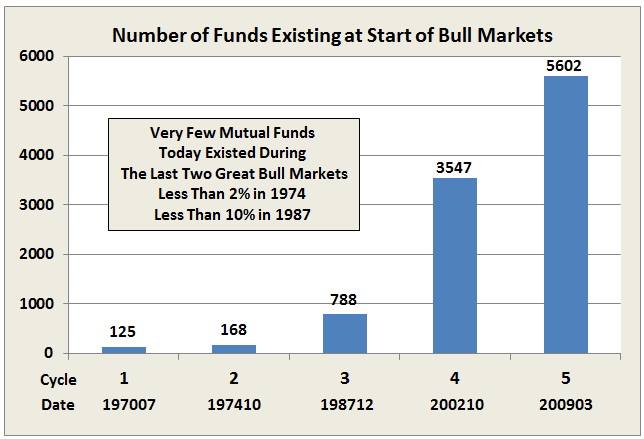
But how many funds were around to take advantage 40 years ago? Answer: Not many. Here’s a count of today’s funds that also existed at the start of the last five bull markets:
Makes you wonder whether the current mediocrity is simply due to too many people and perhaps too much money chasing too few good ideas?
The long-term annualized absolute return for the S&P 500 is 10%, dating back to January 1926 through September 2014, about 89 years (using database derived from Goyal and Shiller websites). But the position held currently by many value oriented investors, money-managers, and CAPE Crusaders is that we will have to suffer mediocre returns for the foreseeable future…at some level to make-up for excessive valuations at the end of the last century. Paying it seems for sins of our fathers.
Of course, high valuation isn’t the only concern expressed about the US stock market. Others believe that the economy will face significant headwinds, making it hard to repeat higher market returns of years past. Rob Arnott describes the “3-D Hurricane Force Headwind” caused by waves of Deficit spending, which artificially props-up GDP, higher than published Debt, and aging Demographics.
Expectations for US stocks for the next ten years is very low, as depicted in the new risk and return tool on Research Affiliates’ website (thanks to Meb Faber for heads-up here). Forecast for large US equities? Just 0.7% total return per year. And small caps? Zero.
Good grief.
What about bonds?
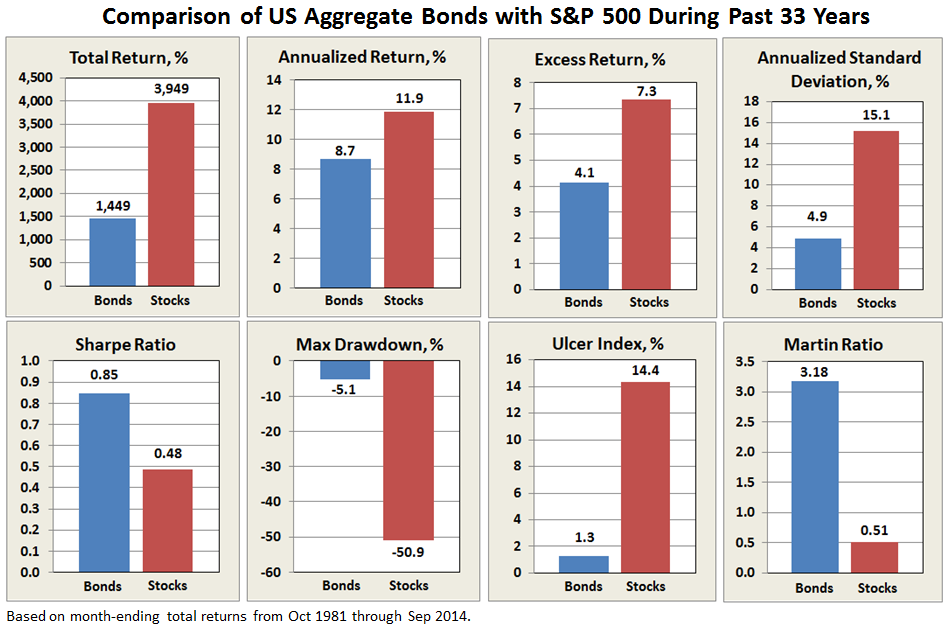
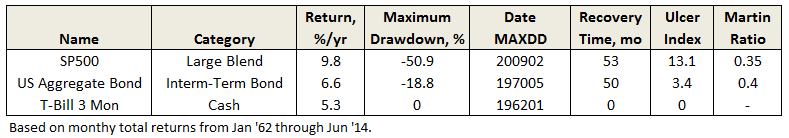
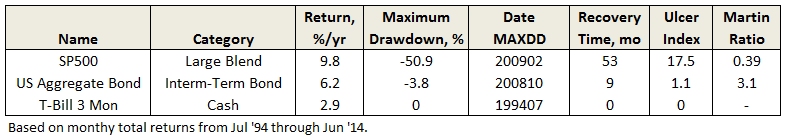
Plotted also on the first chart presented above is 10-year average T-Bill interest rate. While it has trended down since the early 1980’s, if there is a correlation between it and stock performance, it is not obvious. What is obvious is that since interest rates peaked in 1981, US aggregate bonds have been hands-down superior to US stocks for healthy, stable, risk-adjusted returns, as summarized below:
Sure, stocks still triumphed on absolute return, but who would not take 8.7% annually with such low volatility? Based on comparisons of absolute return and Ulcer Index, bonds returned more than 70% of the gain with just 10% of the pain.
With underlining factors like 33 years of declining interest rates, it is no wonder that bond funds proliferated during this period and perhaps why some conservative allocation funds, like the MFO Great Owl and Morningstar Gold Metal Vanguard Wellesley Income Fund (VWINX), performed so well. But will they be as attractive the next 33 years, or when interest rates rise?
As Morningstar’s Kevin McDevitt points out in his assessment of VWINX, “the fund lagged its average peer…from July 1, 1970, through July 1, 1980, a period of generally rising interest rates.” That said, it still captured 85% of the S&P500 return over that period and 76% during the Cycle 2 bull market from October 1974 through August 1987.
Of course, predicting interest rates will rise and interest rates actually rising are two different animals, as evidenced in bond returns YTD. In fact, our colleague Ed Studzinski recently pointed out the long term bonds have done exceptionally well this year (e.g., Vanguard Extended Duration Treasury ETF up 26.3% through September). Who would have figured?
I’m reminded of the pop quiz Greg Ip presents in his opening chapter of “Little Book of Economics”: The year is 1990. Which of the following countries has the brighter future…Japan or US? In 1990, many economists and investors picked Japan. Accurately predicting macroeconomics it seems is very hard to do. Some say it is simply not possible.
Similarly, the difficulty mutual funds have to consistently achieve top-quintile performance, either across fixed time periods or market cycles, or using absolute or risk-adjusted measures, is well documented (e.g., The Persistence Scorecard – June 2014, Persistence is a Killer, In Search of Persistence, and Ten Market Cycles). It does not happen. Due to the many underlying technical and psychological variables of the market place, if not the shear randomness of events.
In his great book “The Most Important Thing,” Howard Marks describes the skillful defensive investor as someone who does not lose much when the market goes down, but gains a fair amount when the market goes up. But this too appears very hard to do consistently.
Vanguard’s Convertible Securities Fund (VCVSX), sub-advised by OakTree Capital Management, appears to exhibit this quality to some degree, typically capturing 70-100% of upside with 70-80% of downside across the last three market cycles.
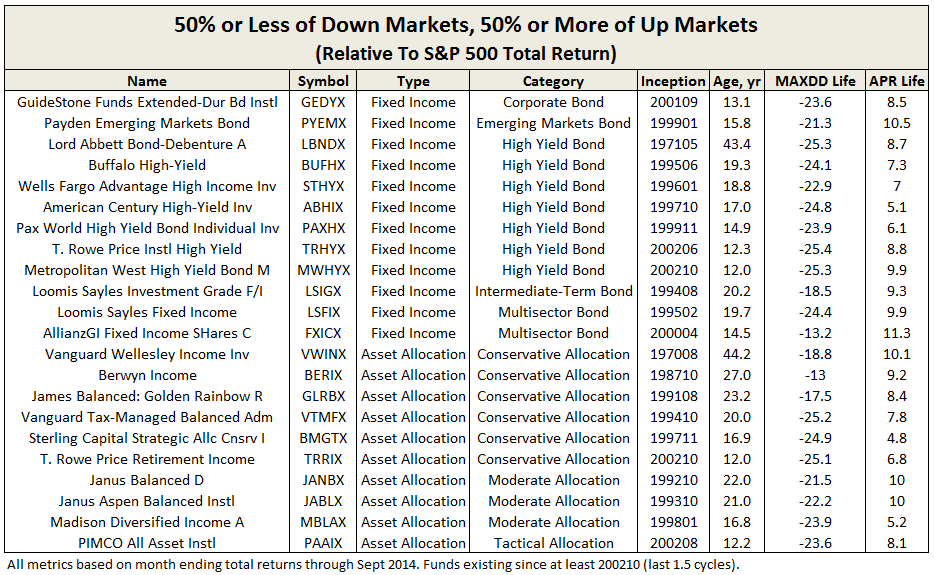
Since bull markets tend to last much longer than bear markets and produce returns well above the average, capturing a “fair amount” does not need to be that high. Examining funds that have been around for at least 1.5 cycles (since October 2002, oldest share class only), the following delivered 50% or more total return during bull markets, while limiting drawdowns to 50% during bear markets, each relative to S&P 500. Given the 3500 funds evaluated, the final list is pretty short.
VWINX is the oldest, along with Lord Abbett Bond-Debenture Fund (LBNDX) . Both achieved this result across the last four full cycles. As a check against performance missing the 50% threshold during out-of-cycle or partial-cycle periods, all funds on this list achieved the same result over their lifetimes.
For moderately conservative investors, these funds have not been mediocre or frustrating at all, quite the contrary. For those with an appetite for higher returns and possess the attendant temperament and investing horizon, here is a link to similar funds with higher thresholds: MFO Pain-To-Gain Funds.
We can only hope to have it so good going forward.
I fear that Charles and I may have driven poor Ed over the edge. After decades of outstanding work as an investment professional, this month he’s been driven to ask …
 Investing – Why?
Investing – Why?
By Edward Studzinski
“The most costly of all follies is to believe passionately in the palpably not true. It is the chief occupation of mankind.”
H.L. Mencken
I will apologize in advance, for this may end up sounding like the anti-mutual fund essay. Why do people invest, and specifically, why do they invest in mutual funds? The short answer is to make money. The longer answer is hopefully more complex and covers a multitude of rationales. Some invest for retirement to maintain a standard of living when one is no longer working full-time, expecting to achieve returns through diversified portfolios and professional management above and beyond what they could achieve by investing on their own. Others invest to meet a specific goal along the path of life – purchase a home, pay for college for the children, be able to retire early. Rarely does one hear that the goal of mutual fund investing is to become wealthy. In fact, I can’t think of any time I have ever had anyone tell me they were investing in mutual funds to become rich. Indeed if you want to become wealthy, your goal should be to manage a mutual fund rather than invest in one.
How has most of the great wealth been created in this country? It has been created by people who started and built businesses, and poured themselves (and their assets) into a single-minded effort to make those businesses succeed, in many instances beyond anyone’s wildest expectations. And at some point, the wealth created became solidified as it were by either selling the business (as the great philanthropist Irving Harris did with his firm, Toni Home Permanents) or taking it public (think Bill Gates or Jeff Bezos with Microsoft and Amazon). And if one goes further back in time, the example of John D. Rockefeller with the various Standard Oil companies would loom large (and now of course, we have reunited two of those companies, Standard Oil Company of New Jersey aka Exxon and Standard Oil Company of New York aka Mobil as Exxon-Mobil, but I digress).
So, this begs the question, can one become wealthy by investing in a professionally-managed portfolio of securities, aka a mutual fund? The answer is – it depends. If one wants above-average returns and wealth creation, one usually has to concentrate one’s investments. In the mutual fund world you do this by investing in a concentrated or non-diversified fund. The conflict comes when the non-diversified fund grows beyond a certain size of assets under management and number of investments. It then morphs from an opportunistic investment pool into a large or mega cap investment pool. The other problem arises with the unlimited duration of a mutual fund. Daily fund pricing and daily fund flows and redemptions do have a cost. For those looking for a real life example (I suspect I know the answer but I will defer to Charles to provide the numbers in next month’s MFO), contrast the performance over time of the closed-end fund, Source Capital (SOR) run by one of the best value investment firms, First Pacific Advisors with the performance over time of the mutual funds run by the same firm, some with the same portfolio managers and strategy.
The point of this is that having a fixed capital structure lessens the number of issues with which an investment manager has to deal (focus on the investment, not what to do with new money or what to sell to meet redemptions). If you want a different real life example, take a look at the long-term performance of one of the best investment managers to come out of Harris Associates, whom most of you have never heard of, Peter B. Foreman, and his partnership Hesperus Partners, Ltd.
Now the point of this is not to say that you cannot make money by investing in a mutual fund or a pool of mutual funds. Rather, as you introduce more variables such as asset in-flows, out-flows, pools of analysts dedicated to an entire fund group rather than one investment product, and compensation incentives or disincentives, it becomes harder to generate consistent outperformance. And if you are an individual investor who keeps increasing the number of mutual funds that he or she has invested in (think Noah and the Ark School of Personal Investment), it becomes even more difficult
A few weeks ago it struck me that in the early 1980’s, when I figured out that I was a part of the sub-species of investor called value investor (not “value-oriented investor” which is a term invented by securities lawyers for securities lawyers), I made my first investment in Berkshire Hathaway, Warren Buffett’s company. That was a relatively easy decision to make back then. I recently asked my friend Greg Jackson if he could think of a handful of investments, stocks like Berkshire (which has in effect been a closed-end investment portfolio) that today one could invest in that were one-decision investments. Both of us are still thinking about the answer to that question.
Has something changed in the world in investing in the last fifteen or twenty years? Yes, it is a different world, in terms of information flows, in terms of types of investments, in terms of derivatives, in terms of a variety of things. What it also is is a different world in terms of time horizons and patience. There is a tremendous amount of slippage that can eat into investment returns today in terms of trading costs and taxes (even at capital gains rates). And as a professional investment manager you have lots of white noise to deal with – consultants, peer pressure both internal and external, and the overwhelming flow of information that streams by every second on the internet. Even sitting in Omaha, the net of modern communications still drops over everything.
So, how does one improve the odds of superior long-term performance? One has to be prepared to step back and stand apart. And that is increasingly a difficult proposition. But the hardest thing to do as an investment manager, or in dealing with one’s own personal portfolio, is to sometimes just do nothing. And yes, Pascal the French philosopher was right when he said that most of men’s follies come from not being able to sit quietly in one room. Even more does that lesson apply to one’s investment portfolio. More in this vein at some future date, but those are the things that I am musing about now.
“ … if you want to become wealthy, your goal should be to manage a mutual fund rather than invest in one.” It’s actually fairer to say, “manage a large firm’s mutual fund” since many of the managers of smaller, independent funds are actually paying for the privilege of investing your money: their personal wealth underwrites some of the fund’s operations while they wait for performance to draw enough assets to cross the financial sustainability threshold. One remarkably successful manager of a small fund joked that “you and I are both running non-profits. The difference is that I hadn’t intended to.”
In the Courts: Top Developments in Fund Industry Litigation
![]() Fundfox, launched in 2012, is the mutual fund industry’s only litigation intelligence service, delivering exclusive litigation information and real-time case documents neatly organized and filtered as never before.
Fundfox, launched in 2012, is the mutual fund industry’s only litigation intelligence service, delivering exclusive litigation information and real-time case documents neatly organized and filtered as never before.
“We built Fundfox from the ground up for mutual fund insiders,” says attorney-founder David M. Smith. “Directors and advisory personnel now have easier and more affordable access to industry-specific litigation intelligence than even most law firms had before.”
The core offering is a database of case information and primary court documents for hundreds of industry cases filed in federal courts from 2005 through the present. A Premium Subscription also includes robust database searching—by fund family, subject matter, claim, and more.
Settlement
- Fidelity settled a six-year old whistleblower case that had been green-lighted by the U.S. Supreme Court earlier this year. (Zang v. Fid. Mgmt. & Research Co.)
Briefs
- American Century defendants filed their opening appellate brief (under seal) in a derivate action regarding the Ultra Fund’s investments in gambling-related securities. Defendants include independent directors. (Seidl v. Am. Century Cos.)
- Fidelity filed a motion to dismiss a consolidated ERISA class action that challenges Fidelity’s practices with respect to “redemption float” (i.e., the cash held to pay checks sent to 401(k) plan participants who have withdrawn funds from their 401(k) accounts). (In re Fid. ERISA Float Litig.)
- First Eagle filed a reply brief in support of its motion to dismiss fee litigation regarding two international equity funds: “Plaintiffs have not identified a single case in which a court allowed a § 36(b) claim to proceed based solely on a comparison of the adviser’s fee to a single, unknown fee that the adviser receives for providing sub-advisory services to another client.” (Lynn M. Kennis Trust v. First Eagle Inv. Mgmt., LLC.)
Amended Complaints
- Plaintiffs filed an amended complaint in the excessive-fee litigation regarding five SEI funds, adding a new claim regarding the level of transfer agent fees. (Curd v. SEI Invs. Mgmt. Corp.)
- ERISA class-action plaintiffs filed an amended complaint alleging that TIAA-CREF failed to honor customer requests to pay out funds in a timely fashion. (Cummings v. TIAA-CREF.)
Answer
Having lost its motion to dismiss, Principal filed an answer in excessive-fee litigation regarding six of its LifeTime Funds. (Am. Chems. & Equip., Inc. 401(k) Ret. Plan v. Principal.
For a complete list of developments last month, and for information and court documents in any case, log in at www.fundfox.com and navigate to Fundfox Insider.
The Alt Perspective: Commentary and News from DailyAlts.

PREPARE FOR VOLATILITY
The markets delivered investors both tricks and treats in October. Underlying the modestly positive top-line U.S. equity and bond market returns for the month was a 64% rise, and subsequent decline, in the CBOE Volatility Index, otherwise known as VIX. This dramatic rise in the VIX coincided with a sharp, mid-month decline in equity markets. But with Halloween looming, the market goblins wanted to deliver some treats, and in fact did so as they pushed the VIX down to end the month 12.3% lower than it started. In turn, the equity markets rallied to close the month at all-time highs on Halloween day.
But as volatility creeps back into the markets, opportunities arise. Investment strategies that rely on different segments of the market behaving differently, such as managed futures and global macro, can thrive as global central bank policies diverge. And indeed they have. The top three managed futures funds have returned an average of 14.7% year-to-date through Oct. 31, according to data from Morningstar.
Other strategies that rely heavily on greater dispersion of returns, such as equity market neutral strategies, are also doing well this year. Whereas managed futures and global macro strategies take advantage of diverging prices at a macro level (U.S equities vs. Japanese equities, or Australian dollar vs. the Euro), market neutral funds take advantage of differences in individual stock price performance. And many of these funds have done just that this year. Through October 31, the three best performing equity market neutral funds have an average return of 11.9% year-to-date, according to data from Morningstar.
All three of these strategies generate returns by investing both long and short, generally in equal amounts, and maintain low levels of net exposure to individual markets. As a result, they can be used to effectively diversify portfolios away from stocks and bonds. And as volatility picks up, these funds have a greater opportunity to add value.
NEW FUND LAUNCHES IN OCTOBER
As of this writing, seven new alternative funds have been launched in October, and like last month when four new funds launched on the last day of the month, we expect to add a few more to the October count. Five of the new funds are packaged as mutual funds, and two are ETFs, while five are multi-strategy funds, one is long/short, one is managed futures and one is market neutral. Two notable launches that dovetail on the discussion above are as follows:
- ProShares Managed Futures Strategy Fund (FUTS) – This is a low cost, systematic managed futures fund that invests across multiple asset classes.
- AQR Equity Market Neutral Fund (QMNIX) – This is a pure equity market neutral fund that will target a beta of 0 relative to the US equity markets.
NEW FUNDS REGISTERED IN OCTOBER
October saw 13 new alternative funds register with the S.E.C. covering a wide swath of strategies including multi-strategy, long/short equity, arbitrage, global macro and managed futures. Two notable funds are:
- Balter Discretionary Global Macro Fund – This is the second mutual fund from Balter Liquid Alternatives and will provide investors with exposure to Willowbridge Associates, a discretionary global macro manager that was formed in 1988.
- PIMCO Multi-Strategy Alternative Fund – This fund will be sub-advised by Research Affiliates and will invest in a range of alternative mutual funds and ETFs managed and offered by PIMCO.
OTHER NOTABLE NEWS
- The SEC rejected two proposals for non-transparent ETFs (exchange traded funds that don’t have to disclose their holdings on a daily basis). This is a setback for this new product structure that may ultimately bring more alternative strategies to the ETF marketplace.
- Education continues to be a hot topic among advisors and other investors looking to use alternative mutual funds and ETFs. The two most viewed articles on DailyAlts in October had to do with investor education and related research articles: AllianceBernstein Provides Thought Leadership on Liquid Alts and Neuberger Berman Calls Alts ‘The New Traditionals’.
- The S.E.C. continues to examine liquid alternative funds, and potentially has an issue with some fund disclosures. Norm Champ, the S.E.C. director leading the investigations, spoke recently at an industry event and noted that there appears to be some discrepancies between what funds are permitted to do per their prospectuses, and what is actually being done in the funds. Interestingly, he noted that prospectuses sometimes disclose more strategies than are actually being used in the funds.
Have a joyful Thanksgiving, and feel free to stop by DailyAlts.com for more updates on the liquid alternatives market.
Observer Fund Profiles:
Each month the Observer provides in-depth profiles of between two and four funds. Our “Most Intriguing New Funds” are funds launched within the past couple years that most frequently feature experienced managers leading innovative newer funds. “Stars in the Shadows” are older funds that have attracted far less attention than they deserve.
FPA Paramount (FPRAX): Paramount has just completed Year One under its new global, absolute value discipline. If it weren’t for those danged emerging markets (non) consumers and anti-corruption drives, the short term results would likely have been as bright as the long-term promise.
Launch Alert: US Quantitative Value (QVAL)
![]()
My colleague Charles Boccadoro has been in conversation with Wesley Gray and the folks at Alpha Architect. While ETFs are not our traditional interest, the rise of actively managed ETFs and the recently thwarted prospect for non-transparent, actively managed ETFs, substantially blurs the line between them and open-end mutual funds. When we encounter particularly intriguing active ETF options, we’re predisposed to share them with you. Based on the investing approach detailed in his highly praised 2013 book Quantitative Value, this fund qualifies. Wesley Gray launched the U.S. Quantitative Value ETF (QVAL) on 22 October 2014.
Dr. Gray gave an excellent talk at the recent Morningstar conference with a somewhat self-effacing title borrowed from Warren Buffet: Beware of Geeks Bearing Formulas. His background includes serving as a US Marine Corps intelligence officer and completing both an MBA and a PhD from the University of Chicago’s Booth School of Business. He appears well prepared to understand and ultimately exploit financial opportunities created by behavioral biases and inefficiencies in the market.
The fund employs a Benjamin Graham value philosophy, which Dr. Gray has been studying since his 12th birthday, when his late grandmother gave him a copy of The Intelligent Investor. In quant-fashion, the fund attempts to implement the value strategy in systematic fashion to help protect against behavioral errors. Behaviors, for example, that led to the worst investor returns for the past decade’s best performing fund – CGM Focus Fund (2000-09). “We are each our own worst enemy,” Dr. Gray writes.
The fund uses academically-based and empirically-validated approaches to identify quality and price. In this way, Dr. Gray has actually challenged a similar strategy, called “The Magic Formula,” made popular by Joel Greenblatt’s book The Little Book That Beats the Market. The issue appears to be that The Magic Formula systematically forces investors to pay too high for quality. Dr. Gray argues that price is actually a bigger determinant of ultimate return than quality.
QVAL currently holds 40 stocks so we classify it as a concentrated portfolio, though not technically non-diversified. Its expense ratio is 0.79%, substantially less than the former Formula Investing funds (now replaced by even more expensive Gotham funds). The fund has quickly collected $8M in AUM. An international version (IVAL) is pending. We plan to do an in-depth profile of QVAL soon.
Alpha Shares maintains separate sites for its Alpha Shares advisory business and its Value Shares active ETFs. Folks trying to understand the evidence behind the strategy would be well-advised to start with the QVAL factsheet, which provides the five cent tour of the strategy, then look at the research in-depth on the “Our Ideas” tab on the advisor’s homepage
Funds in Registration
The intrepid David Welsch, spelunker in the SEC database, tracked down 23 new no-load, retail funds in registration this month. In general, these funds will be available for purchase at the very end of December. Advisors really want to have a fund live by December 30th or reporting services won’t credit it with “year to date” results for all of 2015. A number of the prospectuses are incredibly incomplete (not listing, for example, a fund manager, minimums, expenses or strategies) which suggests that they’re panicked about having something on file.
Highlights among the registrants:
- Arbitrage Tactical Equity Fund will inexplicably do complicated things in pursuit of capital appreciation. Given that all of the Arbitrage funds could be described in the same way, and all of them are in the solid-to-excellent range, that’s apparently not a bad thing.
- Greenhouse MicroCap Discovery Fund will pursue long-term capital appreciation by investing in 50-100 microcaps “run by disciplined management teams possessing clear strategies for growth that … trade at a discount to intrinsic value.” The fund intrigues me because Joseph Milano is one of its two managers. Milano managed T. Rowe Price New America Growth Fund (PRWAX) quite successfully from 2002-2013. PRWAX is a large growth fund but a manager’s disciplines often seem transferable across size ranges.
- Intrepid International Fund will seek long-term capital appreciation by investing in foreign stocks but it is, by prospectus, bound to invest only 40% of its portfolio overseas. Curious. The Intrepid funds are all built around absolute value disciplines: if the case for risky assets isn’t compelling, they won’t buy them. That’s led to some pretty strong records across full market cycles, and pretty disappointing ones if you look only at little slices of time. One of the managers of Intrepid Income was handle the reins here.
Manager Changes
This month saw 67 manager changes including the departures of several high profile professionals, including Abhay Deshpande of the First Eagle Funds.
Updates
PIMCO has been punted from management of Forward Investment Grade Fixed-Income Fund (AITIX) and Principal Global Multi-Strategy Fund (PMSAX). I’m afraid that the folks at the erstwhile “happiest place on earth” must be a bit shell-shocked. Since Mr. Gross stomped off, they’ve lost contracts – involving either the Total Return Fund or all of their services – with the state retirement systems in New Hampshire and Florida, the teachers’ retirement system in Arkansas, Ford Motor’s 401(k), Advanced Series Trust, Massachusetts Mutual Life Insurance Co., Alabama’s and California’s 529 College Savings accounts, Russell Investments, British wealth manager St. James Place, Schwab’s Target Date funds and a slug of city retirement plans. Consultant DiMeo Schneider & Associates, whose clients have about a billion in PIMCO Total Return, has issued “a universal sell recommendation” on PIMCO and Schwab reportedly is saying something comparable to its private clients.
Three short reactions:
The folks firing PIMCO are irresponsible. The time to dump PIMCO would have been during the period that Gross was publicly unraveling. Leaving after you replace the erratic titan with a solid, professional team suggests either they weren’t being diligent or they’re grabbing for headlines or both.
PIMCO crisis management appears inept. “We are PIMCO (dot com)!” Really? I don’t tweet but enormous numbers of folks do and PIMCO’s Twitter feed is lame. One measure of impact is retweeting and only three of the past 20 tweets have been retweeted 10 or more times. There appears to be no coherent focus or intensity, just clutter and business-as-usual as the wobble gets worse.
Financial writers should be ashamed. In the months leading up to Gross’s departure, I found just three or four people willing to state the obvious. Now many stories, if not virtually every story, about PIMCO being sacked pontificates about the corrosive effect of months of increasingly erratic behavior. Where we these folks when their readers needed them? Oh right, hiding behind “the need to maintain access.”
By the way, the actual Pontiff seems to be doing a remarkably good job of pontificating. He seems an interesting guy. It will be curious to see whether his efforts are more than just a passing ripple on a pond, since the Vatican specializes in enduring, absorbing then forgetting reformist popes.
Grandeur Peak Global Opportunities (GPGOX) and Grandeur Peak International Opportunities (GPIOX) have now changed their designation from “non-diversified” to “diversified” portfolios. Given that they hold more than 200 stocks each, that seems justified.
photo courtesy of Augustana Photo Bureau
Briefly Noted . . .
Kent Gasaway has resigned as president of the Buffalo Funds, though he’ll continue to co-manage Buffalo Small Cap Fund (BUFSX) and the Buffalo Mid Cap Fund (BUFMX).
At about the same time, Abhay Deshpande has resigned as manager of the First Eagle Global (SGENX), Overseas (SGOVX) and US Value (FEVAX) funds. It’s curious that his departure, described as “amicable,” has drawn essentially no notice given his distinguished record and former partnership with Jean-Marie Eveillard.
Chou America makes it definite. According to their most recent SEC filing, the unexplained changes that might happen on December 6 now definitely will happen on December 6:
Robeco Boston Partners Long/Short Research Fund (BPRRX) is closed to new investors, which is neither news (it happened in spring) nor striking (Robeco has a long record of shuttering funds). What is striking is their willingness to announce the trigger that will lead them to reopen the fund:
Robeco reserves the right to reopen the Fund to new investments from time to time at its discretion, should the assets of the Fund decline by more than 5% from the date of the last closing of the Fund. In addition, if Robeco reopens the Fund, Robeco has discretion to close the Fund thereafter should the assets of the Fund increase by more than 5% from the date of the last reopening of the Fund.
Portfolio 21 Global Equity Fund (PORTX) “is excited to announce” that it’s likely to be merge with Trillium Asset Management and that its president, John Streur, has resigned.
Wasatch Funds announced the election of Kristin Fletcher to their board of trustees. I love it when funds have small, highly qualified boards. Ms. Fletcher surely qualifies, with over 35 years in the industry including a stint as the Chairman and CEO of ABN AMRO, and time at First Interstate Bank, Standard Chartered Bank, Export-Import Bank of the U.S., and Wells Fargo Bank.
SMALL WINS FOR INVESTORS
Aristotle International Equity (ARSFX) and Aristotle/Saul Global Opportunities Fund (ARSOX) have reduced their initial purchase minimum from $25,000 to $2,500 and their subsequent investment minimum to $100. Both funds have been cellar-dwellers over their short lives; presumably rich folks have enough wretched opportunities in hedge funds and so weren’t drawn here.
Effective November 1, Forward trimmed five basis points of the management fee for the various classes of Forward Emerging Markets Fund (PGERX). The fund is tiny, mediocre and running at a loss of .68%, so this is a marketing move rather than an adjustment to the economies of scale.
The trustees for O’Shaughnessy Enhanced Dividend (OFDAX/OFDCX) and O’Shaughnessy Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund (OFMAX) voted to eliminate the fund’s “A” and “C” share classes and transitioning those investors into the lower-cost Institutional share class. Neither makes a compelling case for itself.
On October 9, 2014, the Board of Trustees of Philadelphia Investment Partners New Generation Fund (PIPGX) voted to remove the fund’s sales charge. The fund has earned just under 5% per year for the past three years, handily trailing its long-short peer group.
Break out the bubbly! PSP Multi-Manager Fund (CEFFX/CEFIX) has slashed its expenses – exclusive of a long list of exceptions – from 3.0% to 2.64%. The fund inherits its predecessor Congressional Effect Fund’s dismal record, so don’t hold bad long-term returns against the current team. They’ve only been on-board since late August 2014. If you’d like, you’re more than welcome to hold a 2.64% e.r. against them instead.
Hartford Total Return Bond Fund (HABDX) has dropped its management fee by 12 basis points. I’m not certain that the reduction is related to the departure of the $200 Million Man, manager Bill Gross, but the timing is striking.
As of October 1, 2014, the investment advisory fee paid to Charles Schwab for the Laudus Mondrian International Equity Fund (LIEQX) was dropped by 10 basis points to 0.75%.
Each of the Litman Gregory Masters Fund’s Investor Class shares is eliminating its redemption fee.
PIMCO Emerging Markets Bond Fund (PAEMX) has dropped its management charge by 5 basis points to 50 basis points.
Similarly, RBC Global Asset Management will see its fees reduced by 10 basis points for the RBC BlueBay Emerging Market Corporate Bond Fund (RECAX) and by 5 basis points for the RBC BlueBay Emerging Market Select Bond Fund (RESAX), RBC BlueBay Global High Yield Bond Fund (RHYAX) and RBC BlueBay Global Convertible Bond Fund.
CLOSINGS (and related inconveniences)
The American Beacon International Equity Index Fund (AIIIX) will close to new investors on December 31, 2014. Uhhh … why? It’s an index fund tracking the largest international index.
Effective December 1, 2014, American Century One Choice 2015 Portfolio (ARFAX) will be closed to new investors. One presumes that the fund is in the process of liquidating as it reaches its target date, which its assets transferring to a retirement income fund.
OLD WINE, NEW BOTTLES
Just before Christmas, the AllianzGI Wellness Fund (RAGHX) will change its name to the AllianzGI Health Sciences Fund and it will begin investing in, well, health sciences-related companies. Currently it also invests in “wellness companies,” those promoting a healthy lifestyle. Not to dismiss the change, but pretty much all of the top 25 holdings are health-sciences companies already and Morningstar places 98% of its holdings in the healthcare field.
Effective January 15, 2015, Calvert High Yield Bond Fund (CYBAX) will shift its principal investment strategy from investing in bonds with intermediate durations to those “with varying durations,” with the note that “duration and maturity will be managed tactically.” At the same time Calvert Global Alternative Energy Fund (CGAEX) will be renamed Calvert Global Energy Solutions Fund, presumably because “alternative energy” is “so Obama.” I’ll note in passing that I really like the clarity of Calvert’s filings; they make it ridiculously easy to understand exactly what they do now and what they’ll be doing in the future. Thanks for that.
Effective December 30, 2014, CMG Managed High Yield Fund (CHYOX) will be renamed CMG Tactical Bond Fund. It appears as if the fund’s adviser decided to change its name and principal strategy within two weeks of its initial launch. They had filed to launch this fund in April 2013, appeared to have delayed for nearly 20 months, launched it and then immediately questioned the decision. Why am I not finding this reassuring?
Equinox EquityHedge U.S. Strategy Fund is chucking its “let’s hire lots of star sub-advisers” strategy in favor of investing in derivatives and ETFs on their own. Following the change, the investment advisory fee drops from 1.95% to 0.95% but “the Board also approved a decrease in the fee waiver and expense reimbursement arrangements with the Adviser to correspond with the decreased advisory fee.” The new system caps “A” share expenses at 1.45% except for a long list of uncapped items which might push the total substantially higher.
First Pacific Low Volatility Fund (LOVIX) has been renamed Lee Financial Tactical Fund. Headquartered in Honolulu. I feel a field trip coming on.
On October 1, Forward announced plans to reposition Forward Global Dividend Fund (FFLRX) as Forward Foreign Equity Fund on December 1. The new investment strategy statement is unremarkable, except for the absence of the word “dividend” anywhere in it. Two weeks later Forward filed an indefinite suspension of the change, so FFLRX lives on but conceivably on borrowed time.
Goldman Sachs Municipal Income Fund becomes Goldman Sachs Strategic Municipal Income Fund in December. The strategy in question involves permitting investments in high yield munis and in a 2-8 year duration band.
Effective December 17, Janus’s INTECH subsidiary will be “applying a managed volatility approach” to four of INTECH’s funds, at which point their names will change:
|
Current Name |
New Name |
|
INTECH Global Dividend Fund |
INTECH Global Income Managed Volatility Fund |
|
INTECH International Fund |
INTECH International Managed Volatility Fund |
|
INTECH U.S. Growth Fund |
INTECH U.S. Managed Volatility Fund II |
|
INTECH U.S. Value Fund |
INTECH U.S. Managed Volatility Fund |
Laudus Mondrian Institutional Emerging Markets (LIEMX) and Laudus Mondrian Institutional International Equity (LIIEX) funds are pursuing one of those changes that make sense primarily to the fund’s accountants and lawyers. Instead of being the Institutional EM Fund, it will become the Institutional share class Laudus Mondrian Emerging Markets (LEMIX). Likewise with International Equity.

photo courtesy of Augustana Photo Bureau
OFF TO THE DUSTBIN OF HISTORY
Aberdeen Global Select Opportunities Fund (BJGQX) is going to merge into the Aberdeen Global Equity Fund (GLLAX) following what the adviser refers to as “the completion of certain conditions” a/k/a approval by shareholders. Neither fund is particularly good and they have overlapping management teams, but Select is microscopic and pretty much doomed.
Boston Advisors Broad Allocation Strategy Fund (BABAX) will be liquidated come December 18, 2014. It’s a small, overpriced fund-of-funds that’s managed to lag in both up markets and down markets over its short life.
HNP Growth and Preservation Fund (HNPKX) is slated for liquidation in mid-November. It was a reasonably conservative managed futures fund that was hampered by modest returns and high expenses. We wrote a short profile of it a while ago.
iShares isn’t exactly cleaning house, but they did bump off 18 ETFs in late October. The descendants include their entire Target Date lineup plus a couple real estate, emerging market sector and financial ETFs. The full list is:
- iShares Global Nuclear Energy ETF (NUCL)
- iShares Industrial/Office Real Estate Capped ETF (FNIO)
- iShares MSCI Emerging Markets Financials ETF (EMFN)
- iShares MSCI Emerging Markets Materials ETF (EMMT)
- iShares MSCI Far East Financials ETF (FEFN)
- iShares NYSE 100 ETF (NY)
- iShares NYSE Composite ETF (NYC)
- iShares Retail Real Estate Capped ETF (RTL)
- iShares Target Date Retirement Income ETF (TGR)
- iShares Target Date 2010 ETF (TZD)
- iShares Target Date 2015 ETF (TZE)
- iShares Target Date 2020 ETF (TZG)
- iShares Target Date 2025 ETF (TZI)
- iShares Target Date 2030 ETF (TZL)
- iShares Target Date 2035 ETF (TZO)
- iShares Target Date 2040 ETF (TZV)
- iShares Target Date 2045 ETF (TZW)
- iShares Target Date 2050 ETF (TZY)
Lifetime Achievement Fund (LFTAX) “has concluded that it is in the best interests of the Fund and its shareholders that the Fund cease operations.” The orderly dissolution of the fund will take until March 31, 2015.
Effective October 13, 2014, the Nationwide Enhanced Income Fund and the Nationwide Short Duration Bond Fund were reorganized into the Nationwide HighMark Short Term Bond Fund (NWJSX).
QS LEGG MASON TARGET RETIREMENT 2015,
Speaking of mass liquidations, Legg Mason decided to bump off its entirely target-date lineup, except for Target Retirement 2015 (LMFAX), effective mid-November.
- QS Legg Mason Target Retirement 2020,
- QS Legg Mason Target Retirement 2025,
- QS Legg Mason Target Retirement 2030,
- QS Legg Mason Target Retirement 2035,
- QS Legg Mason Target Retirement 2040,
- QS Legg Mason Target Retirement 2045,
- QS Legg Mason Target Retirement 2050
- QS Legg Mason Target Retirement Fund.
Robeco Boston Partners International Equity Fund merged into John Hancock Disciplined Value International Fund (JDIBX) on September 26, 2014.
Symons Small Cap Institutional Fund (SSMIX) has decided to liquidate, done in by “the Fund’s small asset size and the increasing regulatory and operating costs borne by the adviser.” Trailing 98-99% of its peers over the past 1, 3 and 5 year periods probably didn’t help its case.
Effective immediately, the USFS Funds Limited Duration Government Fund (USLDX) is closed to new purchases, its manager has left and all references to him in the Fund’s Summary Prospectus, Prospectus and SAI have been “deleted in their entirety.” Given that the fund is small and sad, and the adviser’s website doesn’t even admit it exists, I’m thinking the “closed to new investors and the manager’s out the door” might be a prelude to a watery grave.
The Japan Fund (SJPNX) just became The Former Japan Fund as it ended a long and rambling career by being absorbed into the Matthews Japan Fund (MJFOX, as in Michael J. Fox). The Japan Fund, launched in the late 1980s as Scudder Japan, was one of the first funds to target Japan – at just about the time Japan’s market peaked.
Effective October 20, 2014, three Virtus Insight money market funds (Government Money Market, Money Market and Tax-Exempt Money Market) were liquidated.
Bon Voya-age: Voya Global Natural Resources Fund (LEXMX – another of the old Lexington funds, along with our long-time favorite Lexington Corporate Leaders LEXCX) is merging in Voya International Value Equity (NAWGX). LEXMX has led its peers in four of the past five years but seems not to have drawn enough assets to satisfy the adviser’s needs. In the interim, International Value will be rechristened Voya Global Value Advantage.
In Closing . . .
One of our greatest challenges each month is balancing the needs and interests of our regular readers with those of the folks who are encountering us for the first time. Of the 25,000 folks who’ve read the Observer in the past 30 days, 40% ~ say, 10,000 ~ were first-time visitors. That latter group might reasonably be wondering things like “who on earth are these people?” and “where are the ads?” The following is for them and for anyone who’s still wondering “what’s up here?”

photo courtesy of Carolyn Yaschur, Augustana College
Who is the Observer?
The Mutual Fund Observer operates as a public service, a place for individuals to interact, grow, learn and gain confidence. It is a free, independent, non-commercial site, financially supported by folks who value its services. We write for intellectually curious, serious investors – managers, advisers, and individuals – who need to get beyond marketing fluff and computer-generated recommendations.
We have about 25,000 readers, 95% of whom are resident in the US.
The Observer is published by David Snowball, a Professor of Communication Studies and former Director of Debate at Augustana College in Rock Island, Illinois. While I might be the “face” of the Observer, I’m also only one piece of it. The strength of the Observer is the strength of the people it has drawn. There is a community of folks, fantastically successful in their own rights, who provide us with an incredibly powerful advantage. Some (Charles and Edward, as preeminent examples) write for us, some write to us (mostly in private emails) and some (David Smith at Fundfox and Brian Haskin at DailyAlts) share their words and expertise with us. They all share a common passion: to teach and hence to learn. Their presence, and yours, makes this infinitely more than Snowball 24/7.
What’s our mission?
We’ll begin with the obvious: about 80% of all mutual funds could shut their doors today and not be missed. If I had to describe them, I’d use words like
- Large
- Unimaginative
- Undistinguished
- Asset sponges
They thrive by never being bad enough to dump and so, year after year, their numbers swell. By one estimate, 30% of all mutual fund money is invested in closet index funds – nominally active funds whose strategy and portfolio is barely distinguishable from an index. One of Russel Kinnel’s sharper lines of late was, “New funds tend to be mediocre because fund companies make them that way” (“New Funds Generate More Excitement Than Results,” 10/16/14). Add “larger” in front of “fund companies” and I’d nod happily. The situation is worse in ETF-land where the disappearance of 90% of offerings would likely improve the performance of 99% of investor portfolios.
Sadly those are the funds that win analyst coverage and investor attention. The structure of the investment company industry is such that the funds you should consider most seriously are the ones about which you hear the least: small, nimble, independent entities with skilled managers who – in many cases – have left major firms in disgust at the realization that the corporation’s needs were going to trump their investors’ needs. Where the mantra at large companies is “let’s not do anything weird,” the mantra at smaller firms seems to be “let’s do the right thing for our investors.”
That’s who we write about, convinced that there are opportunities there that you really should recognize and consider with all seriousness.
How can you best use it?
Give yourself time and go beyond the obvious.
We tend to publish longer pieces that most sites and many of those essays assume that you’re smart, interested and thoughtful. We don’t do fluff though we celebrate quirky. The essays that Charles posts tend to be incredibly data-rich. Ed’s essays tend to be driven by a sharply trained, deeply inquisitive mind and decades of experience; he understands more about what’s going on just under the surface or behind closed doors than most of us could ever aspire to. They bear re-reading.
We have a lot of resources not immediately evident in the monthly update you’ve just read. I’ll highlight four and suggest you click around a bit on the top menu bar.
- We share content from, and link to, people who impress us. David Smith and FundFox do an exceptional job of following and organizing the industry’s legal travails; it strikes me as an indispensable tool for trustees, reporters and folks whose names are followed by the letters J and D. Brian Haskin and the folks are DailyAlts are dedicated to comprehensive tracking of the industry’s fastest growing, most complex corner. Both offer resources well beyond our capacity and strike us as really worth following.
- We offer tools that do cool things. Want detailed, current, credible risk measures for any fund? Risk Profile Search. A searchable list of every fund whose risk-adjusted returns beat its peers in every trailing period? Great Owls. A quick way to generate lists of candidates for a portfolio? Miraculous Multi-Search. Every manager change at an equity, balanced or alts fund over the past three years. Got it. Chip’s Manager Changes master list. Most of them are under the Search Tools tab, but the Navigator – which links you directly to any specified fund’s page on a dozen credible news and rating sites – is a Resource.
- We have profiles of over 100 funds, generally small, new and distinctive. Charles’s downloadable dashboard gives you quick access to updated risk and return information on each. There are archived audio interviews with the managers of some of the most intriguing of them. We present the active share calculations for every fund we profile and host one of the web’s largest collections of current active share data.
- We have searchable editorial and analytic content back to our inception. Curious about everything we’ve reported on Seafarer Growth & Income (SFGIX) since its inception? It’s there. Our discussion of the fall o’ Fidelity funds?
Quite independent of which (fiercely independent of which, I dare say) is the Observer’s mutual fund discussion board, which has had 1600 users and 65,000 posts.
We also answer our mail.
How do we pay for it?
Because the folks most in need of a quiet corner and reasonable people are those least able to pay a subscription, we’ve never charged one. When readers wish to support the Observer, they have four pretty simple, entirely voluntary channels:
- They can use our Amazon.com link for their online shopping. On average, Amazon rebates to us an amount equivalent to about 7% of your purchase. Hint! Hint! There are holidays coming. If you’re one of those people who participate in “holiday shopping”, use this link. It costs you nothing. There really are no strings attached.
- They can contribute directly through PayPal.
- They can become de facto subscribers through an automatic monthly contribution through PayPal.
- They can send a check. Or cash. Heck, we’d take fruitcakes and would delight in good chocolates.
All of that is laid out on our Support Us page.
Our goal each month is not to be great. It’s to be a bit better than we were last month. Frankly, the more you help – with ideas, encouragement, criticism and support – the likelier that is to occur.
Speaking of de facto subscribers, the number has doubled in the last month. Thanks Greg, Deb appreciates the company! Charles is developing a remarkably sophisticated fund search function; in thanks and in hopes of getting feedback, we’ve extended access to our subscribers. If our recent rate of subscriber growth (i.e., doubling monthly) keeps up, we’ll crack 8200 in a year and I think we’d hit 16,777,216 by the end of the following year. Charles, the energetic one among us, has promised to greet each of you at the door.
 I’m sure by now that you’ve set your clocks back. But what about your other fall chores? Change the batteries in your smoke detectors. If you don’t have spare batteries on hand, leave a big Post-It note on the door to the garage so you remember to buy some. If your detector predates the Obama administration, it’s time for a change. And when was the last time you called your mom, changed your furnace filters or unwrapped that mysterious aluminum foil clad nodule in the freezer? Time to get to it, friends!
I’m sure by now that you’ve set your clocks back. But what about your other fall chores? Change the batteries in your smoke detectors. If you don’t have spare batteries on hand, leave a big Post-It note on the door to the garage so you remember to buy some. If your detector predates the Obama administration, it’s time for a change. And when was the last time you called your mom, changed your furnace filters or unwrapped that mysterious aluminum foil clad nodule in the freezer? Time to get to it, friends!
For December, we’ll profile three new funds and think with you about the results of our latest research project focusing on the extent to which fund trustees are willing to entrust their own money to the funds they oversee. We’ve completed reviews of 80 of our target 100 funds and, so far, 515 trustees might have a bit of explaining to do.
Also coming in December, our pilot episode of the soon-to-be-hit reality TV show: So you think you can be an equity fund manager! It’ll be hosted by some cheeky chick from Poughkeepsie who sports a faux British accent.
It looks so easy. And so profitable. Our British confreres boiled the attraction down in a single three minute video.
Wealth Management Parody from SCM on Vimeo. Thanks to Ted, one of the discussion board’s senior members, for bringing it to our attention.
In December we’ll look at Motif, a service mentioned to us by actual fund managers who are intrigued by it and which would let you run your own mutual fund (or six), in real time with real money.
Your money.
See you then!









 If you actually believed the credo that you so piously pronounce, there’d be about three ETFs in existence, each with a trillion in assets. They’d be overseen by a nonprofit corporation (hi, Jack!) which would charge one basis point. All the rest of you would be off somewhere, hawking nutraceuticals and testosterone supplements for a living. We’ll get to you later.
If you actually believed the credo that you so piously pronounce, there’d be about three ETFs in existence, each with a trillion in assets. They’d be overseen by a nonprofit corporation (hi, Jack!) which would charge one basis point. All the rest of you would be off somewhere, hawking nutraceuticals and testosterone supplements for a living. We’ll get to you later.






 Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.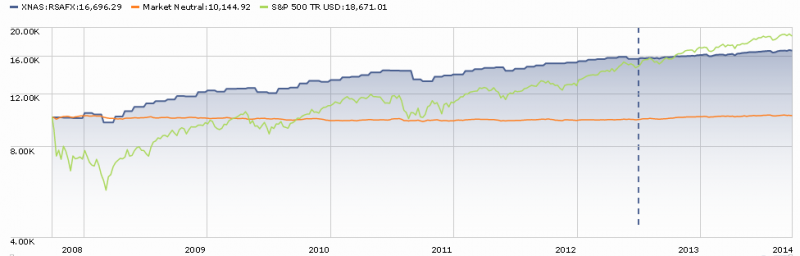


 It’s rare that a newly launched fund receives both a “Great Owl” (top quintile risk-adjusted returns in all trailing periods longer than a year) and Morningstar five star rating, but Price’s International Concentrated Equity Fund (PRCNX) managed the trick. On August 22, 2014, T. Rowe released a retail version of its outstanding Institutional International Concentrated Equity Fund (RPICX). That fund launched in July 2010. Federico Santilli, who has managed the RPICX since inception, will manage the new fund. He claims to be style, sector and region-agnostic, willing to go wherever the values are best. He targets “companies that have solid positions in attractive industries, have an ability to generate visible and durable free cash flow, and can create shareholder value over time.”
It’s rare that a newly launched fund receives both a “Great Owl” (top quintile risk-adjusted returns in all trailing periods longer than a year) and Morningstar five star rating, but Price’s International Concentrated Equity Fund (PRCNX) managed the trick. On August 22, 2014, T. Rowe released a retail version of its outstanding Institutional International Concentrated Equity Fund (RPICX). That fund launched in July 2010. Federico Santilli, who has managed the RPICX since inception, will manage the new fund. He claims to be style, sector and region-agnostic, willing to go wherever the values are best. He targets “companies that have solid positions in attractive industries, have an ability to generate visible and durable free cash flow, and can create shareholder value over time.” Fundfox is the only intelligence service to focus exclusively on litigation involving U.S.-registered investment companies, their directors and advisers. Each month editor David Smith shares word of the month’s litigation-related highlights. Folks whose livelihood ride on such matters need to visit
Fundfox is the only intelligence service to focus exclusively on litigation involving U.S.-registered investment companies, their directors and advisers. Each month editor David Smith shares word of the month’s litigation-related highlights. Folks whose livelihood ride on such matters need to visit 
 Appleseed (APPLX/APPIX) is lowering their expenses for both investor and institutional classes. Manager Joshua Strauss writes: “As we begin a new fiscal year Oct. 1, we will be trimming four basis points off Appleseed Fund Investor shares, resulting in a 1.20% net expense ratio. At the same time, we will be lowering the net expense ratio on Institutional shares by four basis points, to 0.95%.” It’s a risk-conscious, go-anywhere sort of fund that Morningstar has recognized as one of the few smaller funds that’s impressed them.
Appleseed (APPLX/APPIX) is lowering their expenses for both investor and institutional classes. Manager Joshua Strauss writes: “As we begin a new fiscal year Oct. 1, we will be trimming four basis points off Appleseed Fund Investor shares, resulting in a 1.20% net expense ratio. At the same time, we will be lowering the net expense ratio on Institutional shares by four basis points, to 0.95%.” It’s a risk-conscious, go-anywhere sort of fund that Morningstar has recognized as one of the few smaller funds that’s impressed them.
 From the perspective of most journalists, many advisors and a clear majority of investors, this gathering of mutual fund managers and of the professionals who make their work possible looks to be little more than a casting call for the Zombie Apocalypse. You are seen, dear friends, as “the walking dead,” a group whose success is predicated upon their ability to do … what? Eat their neighbors’ brains which are, of course, tasty but, and this is more important, once freed of their brains these folks are more likely to invest in your funds.
From the perspective of most journalists, many advisors and a clear majority of investors, this gathering of mutual fund managers and of the professionals who make their work possible looks to be little more than a casting call for the Zombie Apocalypse. You are seen, dear friends, as “the walking dead,” a group whose success is predicated upon their ability to do … what? Eat their neighbors’ brains which are, of course, tasty but, and this is more important, once freed of their brains these folks are more likely to invest in your funds.
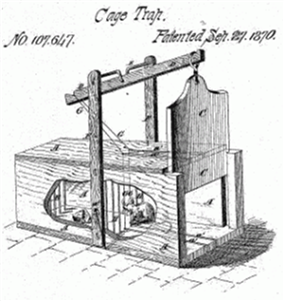 Remember that “build a better mousetrap and people will beat a path to your door” promise. Nope. Not true, even for mousetraps. There have been over 4400 patents for mousetraps (including a bunch labeled “better mousetrap”) issued since 1839. There are dozens of different subclasses, including “Electrocuting and Explosive,” “Swinging Striker,” “Choking or Squeezing,” and 36 others. One device, patented in 1897, controls 60% of the market and a modification of it patented in 1903 controls another 15-20%. About 0.6% of patented mousetraps were able to attract a manufacturer.
Remember that “build a better mousetrap and people will beat a path to your door” promise. Nope. Not true, even for mousetraps. There have been over 4400 patents for mousetraps (including a bunch labeled “better mousetrap”) issued since 1839. There are dozens of different subclasses, including “Electrocuting and Explosive,” “Swinging Striker,” “Choking or Squeezing,” and 36 others. One device, patented in 1897, controls 60% of the market and a modification of it patented in 1903 controls another 15-20%. About 0.6% of patented mousetraps were able to attract a manufacturer.

 Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more. Brent Olson knows the tale, having co-managed for three years a fund with a similar discipline. He recognizes the importance of risk control and thinks that he and the folks at Scout have found a way to manage some of the strategy’s downside.
Brent Olson knows the tale, having co-managed for three years a fund with a similar discipline. He recognizes the importance of risk control and thinks that he and the folks at Scout have found a way to manage some of the strategy’s downside.

 Jeffrey Gundlach, DoubleLine’s founder, is apparently in talks about
Jeffrey Gundlach, DoubleLine’s founder, is apparently in talks about 
 Ron Rowland, founder of Invest With an Edge and editor of AllStarInvestor.com, maintains the suitably macabre ETF Deathwatch which each month highlights those ETFs likeliest to be described as zombies: funds with both low assets and low trading volumes. The
Ron Rowland, founder of Invest With an Edge and editor of AllStarInvestor.com, maintains the suitably macabre ETF Deathwatch which each month highlights those ETFs likeliest to be described as zombies: funds with both low assets and low trading volumes. The 


 Mr. Cunnane manages Advisory Research MLP & Energy Infrastructure Fund which started life as a Fiduciary Asset Management Company (FAMCO) fund until the complex was acquired by Advisory Research. He’d been St. Louis-based FAMCO’s chief investment officer for 15 years. He’s the CIO for the MLP & Energy Infrastructure team and chair of AR’s Risk Management Committee. He also manages two closed-end funds which also target MLPs: the Fiduciary/Claymore MLP Opportunity Fund (FMO) and the Nuveen Energy MLP Total Return Fund (JMF). Here are his 200 words (and one picture) on why you might consider INFRX:
Mr. Cunnane manages Advisory Research MLP & Energy Infrastructure Fund which started life as a Fiduciary Asset Management Company (FAMCO) fund until the complex was acquired by Advisory Research. He’d been St. Louis-based FAMCO’s chief investment officer for 15 years. He’s the CIO for the MLP & Energy Infrastructure team and chair of AR’s Risk Management Committee. He also manages two closed-end funds which also target MLPs: the Fiduciary/Claymore MLP Opportunity Fund (FMO) and the Nuveen Energy MLP Total Return Fund (JMF). Here are his 200 words (and one picture) on why you might consider INFRX: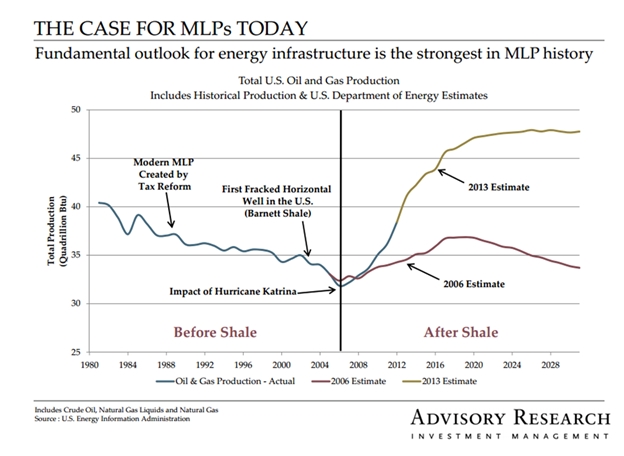
 Here’s a major vote of confidence: Effective August 1, 2014, John Neff and Thomas Saberhagen were named as co-portfolio managers for the
Here’s a major vote of confidence: Effective August 1, 2014, John Neff and Thomas Saberhagen were named as co-portfolio managers for the  Citing “the lack of investment opportunities” and “high current cash levels” occasioned by the five year run-up in global stock prices, Tweedy Browne announced the impending soft close of Tweedy, Browne Global Value II (TBCUX). TBCUX is an offshoot of Tweedy, Browne Global Value (TBGVX) with the same portfolio and managers but Global Value often hedges its currency exposure while Global Value II does not. The decision to close TBCUX makes sense as a way to avoid “diluting our existing shareholders’ returns in this difficult environment” since the new assets were going mostly to cash. Will Browne planned “to reopen the Fund when new idea flow improves and larger amounts of cash can be put to work in cheap stocks.”
Citing “the lack of investment opportunities” and “high current cash levels” occasioned by the five year run-up in global stock prices, Tweedy Browne announced the impending soft close of Tweedy, Browne Global Value II (TBCUX). TBCUX is an offshoot of Tweedy, Browne Global Value (TBGVX) with the same portfolio and managers but Global Value often hedges its currency exposure while Global Value II does not. The decision to close TBCUX makes sense as a way to avoid “diluting our existing shareholders’ returns in this difficult environment” since the new assets were going mostly to cash. Will Browne planned “to reopen the Fund when new idea flow improves and larger amounts of cash can be put to work in cheap stocks.” Thanks, as always, go to The Shadow – an incredibly vigilant soul and long tenured member of the Observer’s discussion community for his contributions to this section. Really, very little gets past him and that gives me a lot more confidence in saying that we’ve caught of all of major changes hidden in the ocean of SEC filings.
Thanks, as always, go to The Shadow – an incredibly vigilant soul and long tenured member of the Observer’s discussion community for his contributions to this section. Really, very little gets past him and that gives me a lot more confidence in saying that we’ve caught of all of major changes hidden in the ocean of SEC filings.
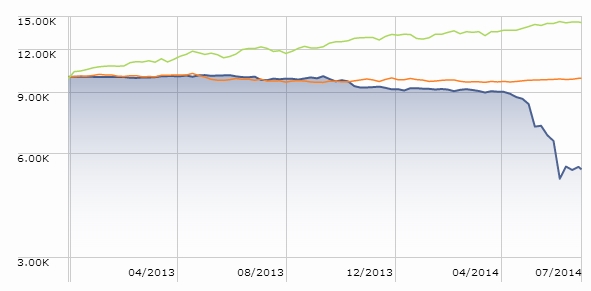
 My son Will, still hobbled after dropping his iPad on a toe, has taken to wincing every time we approach the mall. It’s festooned with “back to school sale! Sale! sale!” banners which seem, somehow, to unsettle him.
My son Will, still hobbled after dropping his iPad on a toe, has taken to wincing every time we approach the mall. It’s festooned with “back to school sale! Sale! sale!” banners which seem, somehow, to unsettle him.
 feel free to resort to PayPal or the USPS. It all helps and it’s all detailed on our
feel free to resort to PayPal or the USPS. It all helps and it’s all detailed on our 



 For a complete list of developments last month, and for information and court documents in any case, log in at
For a complete list of developments last month, and for information and court documents in any case, log in at  One of the best expressions of the problem was offered by Leo Strauss, a 20th century political philosopher and classicist:
One of the best expressions of the problem was offered by Leo Strauss, a 20th century political philosopher and classicist:





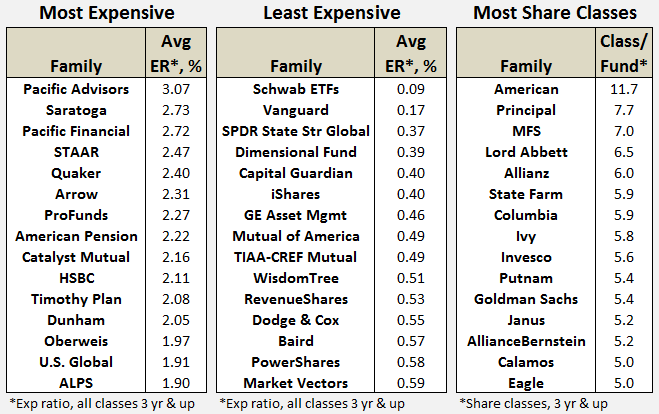
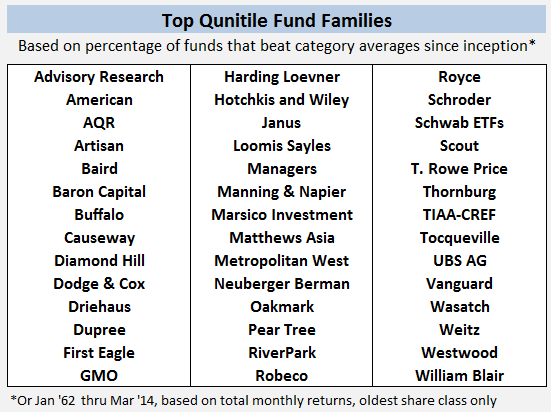
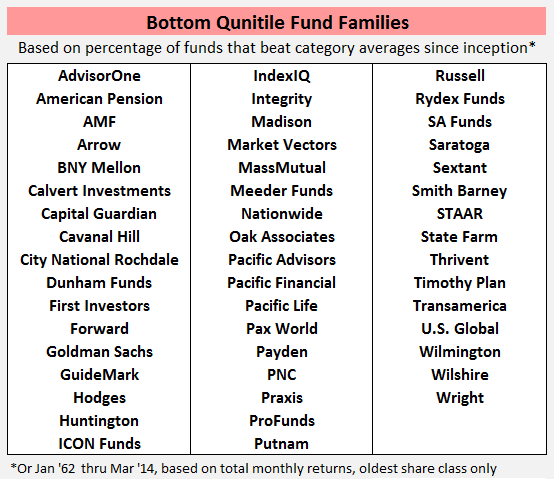
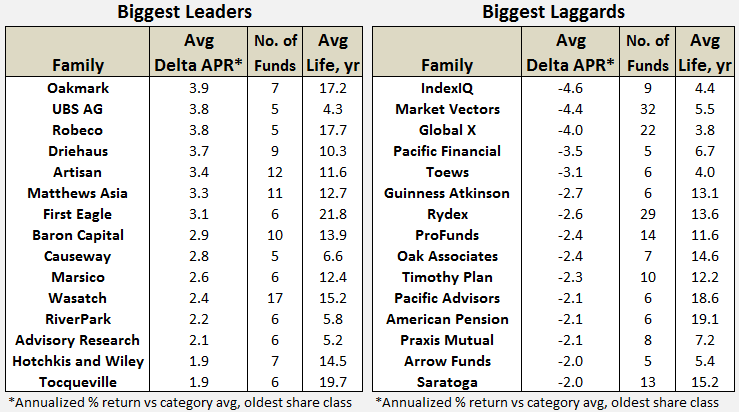







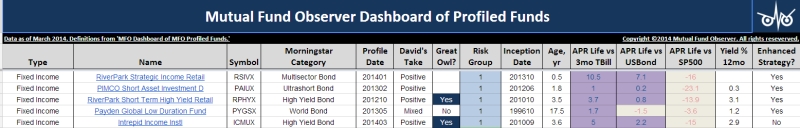






 It’s been that kind of month. Oh so very much that kind of month. In addition to teaching four classes and cheering Will on through 11 baseball games, I’ve spent much of the past six weeks buying a new (smaller, older but immaculate) house and beginning to set up a new household. It was a surprisingly draining experience, physically, psychologically and mentally. Happily I had the guidance and support of family and friends throughout, and I celebrated the end of April with 26 signatures, eight sets of initials, two attorneys, one large and one moderately-large check, and the arrival of a new set of keys and a new garage door clicker. All of which slightly derailed my focus on the world of funds. Fortunately the indefatigable Charles came to the rescue with …
It’s been that kind of month. Oh so very much that kind of month. In addition to teaching four classes and cheering Will on through 11 baseball games, I’ve spent much of the past six weeks buying a new (smaller, older but immaculate) house and beginning to set up a new household. It was a surprisingly draining experience, physically, psychologically and mentally. Happily I had the guidance and support of family and friends throughout, and I celebrated the end of April with 26 signatures, eight sets of initials, two attorneys, one large and one moderately-large check, and the arrival of a new set of keys and a new garage door clicker. All of which slightly derailed my focus on the world of funds. Fortunately the indefatigable Charles came to the rescue with …
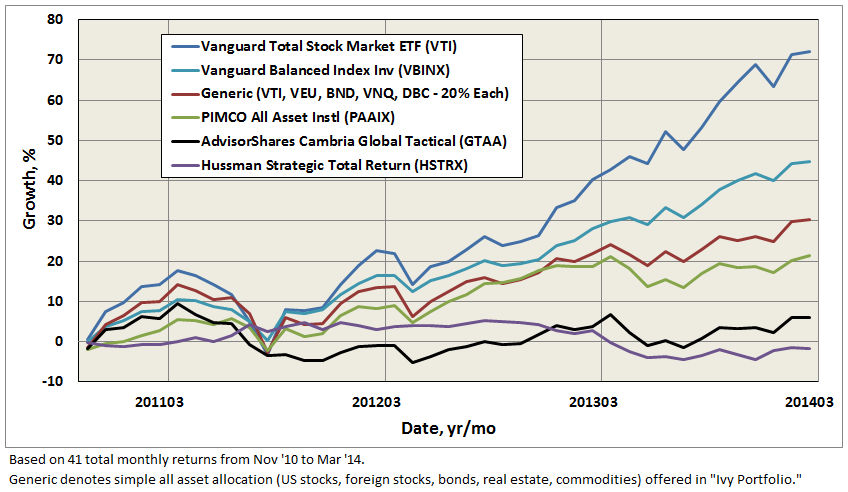
 The folks are MFWire did a nice, nearly snarky story on The Mario’s most recent payday. (
The folks are MFWire did a nice, nearly snarky story on The Mario’s most recent payday. (

 I’ve been asked to provide the keynote address at the Cohen Client Conference, August 20 – 21, 2014. The conference, in Milwaukee, is run by Cohen Fund Audit Services. This will be Cohen’s third annual client conference. Last year’s version, in Cleveland OH, drew about 100 clients from 23 states.
I’ve been asked to provide the keynote address at the Cohen Client Conference, August 20 – 21, 2014. The conference, in Milwaukee, is run by Cohen Fund Audit Services. This will be Cohen’s third annual client conference. Last year’s version, in Cleveland OH, drew about 100 clients from 23 states. Cohen offers the conference as a way of helping fund professionals – directors, compliance officers, tax and accounting guys, operating officers and the occasional curious hedge fund manager –develop both professional competence and connections within the fund community. Which is to say, the Cohen folks promised that there would be both serious engagement – staff presentations, panels by industry experts, audience interaction – and opportunities for fellowshipping. (My first, unworthy impulse is to drive a bunch of compliance officers over to Horny Goat Brewing, buy a round or two, then get them to admit that they’re making stuff up as they go.)
Cohen offers the conference as a way of helping fund professionals – directors, compliance officers, tax and accounting guys, operating officers and the occasional curious hedge fund manager –develop both professional competence and connections within the fund community. Which is to say, the Cohen folks promised that there would be both serious engagement – staff presentations, panels by industry experts, audience interaction – and opportunities for fellowshipping. (My first, unworthy impulse is to drive a bunch of compliance officers over to Horny Goat Brewing, buy a round or two, then get them to admit that they’re making stuff up as they go.) We’ll also spend three full days in and around the Morningstar Investment Conference, June 18 – 20, in Chicago. We try to divide our time there into thirds: interviewing fund managers and talking to fund reps, listening to presentations by famous guys, and building our network of connections by spending time with readers, friends and colleagues. If you’d like to connect with us somewhere in the bowels of McCormick Place,
We’ll also spend three full days in and around the Morningstar Investment Conference, June 18 – 20, in Chicago. We try to divide our time there into thirds: interviewing fund managers and talking to fund reps, listening to presentations by famous guys, and building our network of connections by spending time with readers, friends and colleagues. If you’d like to connect with us somewhere in the bowels of McCormick Place,  Especially for the benefit of the 6000 first-time readers we see each month, if you’re inclined to support the Observer, the easiest way is to use the Observer’s Amazon link. The system is simple, automatic, and painless. We receive an amount equivalent to about 7% of the value of almost anything you purchase through our Amazon link (used books, Kindle downloads, groceries, sunscreen, power tools, pool toys …). You might choose to set it as a bookmark or, in my case, you might choose to have one of your tabs open in Amazon whenever you launch your browser. Some purchases generate a dime, some generate $10-12 and all help keep the lights on!
Especially for the benefit of the 6000 first-time readers we see each month, if you’re inclined to support the Observer, the easiest way is to use the Observer’s Amazon link. The system is simple, automatic, and painless. We receive an amount equivalent to about 7% of the value of almost anything you purchase through our Amazon link (used books, Kindle downloads, groceries, sunscreen, power tools, pool toys …). You might choose to set it as a bookmark or, in my case, you might choose to have one of your tabs open in Amazon whenever you launch your browser. Some purchases generate a dime, some generate $10-12 and all help keep the lights on!

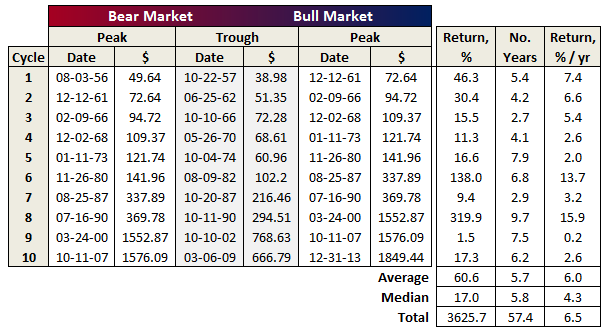
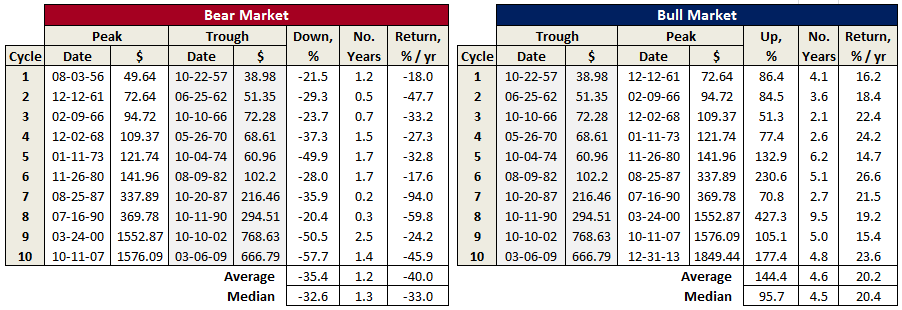
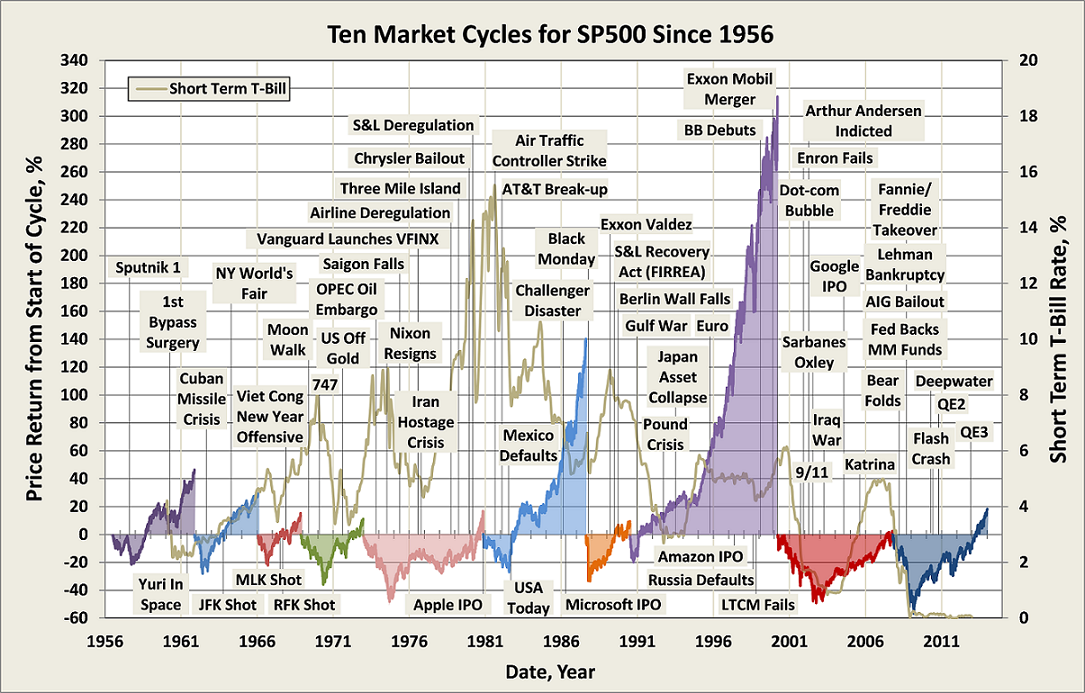
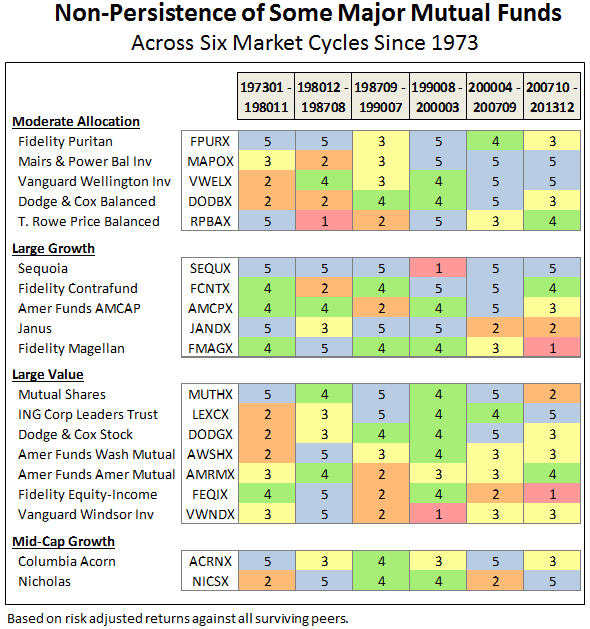
 By Edward Studzinski
By Edward Studzinski Beginning in 1997, the iconically odd-looking Jim Jubak wrote the wildly-popular “Jubak’s Picks” column for MSN Money. In 2010, he apparently decided that investment management looked awfully easy and so launched his own fund.
Beginning in 1997, the iconically odd-looking Jim Jubak wrote the wildly-popular “Jubak’s Picks” column for MSN Money. In 2010, he apparently decided that investment management looked awfully easy and so launched his own fund.
 Our friends at RiverRoad Asset Management report that they have entered a “strategic partnership” with Affiliated Managers Group, Inc. RiverRoad becomes AMG’s 30th partner. The roster also includes AQR, Third Avenue and Yacktman. As part of this agreement, AMG will purchase River Road from Aviva Investors. Additionally, River Road’s employees will acquire a substantial portion of the equity of the business. The senior professionals at RiverRoad have signed new 10-year employment agreements. They’re good people and we wish them well.
Our friends at RiverRoad Asset Management report that they have entered a “strategic partnership” with Affiliated Managers Group, Inc. RiverRoad becomes AMG’s 30th partner. The roster also includes AQR, Third Avenue and Yacktman. As part of this agreement, AMG will purchase River Road from Aviva Investors. Additionally, River Road’s employees will acquire a substantial portion of the equity of the business. The senior professionals at RiverRoad have signed new 10-year employment agreements. They’re good people and we wish them well.

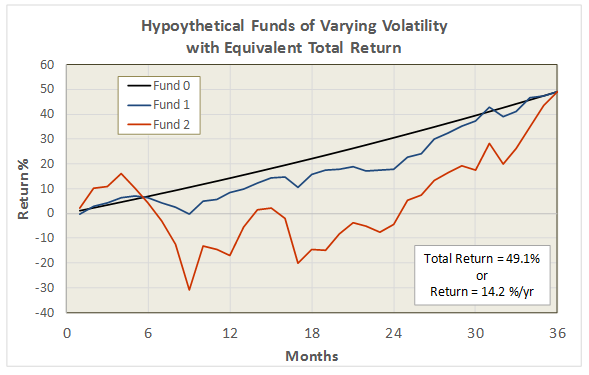
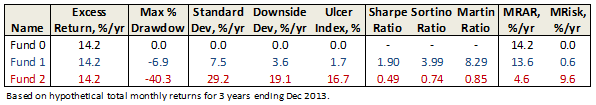
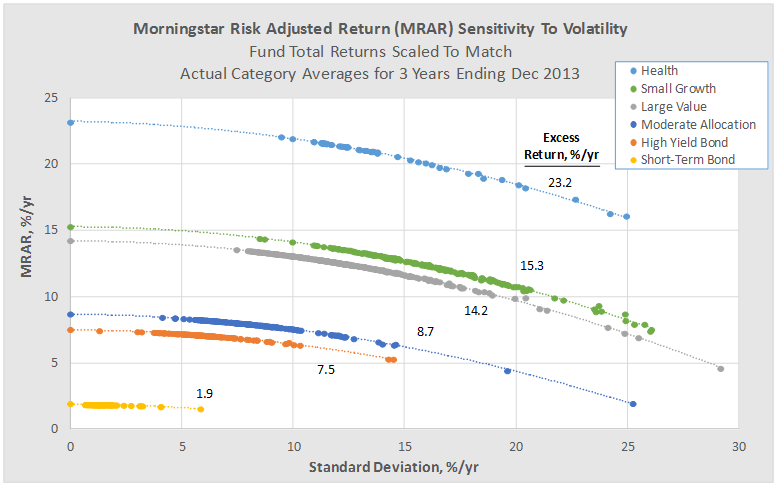
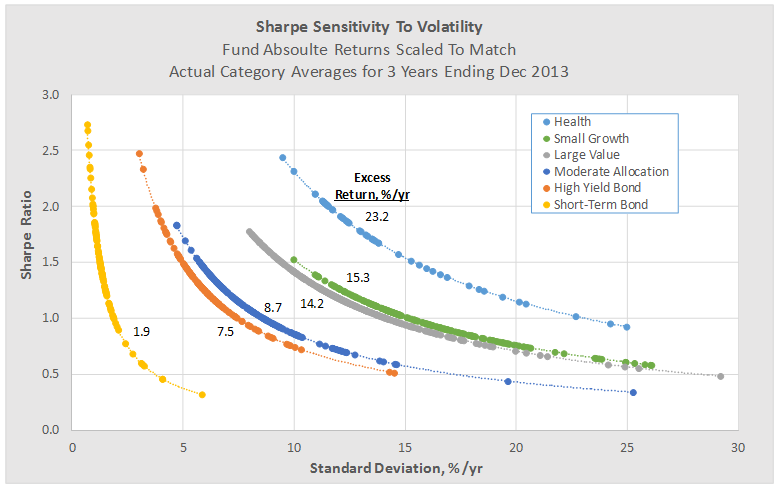
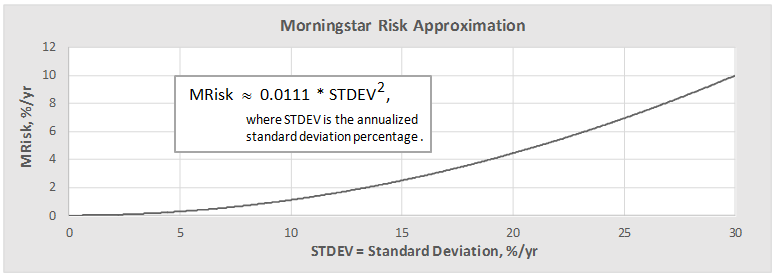
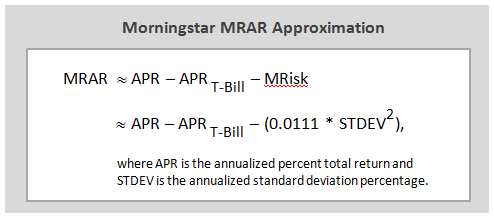
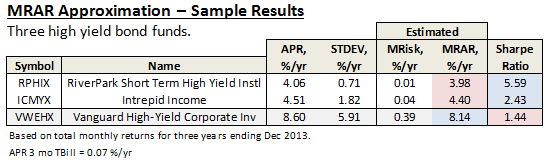
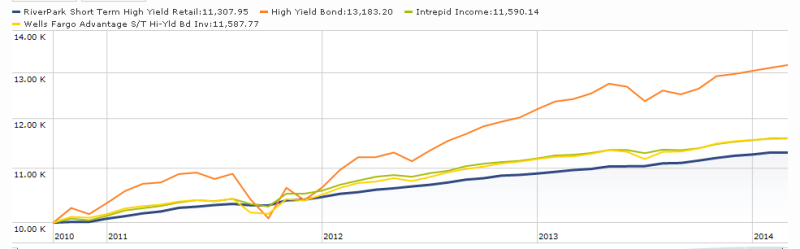

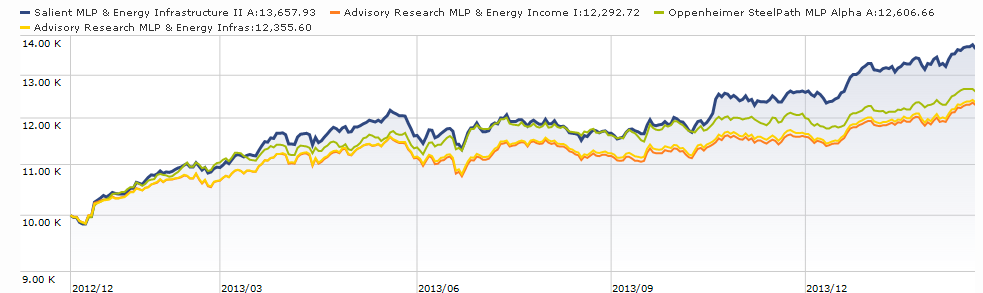
 Ted Gardner is the co‐portfolio manager for Salient’s MLP Complex, one manifestation of which is SMLPX. He oversees and coordinates all investment modeling, due diligence, company visits, and management conferences. Before joining Salient he was both Director of Research and a portfolio manager for RDG Capital and a research analyst with Raymond James. Here are his 200 words on why you should consider getting into the erl bidness:
Ted Gardner is the co‐portfolio manager for Salient’s MLP Complex, one manifestation of which is SMLPX. He oversees and coordinates all investment modeling, due diligence, company visits, and management conferences. Before joining Salient he was both Director of Research and a portfolio manager for RDG Capital and a research analyst with Raymond James. Here are his 200 words on why you should consider getting into the erl bidness:
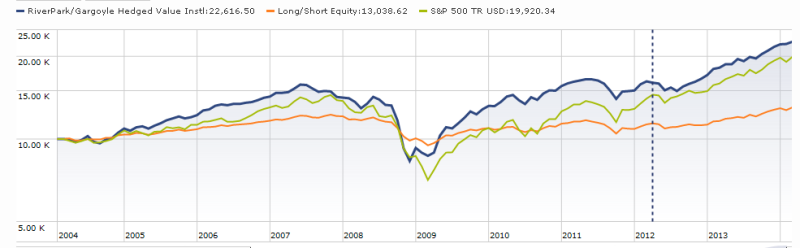



 One of the joys of having entered the investment business in the 1980’s is that you came in at a time when the profession was still populated by some really nice and thoughtful people, well-read and curious about the world around them. They were and are generally willing to share their thoughts and ideas without hesitation. They were the kind of people that you hoped you could keep as friends for life. One such person is my friend, Bruce, who had a thirty-year career on the “buy side” as both an analyst and a director of research at several well-known money management firms. He retired in 2008 and divides his time between homes in western Connecticut and Costa Rica.
One of the joys of having entered the investment business in the 1980’s is that you came in at a time when the profession was still populated by some really nice and thoughtful people, well-read and curious about the world around them. They were and are generally willing to share their thoughts and ideas without hesitation. They were the kind of people that you hoped you could keep as friends for life. One such person is my friend, Bruce, who had a thirty-year career on the “buy side” as both an analyst and a director of research at several well-known money management firms. He retired in 2008 and divides his time between homes in western Connecticut and Costa Rica.
 From Bruce’s perspective, too much money is chasing too few good ideas. This has resulted in what we call “style drift”. Firms that had made their mark as small cap or mid cap investors didn’t want to kill the goose laying the golden eggs by shutting off new money, so they evolved to become large cap investors. But ultimately that is self-defeating, for as the assets come in, you either have to shut down the flows or change your style by adding more and larger positions, which ultimately leads to under-performance.
From Bruce’s perspective, too much money is chasing too few good ideas. This has resulted in what we call “style drift”. Firms that had made their mark as small cap or mid cap investors didn’t want to kill the goose laying the golden eggs by shutting off new money, so they evolved to become large cap investors. But ultimately that is self-defeating, for as the assets come in, you either have to shut down the flows or change your style by adding more and larger positions, which ultimately leads to under-performance.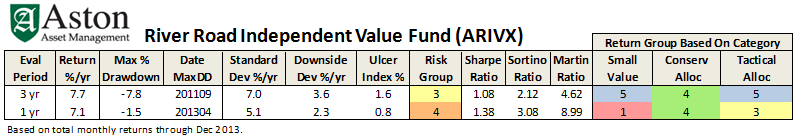
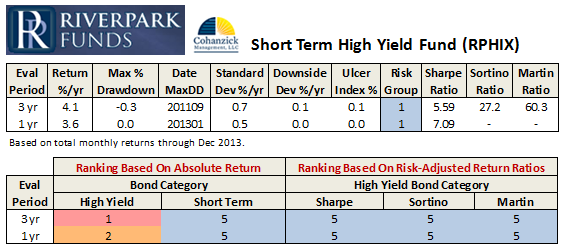
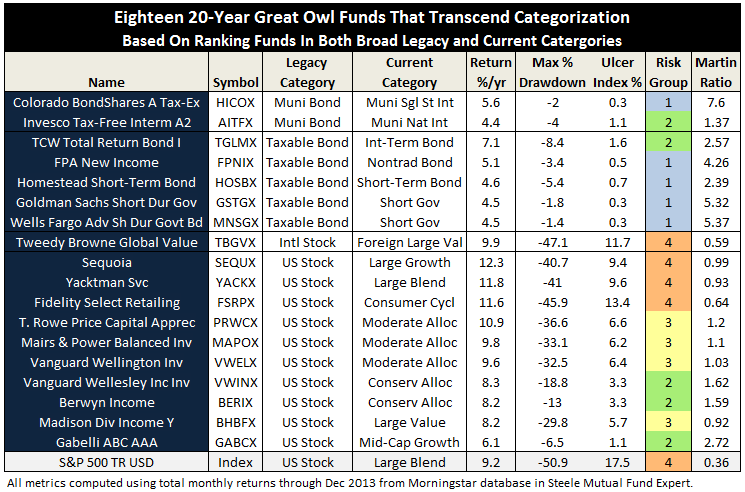 Roy Weitz grouped funds into only five equity and six specialty “benchmark categories” when he established the legacy
Roy Weitz grouped funds into only five equity and six specialty “benchmark categories” when he established the legacy